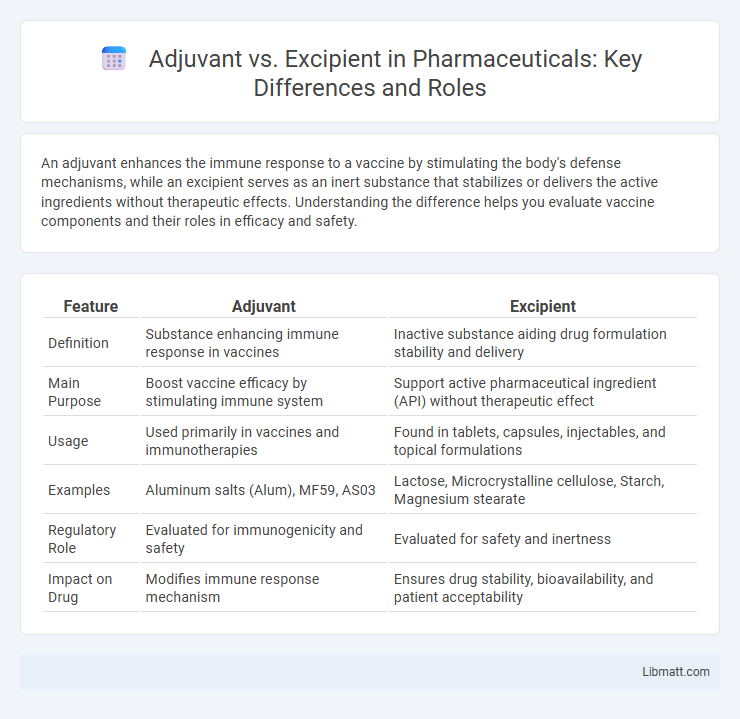
An adjuvant enhances the immune response to a vaccine by stimulating the body's defense mechanisms, while an excipient serves as an inert substance that stabilizes or delivers the active ingredients without therapeutic effects. Understanding the difference helps you evaluate vaccine components and their roles in efficacy and safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Adjuvant | Excipient |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Substance enhancing immune response in vaccines | Inactive substance aiding drug formulation stability and delivery |
| Main Purpose | Boost vaccine efficacy by stimulating immune system | Support active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) without therapeutic effect |
| Usage | Used primarily in vaccines and immunotherapies | Found in tablets, capsules, injectables, and topical formulations |
| Examples | Aluminum salts (Alum), MF59, AS03 | Lactose, Microcrystalline cellulose, Starch, Magnesium stearate |
| Regulatory Role | Evaluated for immunogenicity and safety | Evaluated for safety and inertness |
| Impact on Drug | Modifies immune response mechanism | Ensures drug stability, bioavailability, and patient acceptability |
Introduction to Adjuvants and Excipients
Adjuvants are specialized substances added to vaccines to enhance the body's immune response to the antigen, improving vaccine efficacy. Excipients, by contrast, are inactive components in pharmaceutical formulations that serve various roles such as stabilizing the active ingredient, improving solubility, or aiding in drug delivery. Understanding the distinct functions of adjuvants and excipients is critical for optimizing drug and vaccine formulation development.
Defining Adjuvant: Purpose and Types
An adjuvant is a substance added to vaccines to enhance the immune response, improving the effectiveness of the antigen. Common types of adjuvants include aluminum salts, oil-in-water emulsions, and toll-like receptor agonists, each designed to boost immunogenicity through different mechanisms. Understanding the purpose and types of adjuvants can help you appreciate their critical role in vaccine development and efficacy.
Understanding Excipients: Role and Classification
Excipients serve as inactive substances formulated alongside the active pharmaceutical ingredient to facilitate drug delivery, stability, and absorption. Their classification includes binders, disintegrants, fillers, lubricants, and preservatives, each playing a specific role in dosage form performance. Understanding excipients' functions is critical for optimizing drug formulation, enhancing therapeutic efficacy, and ensuring patient safety.
Key Differences Between Adjuvants and Excipients
Adjuvants enhance the immune response in vaccines by stimulating the body's immune system, while excipients serve as inactive substances that stabilize, preserve, or aid in the drug delivery process. Adjuvants are biologically active components such as aluminum salts or oil-in-water emulsions, whereas excipients include fillers, binders, and preservatives like lactose or magnesium stearate. The primary function of adjuvants is immunogenicity enhancement, whereas excipients ensure the safety, efficacy, and manufacturability of pharmaceutical formulations.
Mechanisms of Action: How Adjuvants and Excipients Work
Adjuvants enhance immune response by stimulating antigen-presenting cells, promoting cytokine production, and facilitating stronger, longer-lasting immunity. Excipients improve drug formulation stability, solubility, and bioavailability without directly affecting the biological activity of the active ingredient. The distinct mechanisms highlight adjuvants as active immune modulators, while excipients primarily serve as inert carriers or stabilizers in pharmaceutical products.
Applications in Pharmaceuticals and Vaccines
Adjuvants enhance the immune response in vaccines by stimulating stronger and longer-lasting immunity, making them crucial for vaccine efficacy. Excipients serve as inactive components in pharmaceutical formulations, providing stability, preservation, and improved delivery of active ingredients without affecting the therapeutic activity. Both adjuvants and excipients play essential roles in vaccine and drug development, with adjuvants targeting immunopotentiation and excipients ensuring formulation quality and patient safety.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Adjuvants are substances added to vaccines to enhance the immune response, requiring rigorous safety evaluations due to their active role in immunogenicity, whereas excipients serve primarily as inactive carriers or stabilizers with generally lower regulatory scrutiny. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA demand extensive preclinical and clinical data to ensure adjuvants do not cause adverse effects, reflecting their potential impact on vaccine safety profiles. Your understanding of these differences is crucial for compliance with stringent guidelines ensuring both adjuvant and excipient safety in pharmaceutical formulations.
Common Examples of Adjuvants and Excipients
Common examples of adjuvants include aluminum salts such as aluminum hydroxide and aluminum phosphate, which enhance the immune response in vaccines. Excipients commonly found in pharmaceutical formulations include lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, and magnesium stearate, serving as fillers, binders, or lubricants to ensure proper drug delivery and stability. Understanding the roles of these substances can help you better grasp their importance in medication efficacy and safety.
Importance in Drug Development and Efficacy
Adjuvants enhance the immune response in vaccines, playing a critical role in improving drug efficacy by boosting antigen potency and duration. Excipient components, although pharmacologically inactive, are essential for drug stability, delivery, and bioavailability, directly impacting the effectiveness and safety of pharmaceutical formulations. Both adjuvants and excipients are vital in drug development to optimize therapeutic outcomes and patient compliance.
Future Trends and Innovations
Future trends in adjuvant and excipient development emphasize biocompatible, multifunctional ingredients that enhance vaccine efficacy and drug delivery while minimizing side effects. Innovations include nanotechnology-based adjuvants that stimulate targeted immune responses and advanced excipients designed for improved stability and controlled release profiles. Your formulation strategies will benefit from leveraging these cutting-edge materials to optimize therapeutic outcomes and patient compliance.
Adjuvant vs Excipient Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com