Copolymer consists of two or more different monomers combined, offering enhanced properties like flexibility and chemical resistance compared to a homopolymer, which is made from a single type of monomer providing uniformity and simplicity. Understanding copolymer versus homopolymer differences helps you choose the right polymer for specific applications, balancing performance and cost.
Table of Comparison
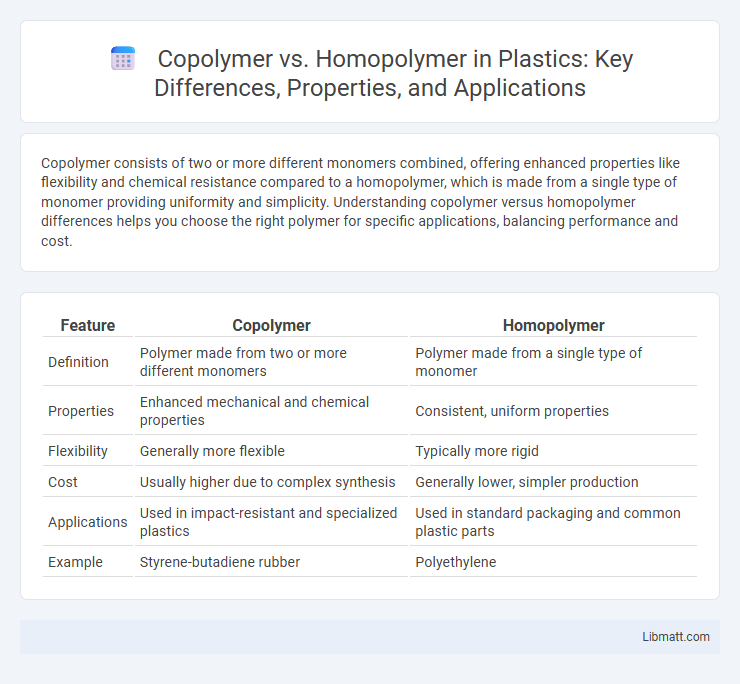
| Feature | Copolymer | Homopolymer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Polymer made from two or more different monomers | Polymer made from a single type of monomer |
| Properties | Enhanced mechanical and chemical properties | Consistent, uniform properties |
| Flexibility | Generally more flexible | Typically more rigid |
| Cost | Usually higher due to complex synthesis | Generally lower, simpler production |
| Applications | Used in impact-resistant and specialized plastics | Used in standard packaging and common plastic parts |
| Example | Styrene-butadiene rubber | Polyethylene |
Introduction to Polymers
Polymers are large molecules composed of repeating units called monomers, which determine their physical properties and applications. Copolymers consist of two or more different types of monomers combined in varying arrangements, offering tailored characteristics like improved strength or flexibility. Homopolymers, made from only one type of monomer, exhibit uniform properties and are typically easier to process, making your material choice crucial based on desired performance.
What is a Homopolymer?
A homopolymer is a polymer consisting of identical monomer units chemically bonded in a repeated sequence, resulting in uniform structural and chemical properties throughout the material. Examples include polyethylene and polystyrene, commonly used in packaging and plastics manufacturing. Understanding homopolymers helps you choose materials with consistent behavior for applications requiring predictable strength, flexibility, and thermal stability.
What is a Copolymer?
A copolymer is a polymer derived from two or more different monomer species, resulting in a material with combined properties tailored for specific applications such as improved strength, flexibility, or chemical resistance. Unlike homopolymers, which consist of identical repeating units, copolymers can be arranged in various architectures including random, alternating, block, or graft sequences, influencing their physical and chemical characteristics. Understanding the structure and composition of your copolymer is essential for optimizing performance in industries like automotive, packaging, and biomedical fields.
Key Differences Between Homopolymers and Copolymers
Homopolymers consist of repeating units derived from a single type of monomer, resulting in uniform physical properties, while copolymers are made from two or more different monomers, offering enhanced versatility and tailored characteristics. The molecular arrangement in copolymers affects properties like strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance, which can be optimized to suit specific applications. Your choice between homopolymer and copolymer depends on the desired material performance for industries such as packaging, automotive, or medical devices.
Physical Properties Comparison
Copolymers exhibit enhanced physical properties such as improved toughness, flexibility, and impact resistance compared to homopolymers, which are composed of a single type of monomer and generally display more uniform characteristics like higher crystallinity and rigidity. The presence of different monomer units in copolymers disrupts regular polymer chain packing, resulting in lower melting points and altered thermal stability compared to homopolymers. Variations in copolymer composition allow for tailored mechanical strength and elasticity, making them more versatile for applications requiring specific physical performance.
Mechanical Performance: Homopolymer vs Copolymer
Homopolymers consist of a single type of monomer, resulting in uniform molecular chains that provide consistent mechanical properties such as high tensile strength and rigidity. Copolymers, made from two or more different monomers, offer enhanced mechanical performance with improved toughness, impact resistance, and flexibility due to their varied molecular structure. Your choice between homopolymer and copolymer materials depends on the specific mechanical requirements of the application, balancing strength versus elasticity.
Common Applications of Homopolymers
Homopolymers, composed of a single type of monomer, are widely used in applications such as packaging films, plastic containers, and fibers due to their consistent properties and ease of processing. Common homopolymers include polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene, which provide durability, chemical resistance, and clarity for consumer goods and industrial products. Your selection of homopolymers can optimize performance in applications requiring uniform mechanical strength and thermal stability.
Common Applications of Copolymers
Copolymers are widely used in applications requiring enhanced material properties such as flexibility, impact resistance, and chemical durability, making them ideal for automotive parts, adhesives, and packaging materials. Their ability to combine different monomers allows for tailored thermal and mechanical characteristics, which is essential in producing medical devices, coatings, and textile fibers. Compared to homopolymers, copolymers provide improved performance in demanding environments like electrical insulation and barrier films.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Copolymer materials often exhibit enhanced environmental performance due to their tailored molecular structure, which can improve biodegradability and reduce resource consumption compared to homopolymers. Homopolymers, composed of identical repeating units, typically demonstrate more straightforward recycling processes but may face limitations in mechanical properties and degradation rates. The recyclability of copolymers can be challenging due to their heterogeneous composition, requiring advanced sorting and chemical recycling technologies for efficient environmental management.
Choosing the Right Polymer for Your Application
Selecting between copolymer and homopolymer depends on desired material properties and application requirements. Copolymers offer enhanced versatility, combining different monomers to achieve improved toughness, flexibility, or chemical resistance, ideal for specialized industries like automotive or packaging. Homopolymers provide consistent structure and strength, making them suitable for applications requiring durability and rigidity, such as construction materials and molded parts.
Copolymer vs Homopolymer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com