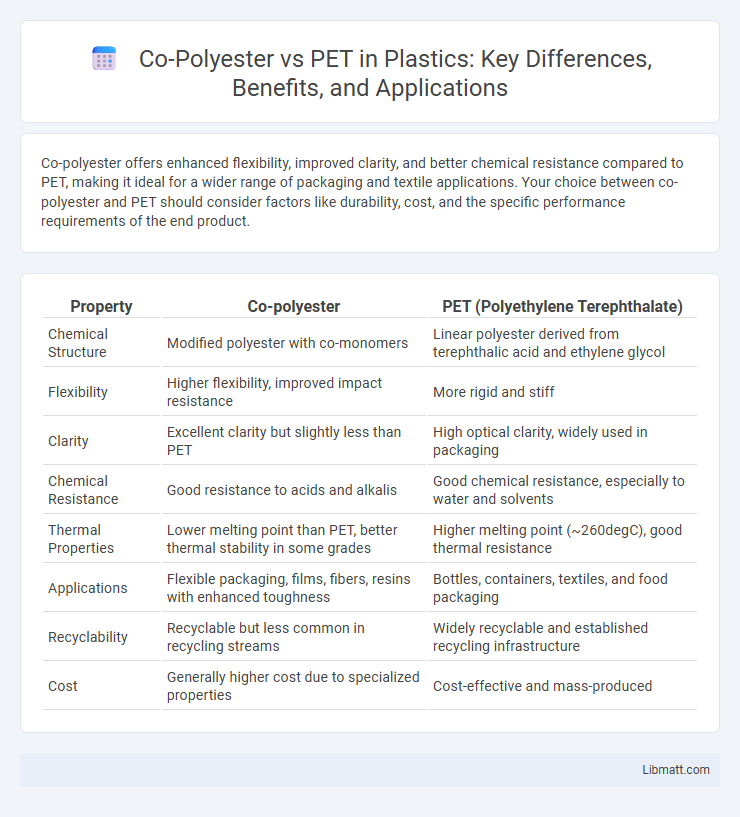
Co-polyester offers enhanced flexibility, improved clarity, and better chemical resistance compared to PET, making it ideal for a wider range of packaging and textile applications. Your choice between co-polyester and PET should consider factors like durability, cost, and the specific performance requirements of the end product.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Co-polyester | PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Modified polyester with co-monomers | Linear polyester derived from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol |
| Flexibility | Higher flexibility, improved impact resistance | More rigid and stiff |
| Clarity | Excellent clarity but slightly less than PET | High optical clarity, widely used in packaging |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Good chemical resistance, especially to water and solvents |
| Thermal Properties | Lower melting point than PET, better thermal stability in some grades | Higher melting point (~260degC), good thermal resistance |
| Applications | Flexible packaging, films, fibers, resins with enhanced toughness | Bottles, containers, textiles, and food packaging |
| Recyclability | Recyclable but less common in recycling streams | Widely recyclable and established recycling infrastructure |
| Cost | Generally higher cost due to specialized properties | Cost-effective and mass-produced |
Introduction to Co-Polyester and PET
Co-polyester features a modified polymer structure that enhances flexibility, clarity, and durability compared to PET, making it ideal for a variety of packaging and textile applications. PET, or polyethylene terephthalate, is a widely used polyester known for its strength, transparency, and recyclability, commonly utilized in beverage bottles and synthetic fibers. Understanding the differences in chemical composition and performance characteristics helps you choose the right material for your specific manufacturing or packaging needs.
Chemical Structure Differences
Co-polyester features a modified chemical structure integrating different diols or acids, which results in enhanced flexibility and durability compared to PET's homopolymer structure primarily composed of polyethylene terephthalate units. PET consists of repeating ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid units, forming a rigid and crystalline polymer chain. Your choice between co-polyester and PET depends on the desired balance between mechanical properties and chemical resistance driven by these structural variations.
Manufacturing Processes
Co-polyester manufacturing involves polymerizing multiple monomers, often combining terephthalic acid with other acids or glycols to enhance flexibility and durability, while PET production uses a single monomer, primarily purified terephthalic acid with ethylene glycol, through melt polymerization and solid-state polycondensation. Co-polyester's adjusted chemical composition allows for varied crystallinity and melting points, impacting processing parameters such as extrusion temperature and cooling rates compared to the more standardized thermal profile in PET fabrication. These differences in polymer chain structure influence the manufacturing steps, making co-polyesters suitable for applications requiring tailored mechanical and optical properties beyond conventional PET capabilities.
Mechanical and Physical Properties Comparison
Co-polyester exhibits higher impact resistance and greater flexibility compared to PET, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and flexibility. PET typically offers better tensile strength and dimensional stability, contributing to its widespread use in packaging and textiles. Both materials demonstrate good chemical resistance, but co-polyester's enhanced toughness makes it preferred in components subjected to mechanical stress.
Applications in Industry
Co-polyester offers enhanced flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for packaging, textiles, and automotive parts where durability and impact resistance are crucial. PET is widely utilized in beverage containers, fibers, and food packaging due to its excellent strength, clarity, and recyclability. Your choice between co-polyester and PET depends on the specific performance requirements and environmental considerations in industrial applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Co-polyester offers enhanced environmental benefits compared to PET due to its improved biodegradability and lower carbon footprint during production. PET is widely recyclable through established collection and processing systems, but Co-polyester's unique chemical structure can present challenges for conventional recycling streams. You should consider Co-polyester for applications prioritizing sustainability, while PET remains a strong choice for efficient, large-scale recycling initiatives.
Cost Considerations
Co-polyester typically offers a cost advantage over PET due to lower production expenses and enhanced processing efficiency, making it attractive for budget-sensitive manufacturing. PET often involves higher raw material costs and more energy-intensive processing, leading to increased overall expenses. Manufacturers must weigh these cost factors against performance requirements when selecting between co-polyester and PET for packaging or textile applications.
Performance in Packaging
Co-polyester offers superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to PET, making it ideal for packaging that requires durability and shape retention. PET provides excellent clarity and barrier properties, ensuring your packaged goods stay fresh and visible to consumers. Choosing co-polyester enhances toughness, while PET excels in maintaining product integrity and shelf appeal.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Co-polyester offers enhanced flexibility, improved impact resistance, and better clarity compared to PET, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and aesthetic appeal. PET, known for its excellent chemical resistance, high tensile strength, and recyclability, provides cost-effective and eco-friendly solutions but can be more rigid and prone to brittleness under stress. Understanding the trade-offs between Co-polyester and PET helps you select the optimal material for your specific packaging or manufacturing needs.
Future Trends and Innovations
Co-polyester is gaining traction over PET due to its enhanced flexibility, recyclability, and potential for bio-based formulations, driving innovation in sustainable packaging and textiles. Emerging technologies emphasize co-polyester's capacity for improved barrier properties and mechanical strength, catering to evolving consumer demands for durability and environmental responsibility. Industry trends indicate a shift towards hybrid materials that blend co-polyester with other polymers to optimize performance and reduce carbon footprints in various applications.
Co-polyester vs PET Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com