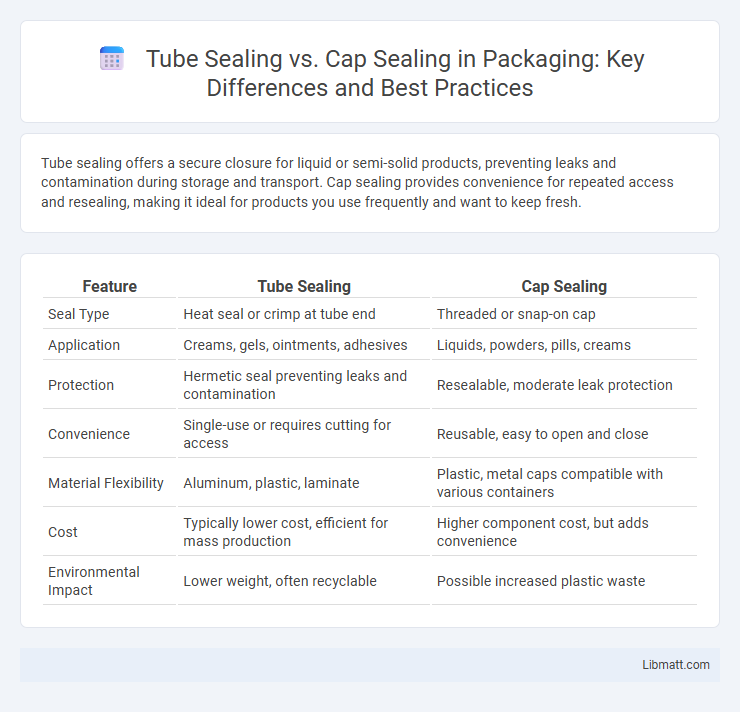
Tube sealing offers a secure closure for liquid or semi-solid products, preventing leaks and contamination during storage and transport. Cap sealing provides convenience for repeated access and resealing, making it ideal for products you use frequently and want to keep fresh.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tube Sealing | Cap Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| Seal Type | Heat seal or crimp at tube end | Threaded or snap-on cap |
| Application | Creams, gels, ointments, adhesives | Liquids, powders, pills, creams |
| Protection | Hermetic seal preventing leaks and contamination | Resealable, moderate leak protection |
| Convenience | Single-use or requires cutting for access | Reusable, easy to open and close |
| Material Flexibility | Aluminum, plastic, laminate | Plastic, metal caps compatible with various containers |
| Cost | Typically lower cost, efficient for mass production | Higher component cost, but adds convenience |
| Environmental Impact | Lower weight, often recyclable | Possible increased plastic waste |
Introduction to Tube Sealing and Cap Sealing
Tube sealing involves closing the open end of flexible packaging tubes using heat or mechanical pressure to maintain product integrity and prevent contamination. Cap sealing secures the container's opening with screw caps, snap lids, or other closures, providing tamper evidence and ease of access. Both methods enhance packaging functionality, ensuring product freshness and consumer safety across various industries.
Fundamental Differences Between Tube Sealing and Cap Sealing
Tube sealing involves closing flexible packaging by heat or ultrasonic methods directly on the tube material, ensuring airtight protection and contamination prevention for liquids, gels, and creams. Cap sealing secures a rigid container using a threaded or press-on cap, providing resealability and tamper-evident features commonly used for bottles in the pharmaceutical and beverage industries. The fundamental difference lies in the packaging type and sealing mechanism: tube sealing creates a hermetic closure on flexible packaging, while cap sealing applies a removable closure on rigid containers.
Common Applications of Tube Sealing
Tube sealing is widely used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food packaging to ensure airtight and contamination-free product preservation. It is ideal for flexible packaging formats like ointments, gels, creams, and pastes, offering precise, leak-proof seals that maintain product integrity. Your choice of tube sealing enhances product safety and shelf life, especially in applications requiring easy, hygienic dispensing.
Typical Uses for Cap Sealing
Cap sealing is commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food packaging to ensure product safety and tamper evidence. Your containers, including bottles and jars, benefit from cap sealing by maintaining freshness and preventing contamination during transportation and storage. This method is ideal for liquids, creams, and powders that require secure closure and easy access for consumers.
Material Compatibility: Tubes vs Caps
Tube sealing materials often include laminates, plastics, and foils tailored for flexible packaging, ensuring chemical resistance and preserving product integrity. Cap sealing typically uses plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene, designed for rigid closure compatibility and preventing leakage. Understanding material compatibility between tubes and caps is essential for ensuring your packaging maintains product safety and shelf life.
Sealing Technologies: Heat, Induction, and Ultrasonic Methods
Tube sealing and cap sealing utilize distinct sealing technologies tailored to specific packaging needs, including heat, induction, and ultrasonic methods. Heat sealing is commonly applied in tube closures, providing a secure bond by melting materials, whereas induction sealing is predominantly used in cap sealing to create tamper-evident liners through electromagnetic induction. Ultrasonic sealing offers precise, clean seals for both tubes and caps by using high-frequency mechanical vibrations, enhancing packaging integrity and shelf life for your products.
Efficiency and Speed: Comparison in Production Lines
Tube sealing offers faster processing speeds due to its automated continuous flow, reducing downtime between sealing operations. Cap sealing, while versatile for various container shapes, often requires more manual handling or slower machinery adjustments, impacting overall efficiency. You can enhance production line speed by choosing tube sealing when high throughput and minimal interruptions are critical.
Cost Analysis: Tube Sealing vs Cap Sealing
Tube sealing generally incurs lower initial equipment costs compared to cap sealing machines, making it more budget-friendly for small to medium-scale operations. Operational expenses for tube sealing are often reduced due to less material usage and simpler sealing processes, whereas cap sealing can increase costs with specialized caps and frequent maintenance. Your choice should weigh the total cost of ownership and production volume to determine the most cost-effective sealing method.
Quality Assurance and Leak Prevention
Tube sealing offers superior quality assurance by creating airtight seals that effectively prevent leaks, making it ideal for sensitive or liquid products. Cap sealing provides reliable protection but may be prone to slight leakage due to improper tightening or cap defects. Ensuring your packaging uses precise tube sealing technology will minimize contamination risks and guarantee consistent leak prevention.
Choosing the Best Sealing Method for Your Product
Tube sealing offers a versatile and efficient solution ideal for flexible packaging, ensuring airtight protection and preserving product freshness. Cap sealing is preferred for rigid containers, providing secure closure and easy resealing for liquids and powders. Assess your product's packaging type, usage requirements, and shelf life to choose the most effective sealing method for your needs.
Tube sealing vs cap sealing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com