Watermarking subtly integrates a transparent or translucent mark into paper or digital content to verify authenticity without altering its appearance, making it ideal for security and copyright protection. Embossing raises or indents a design or text on a surface, providing a tactile, visually striking effect that enhances branding and adds a professional touch to physical documents or products.
Table of Comparison
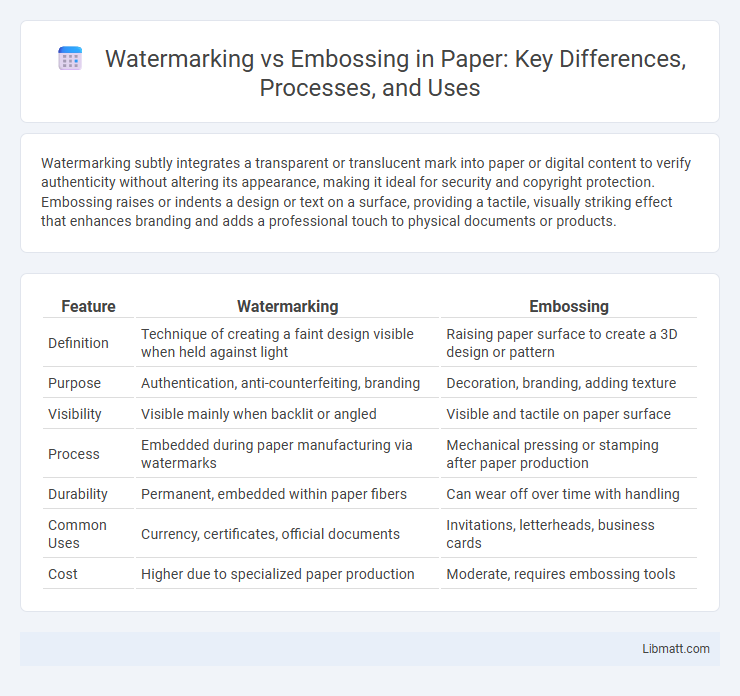
| Feature | Watermarking | Embossing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technique of creating a faint design visible when held against light | Raising paper surface to create a 3D design or pattern |
| Purpose | Authentication, anti-counterfeiting, branding | Decoration, branding, adding texture |
| Visibility | Visible mainly when backlit or angled | Visible and tactile on paper surface |
| Process | Embedded during paper manufacturing via watermarks | Mechanical pressing or stamping after paper production |
| Durability | Permanent, embedded within paper fibers | Can wear off over time with handling |
| Common Uses | Currency, certificates, official documents | Invitations, letterheads, business cards |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized paper production | Moderate, requires embossing tools |
Understanding Watermarking and Embossing
Watermarking involves embedding a subtle, often transparent design into paper or digital media to verify authenticity and prevent counterfeiting, while embossing creates a raised, tactile impression on a surface for decorative or branding purposes. Watermarks are primarily used for security and verification in documents like currency and certificates, whereas embossing enhances physical products such as business cards and stationery by adding texture and visual appeal. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right technique to protect your brand integrity or add a professional touch to your materials.
The Historical Evolution of Security Features
Watermarking and embossing have played critical roles in the historical evolution of security features, dating back to the 13th century when watermarks were first introduced in paper manufacturing to prevent counterfeiting. Embossing emerged later as a tactile security measure, enhancing document authenticity through raised patterns that are difficult to replicate. Your choice between these methods depends on the desired level of visual and physical security for sensitive documents.
Key Differences Between Watermarking and Embossing
Watermarking and embossing are distinct techniques used to enhance document security and authenticity, with watermarking involving translucent patterns embedded within paper fibers and embossing creating raised or recessed designs on the surface. Watermarks are typically visible when held against light, providing covert identification, while embossing offers tactile contrast visible under normal lighting conditions. The primary difference lies in watermarking's integration into the paper itself versus embossing's physical alteration of the paper surface.
Types of Watermarking Techniques
Watermarking techniques include visible, invisible, and digital watermarks, each serving different purposes in document security and brand protection. Visible watermarks are overlaid logos or text on documents or images to deter unauthorized use, while invisible watermarks embed data within the file, detectable only through specific software or hardware. Digital watermarking employs algorithms such as LSB (Least Significant Bit) modification, DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform), and spread spectrum techniques to embed information securely without compromising the original media's quality.
Popular Embossing Methods Explained
Popular embossing methods include blind embossing, which creates raised designs without ink or foil, and foil embossing, combining metallic foils with raised textures for a luxurious finish. Registered embossing aligns precisely with printed elements to enhance brand identity and visual appeal. Debossing, the inverse technique, presses designs into the material, creating recessed patterns for subtle, elegant effects.
Security and Authentication Benefits
Watermarking offers enhanced security by embedding invisible or subtle marks that verify authenticity without altering the original content, making it difficult for counterfeiters to replicate. Embossing provides a tactile and visible authentication method, adding a physical layer of security that is easily recognizable and hard to duplicate. You can combine both techniques to maximize protection, ensuring your documents or products have robust multi-level authentication and tamper-evident features.
Applications in Document and Brand Protection
Watermarking is commonly used in official documents such as passports, currency, and certificates to prevent counterfeiting and ensure authenticity by embedding subtle, often invisible, marks that are difficult to replicate. Embossing adds a raised or recessed design to paper or materials, widely employed in brand protection for packaging, business cards, and labels to provide tactile verification and enhance brand recognition. Both techniques serve as crucial security features, with watermarking offering covert validation and embossing delivering physical texture that deters forgery.
Cost and Implementation Considerations
Watermarking typically involves lower implementation costs due to its digital nature, requiring software integration without specialized hardware. Embossing demands higher upfront investment for physical tools and equipment, making it more suitable for high-volume production. Your choice depends on budget constraints and whether you prioritize cost-effective digital protection or durable physical marking.
Durability and Visual Impact Analysis
Watermarking offers subtle, translucent marks that enhance security without altering the paper's texture, ensuring durability through embedded fibers resistant to tampering. Embossing creates a raised surface pattern with a tactile and visual impact that is instantly recognizable but may wear down over time with frequent handling. Your choice between watermarking and embossing depends on whether you prioritize long-lasting invisibility and protection or a strong, tangible visual impression.
Choosing the Right Solution: Watermarking vs Embossing
Choosing the right solution between watermarking and embossing depends on your specific needs for brand protection and document authenticity. Watermarking offers covert security by embedding an invisible or semi-visible design within paper or digital content, making counterfeiting difficult without specialized equipment. Embossing provides a tactile, raised impression that enhances physical documents' visual appeal and verification, ideal for certificates and official papers requiring tangible validation.
Watermarking vs embossing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com