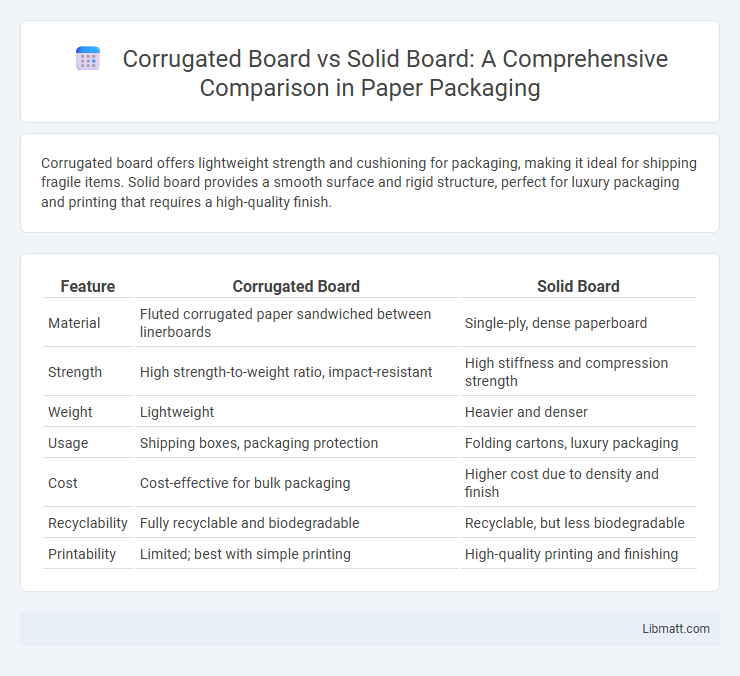
Corrugated board offers lightweight strength and cushioning for packaging, making it ideal for shipping fragile items. Solid board provides a smooth surface and rigid structure, perfect for luxury packaging and printing that requires a high-quality finish.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Corrugated Board | Solid Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Fluted corrugated paper sandwiched between linerboards | Single-ply, dense paperboard |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio, impact-resistant | High stiffness and compression strength |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier and denser |
| Usage | Shipping boxes, packaging protection | Folding cartons, luxury packaging |
| Cost | Cost-effective for bulk packaging | Higher cost due to density and finish |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable and biodegradable | Recyclable, but less biodegradable |
| Printability | Limited; best with simple printing | High-quality printing and finishing |
Introduction to Corrugated Board and Solid Board
Corrugated board consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two liners, offering lightweight strength and cushioning ideal for shipping and packaging fragile items. Solid board, also known as chipboard or paperboard, is a dense, single-layered sheet made from compressed wood fibers, providing rigidity and smooth surfaces suited for retail packaging, bookbinding, and display purposes. The structural differences influence their applications, with corrugated board excelling in protective packaging and solid board preferred for aesthetic and printing qualities.
Key Material Differences
Corrugated board features a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two linerboards, providing lightweight strength and cushioning ideal for shipping. Solid board consists of solid layers of paper pulp, offering a smooth surface and rigid structure suitable for high-quality packaging and printing. Your choice depends on the need for impact resistance from corrugated or the durability and printability of solid board.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Corrugated board offers superior strength and durability due to its multi-layered fluted structure, which provides excellent cushioning and resistance to crushing forces, making it ideal for shipping and packaging heavy items. Solid board, being a single thick sheet, tends to be less flexible and more prone to bending or damage under impact, but it excels in print quality and surface smoothness for product packaging displays. Your choice between corrugated and solid board will depend on whether you prioritize robust protection or aesthetic presentation in your packaging needs.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Corrugated board is significantly lighter than solid board, offering easier handling and reduced shipping costs in packaging applications. The composition of corrugated board, with its fluted inner layer, provides strength while maintaining a lightweight structure. Solid board, being denser and heavier, delivers greater rigidity but requires more effort in transport and handling operations.
Printing and Customization Options
Corrugated board offers versatile printing capabilities with options for flexographic, offset, and digital printing, allowing vibrant graphics and detailed designs suitable for retail packaging and promotional displays. Solid board provides a smoother surface ideal for high-quality offset printing, enabling sharp images and premium finishes for luxury product packaging and specialty boxes. Both materials support various customization techniques such as embossing, foil stamping, and spot UV coating to enhance visual appeal and brand differentiation.
Cost Effectiveness
Corrugated board offers superior cost effectiveness due to its lightweight structure and efficient use of raw materials, reducing shipping and production expenses compared to solid board. Solid board provides enhanced durability and strength but often incurs higher manufacturing and transportation costs. Businesses seeking budget-friendly packaging typically favor corrugated board for its balance of affordability and performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Corrugated board is generally more sustainable than solid board due to its higher recyclability and use of recycled fibers, significantly reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources. Solid board often requires more energy-intense production processes and uses more virgin materials, resulting in a larger carbon footprint. Sustainable packaging initiatives favor corrugated board for its biodegradability and lower environmental impact throughout the lifecycle.
Typical Applications and Industries
Corrugated board is widely used in packaging industries for shipping boxes, retail displays, and protective packaging due to its lightweight yet durable structure suitable for handling and transportation. Solid board finds extensive application in luxury packaging, cosmetic boxes, and book covers where a smooth surface and high rigidity are essential for aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. Industries such as e-commerce, food and beverage, and electronics predominantly utilize corrugated board, while the pharmaceutical, cosmetics, and publishing sectors favor solid board for premium packaging solutions.
Performance in Shipping and Storage
Corrugated board offers superior cushioning and resistance to impact, making it ideal for shipping fragile goods due to its fluted structure that absorbs shocks. Solid board provides excellent rigidity and stacking strength, ensuring your products remain stable during long-term storage and heavy load conditions. Choosing the right board depends on whether your priority is protection during transit or durability in storage environments.
Choosing the Right Board for Your Needs
Selecting the right board involves assessing durability requirements, with corrugated board offering lightweight strength ideal for shipping and protection, while solid board provides a rigid, smooth surface suited for retail packaging and presentation. Corrugated board consists of fluted layers that absorb impact and moisture, enhancing cushioning capabilities, whereas solid board's dense fiber composition ensures superior print quality and stiffness for visual appeal. Understanding the balance between cost-efficiency, protection level, and aesthetic demands guides the optimal choice between corrugated and solid board for specific packaging applications.
Corrugated board vs solid board Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com