Rigid PVC offers exceptional strength and durability, making it ideal for construction and piping applications, while flexible PVC provides greater elasticity and softness, suitable for uses such as electrical cable insulation and inflatable products. Your choice depends on the required flexibility, impact resistance, and environmental exposure of the intended application.
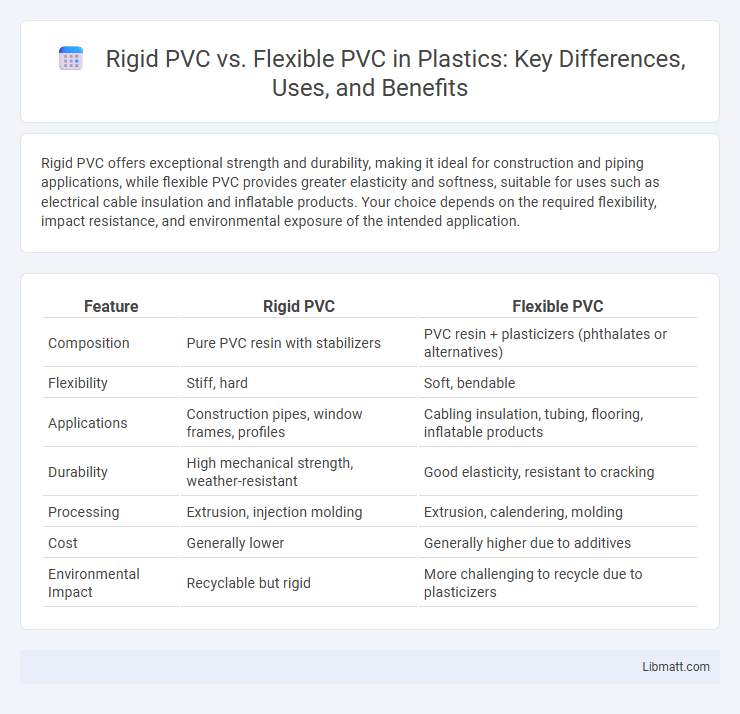
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rigid PVC | Flexible PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure PVC resin with stabilizers | PVC resin + plasticizers (phthalates or alternatives) |
| Flexibility | Stiff, hard | Soft, bendable |
| Applications | Construction pipes, window frames, profiles | Cabling insulation, tubing, flooring, inflatable products |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, weather-resistant | Good elasticity, resistant to cracking |
| Processing | Extrusion, injection molding | Extrusion, calendering, molding |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher due to additives |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but rigid | More challenging to recycle due to plasticizers |
Introduction to Rigid PVC and Flexible PVC
Rigid PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a durable, hard plastic widely used in construction for pipes, window frames, and profiles due to its excellent strength and chemical resistance. Flexible PVC, modified with plasticizers, offers enhanced elasticity and is commonly utilized in electrical cable insulation, hoses, and inflatable products. Both forms share the core PVC polymer but differ significantly in applications driven by their mechanical properties and flexibility.
Chemical Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Rigid PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and flexible PVC differ primarily in their chemical composition and manufacturing processes; rigid PVC contains a higher degree of polymerization with little to no plasticizers, resulting in a hard, durable material used for pipes and construction. Flexible PVC is produced by incorporating plasticizers such as phthalates during manufacturing, which alters the polymer matrix to create a soft, pliable material commonly used in cables, tubing, and clothing. The chemical structure mainly remains PVC, but the presence and concentration of additives during polymer extrusion dictate the final product's rigidity and flexibility.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Rigid PVC offers high tensile strength, excellent chemical resistance, and superior dimensional stability, making it ideal for construction and piping applications. Flexible PVC contains added plasticizers, providing enhanced elasticity, softness, and impact resistance suitable for cable insulation and flexible tubing. Your choice between rigid and flexible PVC depends on the specific mechanical properties and durability requirements of your project.
Common Applications of Rigid PVC
Rigid PVC is widely used in construction for pipes, window frames, and profiles due to its durability and resistance to chemicals and impact. It is also common in electrical cable insulation and signage because of its structural strength and weather resistance. You can rely on rigid PVC for applications requiring stiffness and long-lasting performance.
Common Uses of Flexible PVC
Flexible PVC is widely used in plumbing systems for pipes and fittings due to its durability and resistance to corrosion. It is also common in electrical cable insulation, medical tubing, and inflatable products, where elasticity and flexibility are crucial. Your projects requiring versatile, weather-resistant material often benefit from the adaptability of flexible PVC.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Rigid PVC offers superior mechanical strength and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring high impact resistance and long-lasting structural integrity. Flexible PVC, while less robust, provides excellent elasticity and resistance to wear, suitable for environments where flexibility and repeated bending are necessary. Your choice depends on whether endurance under stress or adaptability to movement is the priority.
Flexibility and Impact Resistance
Rigid PVC offers high impact resistance and structural strength, making it ideal for construction and piping applications, while its limited flexibility restricts its use in dynamic or bending environments. Flexible PVC incorporates plasticizers that enhance its flexibility and elasticity, allowing it to withstand bending and deformation without cracking, though this reduces its impact resistance compared to rigid PVC. The choice between rigid and flexible PVC depends on specific application requirements, balancing durability and flexibility for optimal performance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Rigid PVC exhibits a lower environmental impact due to its longer lifespan and higher recyclability compared to flexible PVC, which often contains plasticizers that complicate recycling processes and increase leaching risks. Flexible PVC's additives reduce recyclability and can release harmful substances during degradation, while rigid PVC is more commonly accepted in recycling streams, enhancing circular economy efforts. Both materials require careful disposal, but rigid PVC's stability and recyclability make it a preferable choice for sustainable applications.
Cost Factors and Economic Considerations
Rigid PVC typically costs less per unit due to lower manufacturing complexity and higher material density, making it a cost-effective choice for structural applications. Flexible PVC incurs higher production expenses because of added plasticizers, which increase durability and versatility but lead to a greater initial investment. Your decision should weigh both upfront costs and long-term performance benefits to optimize economic efficiency in your project.
Choosing Between Rigid PVC and Flexible PVC
Choosing between rigid PVC and flexible PVC depends on your specific project requirements, such as durability, flexibility, and application environment. Rigid PVC offers superior strength and chemical resistance ideal for construction, pipes, and window frames, while flexible PVC provides elasticity suited for cables, hoses, and inflatable products. Evaluating factors like temperature tolerance, bending needs, and exposure conditions will help you select the most efficient PVC type for your needs.
Rigid PVC vs Flexible PVC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com