Chemical recovery maximizes resource efficiency by reclaiming valuable substances from industrial waste, reducing environmental impact and operational costs. Waste disposal, while necessary for non-recoverable materials, often leads to greater environmental harm and lost economic opportunities compared to chemical recovery.
Table of Comparison
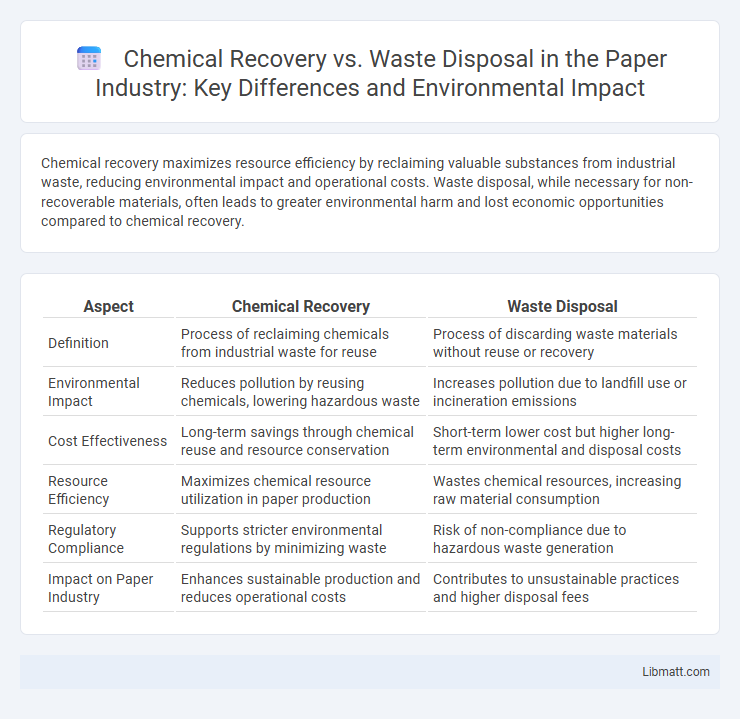
| Aspect | Chemical Recovery | Waste Disposal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of reclaiming chemicals from industrial waste for reuse | Process of discarding waste materials without reuse or recovery |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces pollution by reusing chemicals, lowering hazardous waste | Increases pollution due to landfill use or incineration emissions |
| Cost Effectiveness | Long-term savings through chemical reuse and resource conservation | Short-term lower cost but higher long-term environmental and disposal costs |
| Resource Efficiency | Maximizes chemical resource utilization in paper production | Wastes chemical resources, increasing raw material consumption |
| Regulatory Compliance | Supports stricter environmental regulations by minimizing waste | Risk of non-compliance due to hazardous waste generation |
| Impact on Paper Industry | Enhances sustainable production and reduces operational costs | Contributes to unsustainable practices and higher disposal fees |
Introduction to Chemical Recovery and Waste Disposal
Chemical recovery involves reclaiming valuable chemicals from industrial processes to minimize environmental impact and reduce raw material costs. Waste disposal focuses on safely managing and eliminating waste products to prevent pollution and health hazards. Your choice between chemical recovery and waste disposal impacts sustainability, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
Key Differences Between Chemical Recovery and Waste Disposal
Chemical recovery involves extracting valuable substances from waste materials through processes like solvent extraction or distillation, enabling resource reuse and reducing environmental impact. Waste disposal focuses on eliminating waste by methods such as landfilling, incineration, or deep-well injection, prioritizing containment and isolation rather than reuse. The key difference lies in chemical recovery's emphasis on material reclamation and sustainability, whereas waste disposal centers on safe and permanent waste elimination.
Environmental Impact of Chemical Recovery vs Waste Disposal
Chemical recovery significantly reduces environmental pollution by reclaiming valuable resources and minimizing toxic emissions, whereas waste disposal often leads to harmful landfill leachate and greenhouse gas releases. Chemical recovery processes lower carbon footprints and conserve energy, supporting sustainable waste management compared to traditional disposal methods. Your choice of chemical recovery promotes environmental protection and resource efficiency, aligning with global ecological goals.
Economic Benefits of Chemical Recovery over Waste Disposal
Chemical recovery offers significant economic benefits compared to traditional waste disposal by converting waste materials into valuable resources, thereby reducing raw material costs and minimizing landfill fees. Recovery processes enhance operational efficiency and create revenue streams from byproducts, improving overall profitability. Your business can achieve cost savings and sustainability goals simultaneously by adopting chemical recovery strategies.
Regulatory Frameworks Governing Chemical Recovery and Waste Disposal
Regulatory frameworks governing chemical recovery and waste disposal encompass strict environmental laws such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) and the European Union's Waste Framework Directive (WFD), which mandate proper handling, processing, and disposal of hazardous materials to minimize environmental impact. These regulations promote chemical recovery processes like solvent recycling and metal reclamation to reduce landfill use and resource extraction, ensuring compliance with emissions and toxicity limits set by agencies like the EPA and ECHA. Enforcement mechanisms include permits, audits, and penalties, driving industries to adopt sustainable waste management practices aligned with circular economy principles.
Technological Advances in Chemical Recovery Methods
Technological advances in chemical recovery methods have significantly improved the efficiency of extracting valuable compounds from industrial waste streams, reducing environmental impact and operational costs. Innovations such as membrane filtration, advanced oxidation processes, and bio-electrochemical systems enable selective recovery of chemicals like metals, acids, and solvents, enhancing sustainability in waste management. These methods offer scalable, energy-efficient solutions that transform waste disposal challenges into resource recovery opportunities, promoting circular economy principles in industries such as pulp and paper, mining, and wastewater treatment.
Common Waste Disposal Practices and Their Limitations
Common waste disposal practices include landfill dumping, incineration, and ocean dumping, which often lead to environmental contamination and resource depletion. These methods fail to recover valuable chemicals, resulting in increased pollution and higher operational costs for industries managing hazardous waste. Optimizing your approach by integrating chemical recovery can reduce hazardous waste volume while promoting sustainability and resource efficiency.
Case Studies: Successful Chemical Recovery Applications
Case studies highlight chemical recovery applications in pulp and paper mills, where recovered chemicals reduce raw material costs and environmental impact. One notable example is the kraft process recovery boiler, which recycles inorganic chemicals and generates steam, improving energy efficiency and waste reduction. Your business can benefit from similar implementations by enhancing resource sustainability and minimizing hazardous waste disposal.
Challenges and Barriers in Transitioning from Waste Disposal to Chemical Recovery
Transitioning from waste disposal to chemical recovery faces challenges such as high initial capital investment for advanced recovery technologies and regulatory complexities that hinder widespread adoption. Technical barriers include the difficulty of efficiently separating and purifying valuable chemicals from heterogeneous waste streams and managing hazardous by-products safely. Limited market demand for recovered chemicals and lack of standardized processes further slow the shift towards sustainable chemical recovery solutions.
Future Trends in Chemical Waste Management
Future trends in chemical waste management emphasize advanced recovery technologies that enhance resource efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Innovations such as bio-based catalysts and electrochemical processes enable safer and more cost-effective chemical recovery from industrial waste streams. These developments support circular economy principles by transforming hazardous waste into valuable raw materials, reducing reliance on landfills and incineration.
Chemical recovery vs waste disposal Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com