E-beam sterilization uses high-energy electrons to rapidly eliminate microorganisms on your products, offering precise control and shorter processing times compared to gamma sterilization, which relies on radioactive cobalt-60 sources for deep penetration and proven effectiveness. Choosing between these methods depends on factors like material compatibility, desired sterilization depth, and processing speed.
Table of Comparison
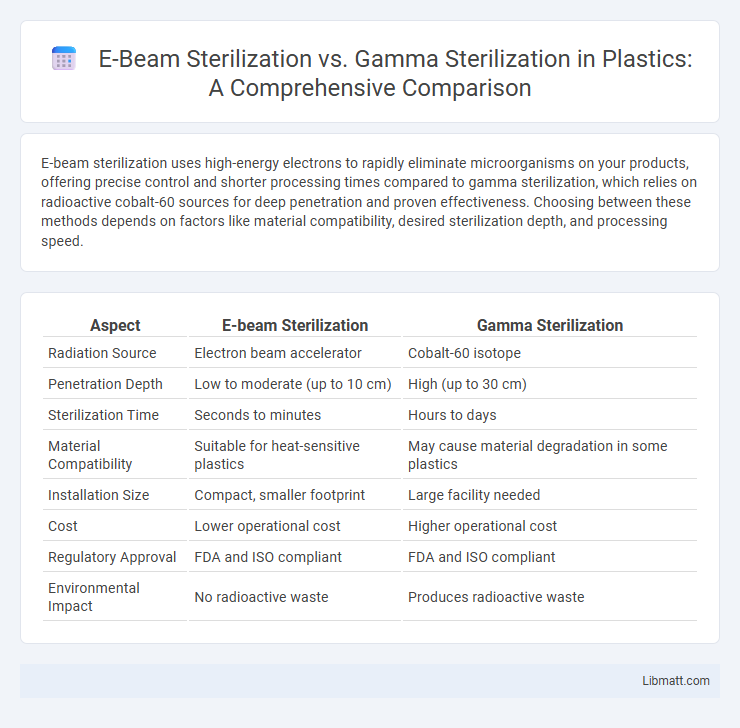
| Aspect | E-beam Sterilization | Gamma Sterilization |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation Source | Electron beam accelerator | Cobalt-60 isotope |
| Penetration Depth | Low to moderate (up to 10 cm) | High (up to 30 cm) |
| Sterilization Time | Seconds to minutes | Hours to days |
| Material Compatibility | Suitable for heat-sensitive plastics | May cause material degradation in some plastics |
| Installation Size | Compact, smaller footprint | Large facility needed |
| Cost | Lower operational cost | Higher operational cost |
| Regulatory Approval | FDA and ISO compliant | FDA and ISO compliant |
| Environmental Impact | No radioactive waste | Produces radioactive waste |
Introduction to E-beam and Gamma Sterilization
E-beam sterilization uses high-energy electron beams to eliminate microorganisms on medical devices, offering rapid processing and no radioactive waste, while gamma sterilization employs gamma rays from isotopes like Cobalt-60, providing deep penetration and proven efficacy for various materials. Both methods ensure product sterility but differ in equipment, processing time, and material compatibility, making your choice critical based on specific sterilization needs and product sensitivity. Understanding these differences helps optimize sterilization processes for safety and compliance in healthcare and industrial applications.
How E-beam Sterilization Works
E-beam sterilization uses high-energy electrons generated by an electron accelerator to penetrate materials and destroy microorganisms by breaking down their DNA and cellular structures. This process occurs rapidly at room temperature, making it suitable for heat-sensitive medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and packaging. Your choice of sterilization method can benefit from E-beam's precise control and shorter processing times compared to gamma sterilization.
How Gamma Sterilization Works
Gamma sterilization uses high-energy gamma rays, typically emitted from Cobalt-60 sources, to penetrate materials and disrupt the DNA of microorganisms, effectively killing bacteria, viruses, and spores. This ionizing radiation causes breaks in microbial DNA strands, preventing replication and ensuring sterilization of medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and food products. Gamma sterilization offers deep penetration, making it suitable for dense or packaged items that require reliable, terminal sterilization.
Key Differences Between E-beam and Gamma Sterilization
E-beam sterilization utilizes high-energy electrons for rapid, surface-level pathogen destruction, while gamma sterilization relies on deep-penetrating gamma rays from radioactive sources like Cobalt-60 to sterilize products thoroughly. E-beam offers shorter processing times and no residual radioactivity, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials, whereas gamma sterilization ensures uniform dosing in dense or bulk items but requires longer exposure periods. Your choice between these methods depends on product composition, required sterilization depth, and processing speed priorities.
Effectiveness Against Microorganisms
E-beam sterilization uses high-energy electrons to disrupt microbial DNA, providing rapid and effective inactivation of bacteria, viruses, and spores on pharmaceutical and medical products. Gamma sterilization penetrates deeply with gamma rays, ensuring thorough eradication of microorganisms even in densely packed or thick materials. Your choice between E-beam and gamma sterilization depends on product sensitivity and required microbial reduction levels, as both methods offer reliable sterilization for critical healthcare applications.
Impact on Material Integrity
E-beam sterilization offers precise control with minimal penetration, reducing the risk of material degradation and preserving the mechanical properties of sensitive products. Gamma sterilization delivers deeper penetration but can cause more significant changes in polymer chains, potentially leading to brittleness or discoloration in certain materials. Your choice between these methods should consider the balance between sterilization efficacy and the material's tolerance to radiation-induced damage.
Processing Speed and Throughput
E-beam sterilization offers significantly faster processing speeds, completing sterilization cycles in minutes compared to several hours for gamma sterilization, which enhances your production throughput. The high dose rate of E-beam accelerators enables rapid sterilization without compromising product integrity, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing environments. Gamma sterilization, while effective for complex or dense materials, typically requires longer exposure times, resulting in lower throughput and extended production cycles.
Cost Comparison of E-beam vs Gamma Sterilization
E-beam sterilization generally offers lower operational costs compared to gamma sterilization due to shorter processing times and no requirement for radioactive material handling and disposal. Gamma sterilization incurs higher expenses related to source replacement, regulatory compliance, and radiation shielding infrastructure. Both methods have initial capital costs; however, e-beam systems often result in reduced long-term throughput costs and energy consumption.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
E-beam sterilization offers enhanced safety by eliminating radioactive sources, reducing the risk of radiation exposure to workers and the environment, unlike gamma sterilization which involves handling and disposing of radioactive isotopes like Cobalt-60. From an environmental perspective, E-beam systems consume less energy and generate no radioactive waste, promoting sustainable sterilization practices. In contrast, gamma sterilization's reliance on radioactive materials poses long-term environmental hazards due to the need for secure storage and eventual disposal of spent sources.
Choosing the Right Sterilization Method
E-beam sterilization offers faster processing times and lower radiation doses, making it ideal for heat-sensitive or moisture-sensitive products. Gamma sterilization provides deeper penetration, making it suitable for bulkier items or densely packed materials requiring uniform sterilization. Your choice depends on product type, packaging, and desired throughput to optimize sterilization efficiency and maintain product integrity.
E-beam Sterilization vs Gamma Sterilization Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com