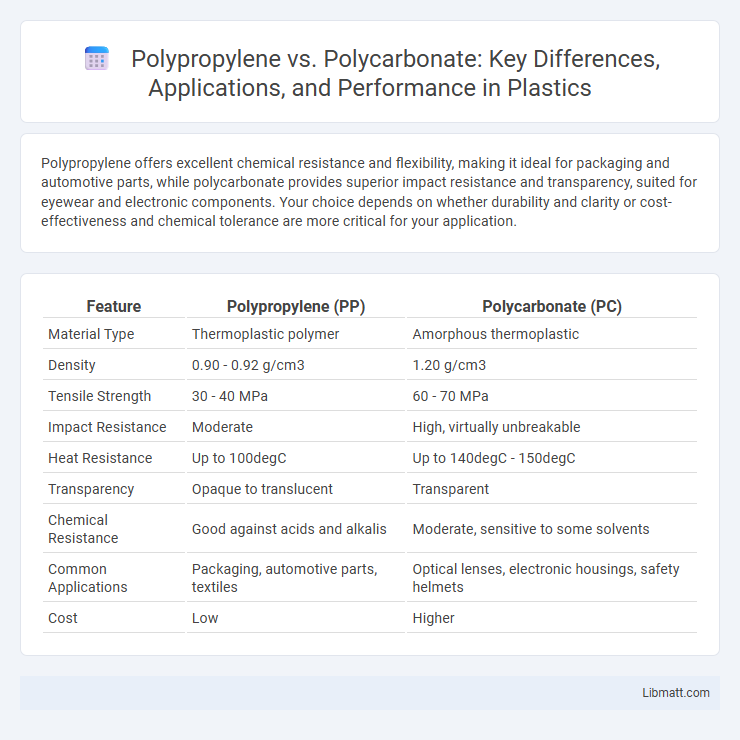
Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for packaging and automotive parts, while polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance and transparency, suited for eyewear and electronic components. Your choice depends on whether durability and clarity or cost-effectiveness and chemical tolerance are more critical for your application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polypropylene (PP) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Amorphous thermoplastic |
| Density | 0.90 - 0.92 g/cm3 | 1.20 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 30 - 40 MPa | 60 - 70 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High, virtually unbreakable |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 140degC - 150degC |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Transparent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis | Moderate, sensitive to some solvents |
| Common Applications | Packaging, automotive parts, textiles | Optical lenses, electronic housings, safety helmets |
| Cost | Low | Higher |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polycarbonate
Polypropylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods due to its excellent chemical resistance, low density, and high impact strength. Polycarbonate is a durable, transparent thermoplastic known for its outstanding toughness, optical clarity, and heat resistance, making it ideal for applications such as eyewear lenses, electronics, and safety equipment. Both materials offer distinct mechanical properties and thermal stability, influencing their suitability across various industrial and commercial uses.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer made from the polymerization of propylene monomers, characterized by a repeating chain of carbon atoms with attached methyl groups, resulting in a semi-crystalline structure. Polycarbonate, on the other hand, consists of aromatic carbonate groups linked by bisphenol A units, giving it an amorphous, transparent structure with high impact resistance. The chemical structure of polypropylene provides flexibility and chemical resistance, while polycarbonate's composition imparts rigidity and thermal stability.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance, lightweight properties, and moderate tensile strength, making it ideal for flexible and impact-resistant applications. Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance, higher tensile strength, and enhanced optical clarity, suitable for durable, transparent, and heat-resistant components. Your choice between these polymers depends on the balance needed between toughness, flexibility, and thermal stability for your specific project.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring high strength and shatterproof properties. Polypropylene is lightweight and resistant to chemical fatigue but is more prone to cracking and deformation under heavy impact. Your choice between these plastics should consider the need for toughness versus cost-effectiveness in durability performance.
Temperature and Chemical Resistance
Polypropylene exhibits excellent chemical resistance against acids, bases, and solvents, and maintains stability up to temperatures around 100-110degC, making it suitable for various industrial applications. Polycarbonate offers superior heat resistance with a glass transition temperature near 147degC and resists many chemicals, but it is vulnerable to strong acids and alkalis, limiting its use in harsh chemical environments. Selecting between polypropylene and polycarbonate depends largely on the specific temperature demands and the chemical exposure of the intended application.
Applications in Various Industries
Polypropylene finds widespread use in packaging, automotive parts, and medical devices due to its lightweight, chemical resistance, and affordability. Polycarbonate dominates applications requiring high impact resistance and optical clarity, such as eyewear lenses, electronic components, and bulletproof glass. Understanding these material differences helps you select the optimal polymer for your industry-specific needs, balancing durability with cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) exhibits a lower environmental impact due to its lightweight nature and efficient recyclability, often processed through mechanical recycling methods that reduce landfill waste. Polycarbonate (PC), while offering superior strength and clarity, has a more complex recycling process involving chemical recycling to break down its polymer chains, which is less common and energy-intensive. Both materials' recyclability depends on local infrastructure, but PP is generally favored for environmentally conscious applications due to its widespread recyclability and lower carbon footprint.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Polypropylene is generally more cost-effective than polycarbonate, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. Polycarbonate offers superior strength and durability but comes with a higher price tag and less widespread availability. You can find polypropylene readily available in various forms and markets, while polycarbonate may require sourcing from specialized suppliers.
Safety Considerations and Food Contact
Polypropylene is widely recognized for its chemical resistance and high melting point, making it a safe choice for food contact applications, especially in microwaving and dishwasher use. Polycarbonate contains bisphenol A (BPA), which raises safety concerns due to potential hormone disruption, leading to restrictions in food-contact products. Regulatory agencies like the FDA have approved polypropylene for food contact, while polycarbonate is being phased out in many food-related uses due to these safety considerations.
Choosing the Right Material: Polypropylene vs Polycarbonate
Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance, lightweight properties, and high impact strength, making it ideal for packaging, automotive parts, and reusable containers. Polycarbonate provides superior clarity, heat resistance, and toughness, which suits applications requiring transparency and durability such as eyewear lenses, medical devices, and electronic components. Understanding your project's specific needs for strength, clarity, and temperature tolerance will help you choose between polypropylene and polycarbonate effectively.
Polypropylene vs Polycarbonate Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com