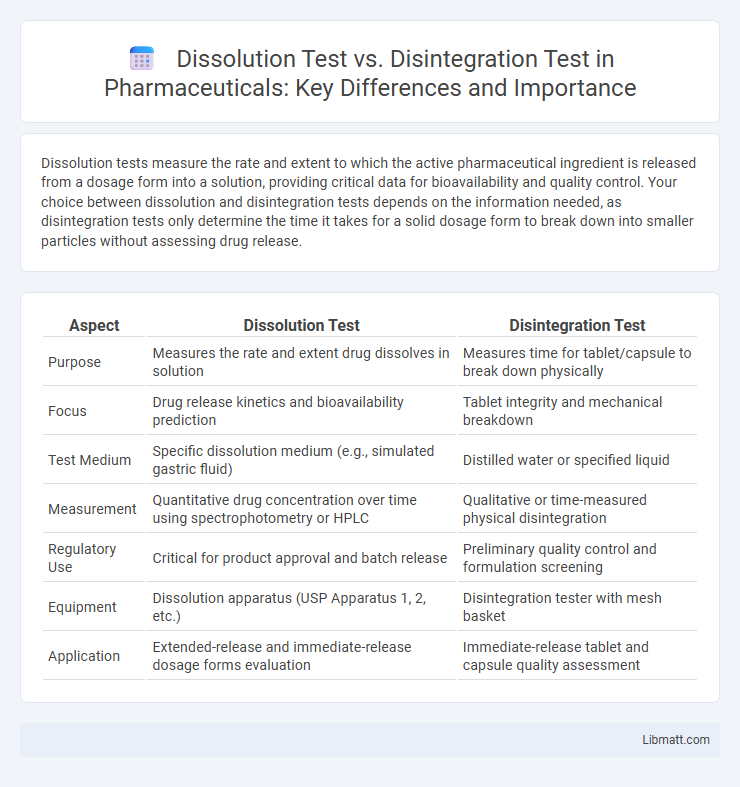
Dissolution tests measure the rate and extent to which the active pharmaceutical ingredient is released from a dosage form into a solution, providing critical data for bioavailability and quality control. Your choice between dissolution and disintegration tests depends on the information needed, as disintegration tests only determine the time it takes for a solid dosage form to break down into smaller particles without assessing drug release.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dissolution Test | Disintegration Test |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures the rate and extent drug dissolves in solution | Measures time for tablet/capsule to break down physically |
| Focus | Drug release kinetics and bioavailability prediction | Tablet integrity and mechanical breakdown |
| Test Medium | Specific dissolution medium (e.g., simulated gastric fluid) | Distilled water or specified liquid |
| Measurement | Quantitative drug concentration over time using spectrophotometry or HPLC | Qualitative or time-measured physical disintegration |
| Regulatory Use | Critical for product approval and batch release | Preliminary quality control and formulation screening |
| Equipment | Dissolution apparatus (USP Apparatus 1, 2, etc.) | Disintegration tester with mesh basket |
| Application | Extended-release and immediate-release dosage forms evaluation | Immediate-release tablet and capsule quality assessment |
Introduction to Dissolution and Disintegration Tests
Dissolution and disintegration tests are critical quality control procedures in pharmaceutical analysis, ensuring proper drug release and absorption. The dissolution test measures the rate and extent at which the active pharmaceutical ingredient dissolves in a specific solvent, providing insight into bioavailability. Disintegration testing assesses how quickly a tablet or capsule breaks down into smaller fragments, indicating its ability to release the drug for absorption; Your choice between these tests depends on the formulation and regulatory requirements.
Definition of Dissolution Test
The dissolution test measures the rate and extent to which the active pharmaceutical ingredient is released from a solid dosage form into a solution under standardized conditions, providing critical data for drug bioavailability and quality control. This test quantifies the percentage of drug dissolved over time, helping to predict the drug's behavior in the gastrointestinal tract. Your understanding of the dissolution test is essential for ensuring consistent therapeutic efficacy and regulatory compliance in pharmaceutical development.
Definition of Disintegration Test
The Disintegration Test evaluates the time required for a tablet or capsule to break down into smaller fragments under specified conditions, ensuring it will dissolve and release the active pharmaceutical ingredient efficiently. Unlike the Dissolution Test, which measures the rate and extent of drug release into solution, the Disintegration Test focuses solely on the physical breakdown of the dosage form. Your understanding of this test is essential for guaranteeing consistent drug performance and patient safety.
Purpose and Importance of Each Test
Dissolution tests measure the rate and extent at which the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) dissolves in a specified solvent, ensuring consistent drug bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. Disintegration tests assess the time it takes for a tablet or capsule to break down into smaller particles, serving as a critical quality control step to predict how quickly the drug will begin to release in your body. Each test plays a vital role in guaranteeing drug performance: dissolution verifies the release profile, while disintegration ensures proper dosage form breakdown for optimal absorption.
Key Differences Between Dissolution and Disintegration
Dissolution test measures the percentage of drug substance released from dosage forms into a solution over time, providing critical data on bioavailability and drug release kinetics. Disintegration test evaluates the time required for a tablet or capsule to break down into smaller fragments under specified conditions, focusing on physical breakdown rather than drug release. While dissolution is a quantitative test essential for quality control and formulation development, disintegration is a qualitative assay mainly used to ensure dosage form integrity and predict in vivo behavior.
Methodology and Equipment Used
Dissolution tests utilize apparatus like USP Apparatus 1 (basket) or Apparatus 2 (paddle) to measure the rate at which an active pharmaceutical ingredient dissolves in a specific medium, often employing UV spectrophotometry for quantification. Disintegration tests use a basket-rack assembly with individual tubes containing tablets submerged in a controlled fluid medium, assessing the time taken for tablets to break down into smaller fragments without fully dissolving. Both methods rely on precise temperature control and agitation, but dissolution testing provides a quantitative measure of drug release, whereas disintegration testing offers a qualitative assessment of tablet breakdown.
Regulatory Guidelines and Standards
Dissolution test and disintegration test are both critical quality control measures governed by regulatory guidelines from agencies such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), European Pharmacopoeia (EP), and International Council for Harmonisation (ICH). The dissolution test assesses the rate and extent of drug release in vitro, aligning with specific monograph specifications and regulatory standards for bioavailability and bioequivalence. Disintegration test focuses on the time required for a dosage form to break down into smaller fragments under standardized conditions, serving as a preliminary quality parameter mandated by regulatory authorities to predict in vivo performance.
Factors Affecting Test Results
Dissolution test results are influenced by factors such as the composition of the drug formulation, agitation speed, dissolution medium pH, and temperature, which affect the rate at which the active pharmaceutical ingredient dissolves. Disintegration test outcomes depend on tablet hardness, excipient properties, moisture content, and test apparatus conditions like medium temperature and volume, impacting the time taken for the dosage form to break down. Both tests require strict control of environmental and formulation variables to ensure reproducible and clinically relevant results.
Applications in Pharmaceutical Quality Control
Dissolution tests quantify the rate and extent of drug release from solid dosage forms, ensuring bioequivalence and predicting in vivo drug performance during pharmaceutical quality control. Disintegration tests assess the time required for tablets or capsules to break down into smaller fragments, which is critical for formulations where rapid release is desired. Both tests are essential for validating product consistency, complying with pharmacopeial standards, and supporting regulatory submissions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Test
Selecting the appropriate test depends on the objective: dissolution testing measures the rate and extent of drug release in a liquid medium, essential for predicting bioavailability, while disintegration testing evaluates how quickly a dosage form breaks down into smaller particles, impacting onset of action. Your choice should align with regulatory requirements and formulation characteristics, ensuring accurate assessment of product performance. Understanding the specific purpose of each test helps optimize drug development and quality control processes.
Dissolution test vs disintegration test Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com