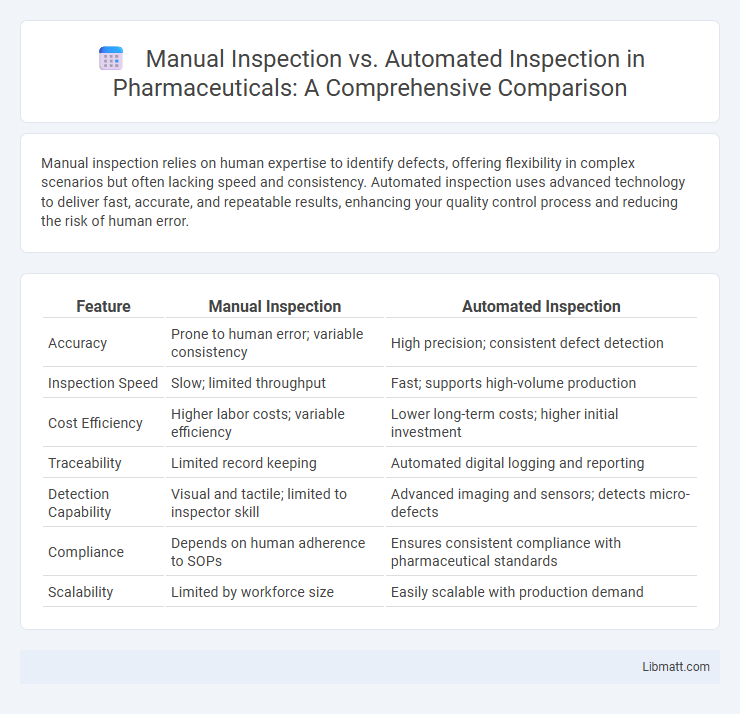
Manual inspection relies on human expertise to identify defects, offering flexibility in complex scenarios but often lacking speed and consistency. Automated inspection uses advanced technology to deliver fast, accurate, and repeatable results, enhancing your quality control process and reducing the risk of human error.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Inspection | Automated Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Prone to human error; variable consistency | High precision; consistent defect detection |
| Inspection Speed | Slow; limited throughput | Fast; supports high-volume production |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher labor costs; variable efficiency | Lower long-term costs; higher initial investment |
| Traceability | Limited record keeping | Automated digital logging and reporting |
| Detection Capability | Visual and tactile; limited to inspector skill | Advanced imaging and sensors; detects micro-defects |
| Compliance | Depends on human adherence to SOPs | Ensures consistent compliance with pharmaceutical standards |
| Scalability | Limited by workforce size | Easily scalable with production demand |
Introduction to Manual and Automated Inspection
Manual inspection involves human operators visually examining products or components to identify defects, relying on experience and sensory judgment. Automated inspection uses advanced technologies such as machine vision, sensors, and AI algorithms to detect inconsistencies and ensure quality with higher speed and accuracy. Both methods play crucial roles in quality control, but automated systems offer enhanced consistency, repeatability, and data integration capabilities.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automated Inspection
Manual inspection relies on human expertise to identify defects through visual or tactile evaluation, while automated inspection uses machines and sensors for consistent, high-speed quality assessment. Key differences include accuracy, with automated systems reducing human error, and scalability, as automated inspections handle large volumes more efficiently. Cost and flexibility also vary: manual inspection is more adaptable but labor-intensive, whereas automation requires higher upfront investment but lowers long-term operational costs.
Advantages of Manual Inspection
Manual inspection offers unparalleled precision when evaluating complex or irregular products that automated systems may misinterpret. It allows human inspectors to apply subjective judgment and experience, identifying subtle defects invisible to machines. Your quality control process benefits from this flexibility, ensuring accurate detection tailored to specific manufacturing nuances.
Limitations of Manual Inspection
Manual inspection faces limitations such as human error, inconsistent quality, and slower processing times, affecting overall reliability and efficiency. Fatigue and subjectivity can lead to missed defects or false positives, reducing inspection accuracy. Limited scalability and higher labor costs also constrain its effectiveness in high-volume or complex manufacturing environments.
Benefits of Automated Inspection Systems
Automated inspection systems enhance accuracy by minimizing human error and ensuring consistent quality control across production lines. These systems increase inspection speed, enabling real-time defect detection and reducing downtime in manufacturing processes. Integration with AI and machine learning algorithms allows automated inspections to adapt to complex patterns and improve over time, providing scalable efficiency for industrial applications.
Challenges in Implementing Automated Inspection
Automated inspection faces challenges including high initial costs, complex integration with existing manufacturing systems, and limitations in detecting subtle defects that human inspectors might identify. Variability in product types and environmental conditions can reduce the accuracy and reliability of automated systems. Ensuring consistent calibration and maintenance of sensors and cameras is essential to maintain inspection quality over time.
Cost Comparison: Manual vs Automated Inspection
Manual inspection incurs higher ongoing labor costs due to time-intensive processes and reliance on skilled inspectors, whereas automated inspection requires significant upfront investment in technology but reduces long-term operational expenses through faster, consistent quality checks. Automated systems improve cost efficiency by minimizing human error and enabling continuous production without breaks, leading to lower defect rates and less rework. While manual inspection remains cost-effective for low-volume or highly customized products, automated inspection is economically advantageous for high-volume manufacturing with strict quality standards.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Manual inspection remains essential in industries requiring detailed human judgment, such as aerospace for defect detection in complex components, while automated inspection excels in high-volume sectors like electronics manufacturing, ensuring consistent quality through machine vision systems. Case studies show automotive manufacturers reducing defect rates by 30% using automated optical inspection, whereas pharmaceuticals rely on manual inspection for verifying packaging integrity due to regulatory demands. Your choice between manual and automated inspection should align with industry-specific quality standards, production scale, and the criticality of human expertise.
Future Trends in Inspection Technologies
Future trends in inspection technologies highlight the growing integration of AI-powered automated inspection systems that offer higher precision and faster defect detection compared to manual inspection. These advanced systems use machine learning algorithms and computer vision to continuously improve accuracy and reduce human error, enhancing product quality control. Embracing these innovations can streamline your inspection processes and significantly boost operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Inspection Method
Selecting the appropriate inspection method hinges on factors such as precision requirements, budget constraints, and production volume. Manual inspection offers flexibility and detailed human judgment for complex or low-volume tasks, while automated inspection provides consistent speed and accuracy suitable for high-throughput environments. Evaluating the trade-offs between human expertise and technological efficiency ensures optimal quality control tailored to specific industry needs.
Manual Inspection vs Automated Inspection Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com