Nutraceuticals provide natural health benefits by supporting overall wellness and preventing diseases through nutrients found in foods, while pharmaceuticals are chemically formulated drugs designed to diagnose, treat, or cure specific medical conditions. Understanding the difference helps You choose between holistic support and targeted medical intervention based on Your health needs.
Table of Comparison
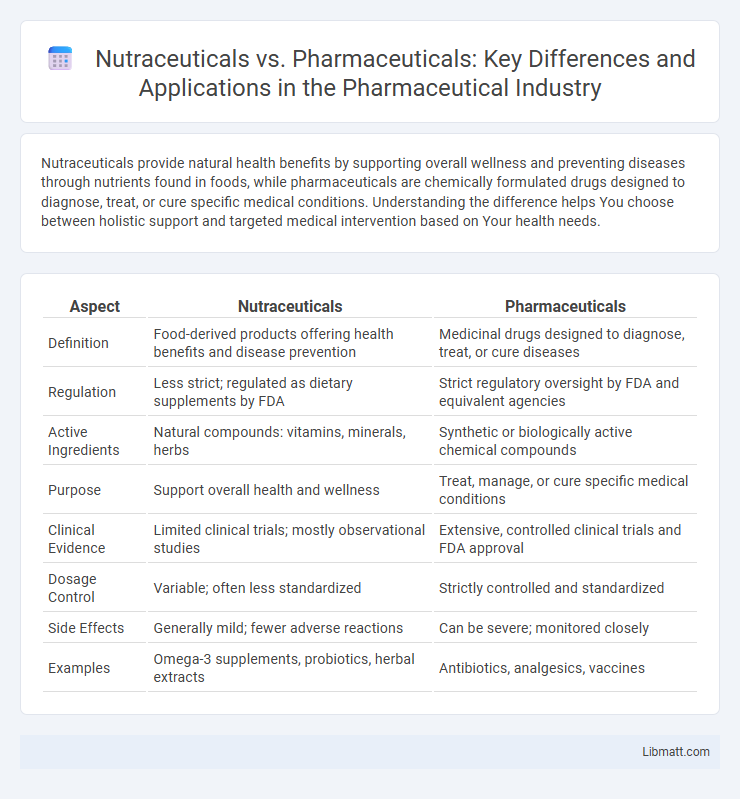
| Aspect | Nutraceuticals | Pharmaceuticals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Food-derived products offering health benefits and disease prevention | Medicinal drugs designed to diagnose, treat, or cure diseases |
| Regulation | Less strict; regulated as dietary supplements by FDA | Strict regulatory oversight by FDA and equivalent agencies |
| Active Ingredients | Natural compounds: vitamins, minerals, herbs | Synthetic or biologically active chemical compounds |
| Purpose | Support overall health and wellness | Treat, manage, or cure specific medical conditions |
| Clinical Evidence | Limited clinical trials; mostly observational studies | Extensive, controlled clinical trials and FDA approval |
| Dosage Control | Variable; often less standardized | Strictly controlled and standardized |
| Side Effects | Generally mild; fewer adverse reactions | Can be severe; monitored closely |
| Examples | Omega-3 supplements, probiotics, herbal extracts | Antibiotics, analgesics, vaccines |
Understanding Nutraceuticals and Pharmaceuticals
Nutraceuticals, derived from food sources, provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition by supporting wellness and preventing chronic diseases, often categorized as dietary supplements or functional foods. Pharmaceuticals consist of chemically synthesized or biologically derived drugs designed to diagnose, treat, or cure specific medical conditions with regulated dosing and clinical testing. Understanding the differences helps you make informed decisions about preventive health versus targeted medical treatment.
Key Definitions and Distinctions
Nutraceuticals refer to food-derived products that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition, often used to prevent or manage chronic diseases, while pharmaceuticals are chemically synthesized or biologically sourced drugs designed to diagnose, treat, or cure specific medical conditions. Nutraceuticals typically have a regulatory status as dietary supplements with less stringent clinical testing requirements compared to pharmaceuticals, which undergo rigorous clinical trials and strict regulatory approval processes through agencies like the FDA. The primary distinction lies in their intended use: nutraceuticals focus on health maintenance and prevention, whereas pharmaceuticals target active treatment of diagnosed illnesses.
Sources and Composition
Nutraceuticals originate primarily from natural sources such as plants, herbs, and food ingredients, often containing bioactive compounds like vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytochemicals. Pharmaceuticals consist of chemically synthesized or biologically-derived active ingredients with specific molecular structures designed for targeted therapeutic effects. Your choice between these depends on whether you prefer naturally sourced compounds with broader health benefits or precisely formulated medications for specific medical conditions.
Mechanisms of Action
Nutraceuticals exert their effects primarily by providing bioactive compounds such as antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support cellular health and modulate metabolic pathways, often enhancing your body's natural defense mechanisms. Pharmaceuticals typically target specific biological receptors or enzymes with synthesized molecules to achieve precise therapeutic effects and rapid symptom relief. Understanding these distinct mechanisms of action helps you make informed decisions about integrating nutraceuticals with traditional pharmaceutical treatments for optimal health outcomes.
Health Benefits and Therapeutic Uses
Nutraceuticals offer health benefits by providing natural compounds like vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall wellness and disease prevention. Pharmaceuticals are specifically formulated for targeted therapeutic uses, such as treating infections, managing chronic diseases, and alleviating symptoms with clinically tested efficacy. Your choice between nutraceuticals and pharmaceuticals depends on whether you seek preventive health support or precise medical treatment.
Safety, Side Effects, and Regulations
Nutraceuticals generally have a strong safety profile due to natural ingredients, though they may cause mild side effects like digestive discomfort, and their regulation is less stringent compared to pharmaceuticals, with oversight varying by country. Pharmaceuticals undergo rigorous clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy, but they often carry higher risks of serious side effects due to potent active compounds. Understanding the differences in regulatory frameworks helps you make informed choices about using nutraceuticals or pharmaceuticals for health management.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
The global nutraceuticals market is experiencing rapid growth, projected to reach over $400 billion by 2027, driven by increasing consumer demand for natural and preventive health solutions. Pharmaceuticals remain dominant in treating acute and chronic conditions, but shifting consumer preferences toward wellness and holistic care are boosting nutraceutical adoption. Understanding these market trends helps you navigate the expanding options for health supplementation versus conventional medicine.
Clinical Evidence and Research Findings
Nutraceuticals are often supported by limited clinical evidence, primarily derived from smaller studies or observational research, whereas pharmaceuticals undergo rigorous, large-scale randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to establish efficacy and safety. Research findings indicate pharmaceuticals must meet stringent regulatory standards before approval, ensuring consistent dosage and therapeutic outcomes, while nutraceuticals lack uniform regulatory oversight, leading to variability in product quality and clinical proof. When considering options for your health, understanding the difference in evidence strength can help guide informed decisions between nutraceutical supplements and pharmaceutical treatments.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Nutraceuticals face challenges such as inconsistent regulatory standards, limited clinical evidence, and variability in bioavailability compared to pharmaceuticals, which benefit from rigorous testing and approval processes. Future prospects include advancements in personalized nutrition, enhanced formulation technologies, and stronger scientific validation to bridge efficacy gaps. Your informed choices can drive demand for integrative approaches combining nutraceutical benefits with pharmaceutical precision.
Choosing Between Nutraceuticals and Pharmaceuticals
Choosing between nutraceuticals and pharmaceuticals depends on your health goals, medical conditions, and desired outcomes. Nutraceuticals, derived from natural sources, offer preventive benefits and support overall wellness, while pharmaceuticals provide targeted treatment for specific illnesses with scientifically validated efficacy. Understanding your individual needs and consulting healthcare professionals can guide the optimal choice for effective health management.
Nutraceuticals vs pharmaceuticals Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com