Food grade plastic is designed to safely store and handle food items without leaching harmful chemicals, ensuring your food remains uncontaminated and fresh. Medical grade plastic meets stricter sterilization and biocompatibility standards, making it suitable for use in healthcare settings where safety and durability are critical.
Table of Comparison
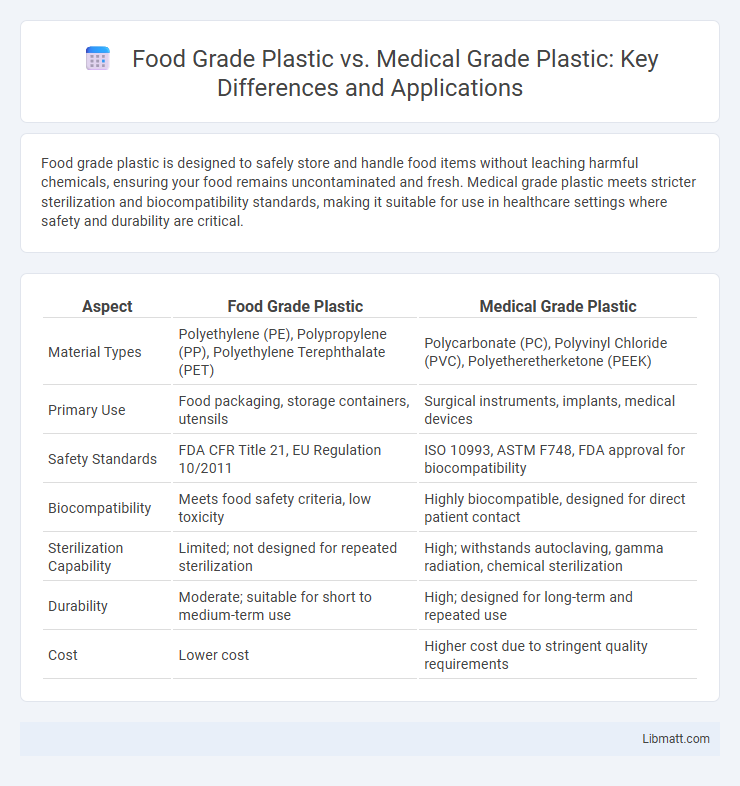
| Aspect | Food Grade Plastic | Medical Grade Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Types | Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Polycarbonate (PC), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) |
| Primary Use | Food packaging, storage containers, utensils | Surgical instruments, implants, medical devices |
| Safety Standards | FDA CFR Title 21, EU Regulation 10/2011 | ISO 10993, ASTM F748, FDA approval for biocompatibility |
| Biocompatibility | Meets food safety criteria, low toxicity | Highly biocompatible, designed for direct patient contact |
| Sterilization Capability | Limited; not designed for repeated sterilization | High; withstands autoclaving, gamma radiation, chemical sterilization |
| Durability | Moderate; suitable for short to medium-term use | High; designed for long-term and repeated use |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to stringent quality requirements |
Understanding Food Grade Plastic
Food grade plastic is specifically designed to meet safety standards that prevent harmful chemicals from leaching into food products, ensuring consumer health and compliance with regulations such as FDA or EFSA. It is made from materials like polyethylene, polypropylene, and PET that have been tested for non-toxicity and resistance to degradation under typical food storage conditions. Your choice of food grade plastic ensures the integrity and safety of the food packaging or containers used in both commercial and household environments.
Defining Medical Grade Plastic
Medical grade plastic is specially designed to meet stringent regulatory standards for biocompatibility, sterility, and chemical resistance, ensuring safety for use in medical devices and implants. Unlike food grade plastic, which is manufactured to prevent contamination and ensure safety for food contact, medical grade plastic undergoes rigorous testing for toxicity, sterilization compatibility, and durability under physiological conditions. Your choice between these plastics depends on the critical requirements of the application, with medical grade plastic being essential for clinical and surgical environments.
Key Differences Between Food and Medical Grade Plastics
Food grade plastics are designed to meet strict safety standards for contact with edibles, ensuring non-toxicity, odorlessness, and resistance to contamination, as regulated by bodies such as the FDA. Medical grade plastics possess higher purity levels, sterilizability, and biocompatibility, complying with rigorous standards like ISO 10993 for safe use in medical devices and implants. Key differences include enhanced chemical resistance, sterilization compatibility, and traceability requirements in medical grade plastics, which are critical for patient safety, unlike food grade plastics that prioritize food safety and storage durability.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Food grade plastic complies with FDA and EFSA regulations ensuring safety for direct food contact, while medical grade plastic meets stringent ISO 10993 biocompatibility standards and FDA medical device requirements for patient safety. Certifications such as NSF, FDA approval, and EU food contact regulations verify food grade plastics, whereas medical grade plastics require ISO 13485 certification and often USP class VI testing for implantable devices. Your choice between these materials should consider these regulatory standards to ensure compliance with industry-specific safety protocols.
Material Composition and Safety
Food grade plastic is typically composed of polyethylene, polypropylene, or PET, designed to be non-toxic and free from harmful chemicals to ensure food safety during storage and handling. Medical grade plastic, including materials like polycarbonate and PVC, undergoes stricter sterilization and biocompatibility standards to prevent contamination and ensure patient safety in medical applications. Understanding the material composition and safety standards of these plastics helps you choose the right type for your specific needs, minimizing health risks.
Common Applications in Food Industry
Food grade plastic is commonly used for packaging materials such as containers, bottles, and wraps designed to store and preserve edible products, ensuring safety and preventing contamination. Medical grade plastic, though primarily formulated for sterility and biocompatibility, is occasionally utilized in food processing equipment components where strict hygiene standards are required. Both types meet regulatory standards but differ in chemical resistance and sterilization capabilities, influencing their specific applications within the food industry.
Typical Uses in Healthcare and Medicine
Food grade plastic in healthcare is primarily used for packaging medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and nutritional supplements due to its safety and non-toxicity. Medical grade plastic is specialized for direct patient contact applications such as surgical instruments, implants, and intravenous tubing, ensuring biocompatibility and sterilization compatibility. Both types comply with strict regulatory standards, but medical grade plastic undergoes more rigorous testing to meet healthcare-specific requirements.
Durability and Chemical Resistance
Food grade plastic offers moderate durability and chemical resistance, designed to withstand typical household food storage conditions and exposure to mild acids and oils without degrading. Medical grade plastic exhibits superior durability and enhanced chemical resistance, engineered to endure sterilization processes, harsh disinfectants, and repeated use without compromising structural integrity or safety. The advanced formulations in medical grade plastics provide critical resistance to corrosion and contamination, making them ideal for sensitive healthcare environments.
Selecting the Right Plastic for Your Needs
Food grade plastic ensures safety for storing edibles by meeting FDA regulations and resisting contamination from chemicals, while medical grade plastic offers superior sterility, biocompatibility, and durability for healthcare applications. Your choice depends on the intended use: opt for food grade plastics for safe food contact and medical grade plastics when sterilization and non-toxicity in sensitive environments are critical. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the right plastic material that complies with both safety standards and performance requirements.
Future Trends in Plastic Technology
Future trends in plastic technology emphasize the development of more sustainable and biocompatible materials, with food grade plastic advancing toward higher safety standards for contamination prevention, while medical grade plastic evolves to enhance sterility and durability under extreme conditions. Innovations in biodegradable polymers and smart plastics with antimicrobial properties are set to redefine applications in both industries, improving consumer safety and environmental impact simultaneously. Your choice between food grade and medical grade plastics will increasingly reflect these technological improvements aimed at health, safety, and sustainability.
Food Grade Plastic vs Medical Grade Plastic Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com