GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) establishes the basic guidelines to ensure product safety and quality, while cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practice) emphasizes adhering to the most up-to-date standards and technologies in manufacturing processes. Your compliance with cGMP guarantees that production continually meets evolving regulatory requirements and maintains high industry standards.
Table of Comparison
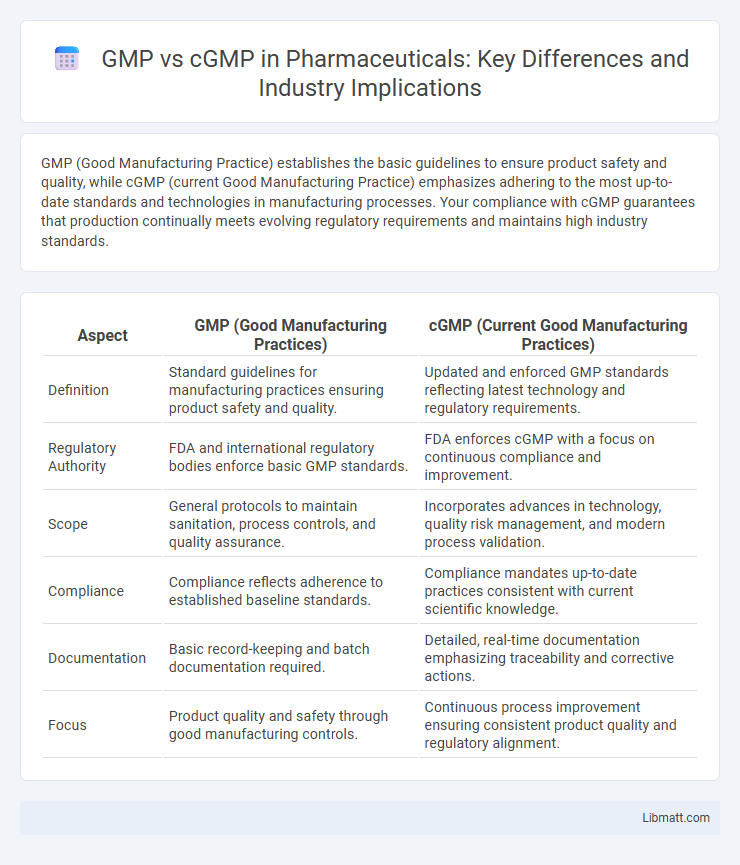
| Aspect | GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) | cGMP (Current Good Manufacturing Practices) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standard guidelines for manufacturing practices ensuring product safety and quality. | Updated and enforced GMP standards reflecting latest technology and regulatory requirements. |
| Regulatory Authority | FDA and international regulatory bodies enforce basic GMP standards. | FDA enforces cGMP with a focus on continuous compliance and improvement. |
| Scope | General protocols to maintain sanitation, process controls, and quality assurance. | Incorporates advances in technology, quality risk management, and modern process validation. |
| Compliance | Compliance reflects adherence to established baseline standards. | Compliance mandates up-to-date practices consistent with current scientific knowledge. |
| Documentation | Basic record-keeping and batch documentation required. | Detailed, real-time documentation emphasizing traceability and corrective actions. |
| Focus | Product quality and safety through good manufacturing controls. | Continuous process improvement ensuring consistent product quality and regulatory alignment. |
Introduction to GMP and cGMP
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) establishes the fundamental quality standards for production processes to ensure product safety and consistency in pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) builds upon GMP by integrating the latest technological advancements and regulatory updates to maintain up-to-date compliance within manufacturing environments. Both GMP and cGMP emphasize stringent documentation, process control, and facility hygiene to minimize risks and protect consumer health.
Defining GMP: What Does It Mean?
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) refers to the established guidelines ensuring that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards designed to minimize risks. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) represents the latest, updated standards reflecting advances in technology and regulatory expectations to ensure optimal product safety and efficacy. Your compliance with GMP or cGMP protocols is crucial for maintaining product integrity and meeting regulatory requirements.
What Is cGMP? Core Concepts
cGMP, or Current Good Manufacturing Practice, represents the updated and more stringent standards for manufacturing processes compared to the original GMP guidelines. It emphasizes continuous improvement and compliance with the latest regulatory requirements to ensure product quality, safety, and efficacy. You must understand that cGMP covers all aspects of production, including materials, facilities, equipment, and employee training to minimize risks and contamination.
Key Differences Between GMP and cGMP
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) refers to the foundation of standards ensuring products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practice) emphasizes the importance of using the most up-to-date guidelines and technologies to improve product safety, quality, and efficacy. The key differences lie in cGMP's requirement for continuous updates and adaptations based on the latest regulatory expectations and scientific advancements, while GMP represents the baseline compliance.
Historical Evolution: From GMP to cGMP
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) originated in the 1960s as a set of guidelines to ensure the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products. The evolution to current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) emerged in the 1970s, emphasizing continuous improvement and stricter regulatory oversight to address emerging challenges in manufacturing processes. This shift from GMP to cGMP reflects the integration of advanced technologies and updated standards to maintain product integrity and compliance in the modern pharmaceutical industry.
Regulatory Bodies and Global Standards
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines are enforced by regulatory bodies such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and the World Health Organization (WHO), ensuring consistent quality in pharmaceutical production. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) represents the most up-to-date standards mandated by these organizations, reflecting continual improvements in technology and processes. These global standards safeguard public health by requiring manufacturers to maintain rigorous documentation, cleanliness, and quality control throughout the production lifecycle.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementation challenges of GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) include inconsistent documentation and lack of staff training, which often lead to compliance gaps. Transitioning to cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practices) requires incorporating real-time quality monitoring and updated regulatory guidelines to ensure product safety and efficacy. Solutions involve investing in automated quality control systems, continuous personnel education, and robust audit mechanisms to maintain compliance with evolving standards.
Industry Impact: Pharmaceuticals, Food, and Biotechnology
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) and cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practices) set essential quality standards in pharmaceuticals, food, and biotechnology industries, ensuring products meet safety and efficacy requirements. Your compliance with cGMP regulations reflects updated protocols that incorporate technological advancements and stricter controls, reducing contamination risks and enhancing product consistency. This adherence significantly impacts regulatory approvals, consumer trust, and overall market competitiveness.
Compliance Requirements and Best Practices
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) establish baseline standards to ensure product quality and safety in manufacturing processes, while cGMP (current GMP) emphasizes the most up-to-date regulations enforced by agencies like the FDA. Compliance with cGMP requires continuous review and integration of evolving industry standards, rigorous documentation, and active quality control systems to meet regulatory inspections. Best practices include implementing preventive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and comprehensive employee training programs to maintain compliance and enhance product consistency.
Future Trends in GMP and cGMP Standards
Future trends in GMP and cGMP standards emphasize the integration of digital technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and advanced analytics to enhance quality control and traceability. Regulatory agencies are increasingly adopting risk-based approaches and real-time monitoring to ensure compliance and product safety. Enhanced guidelines for sustainable manufacturing practices and continuous process verification are shaping the evolution of GMP and cGMP frameworks.
GMP vs cGMP Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com