UV stabilized plastic resists degradation from ultraviolet light exposure, maintaining structural integrity and color over time, whereas non-UV stabilized plastic tends to become brittle, crack, and fade when exposed to sunlight. Choosing UV stabilized plastic ensures your products last longer outdoors, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
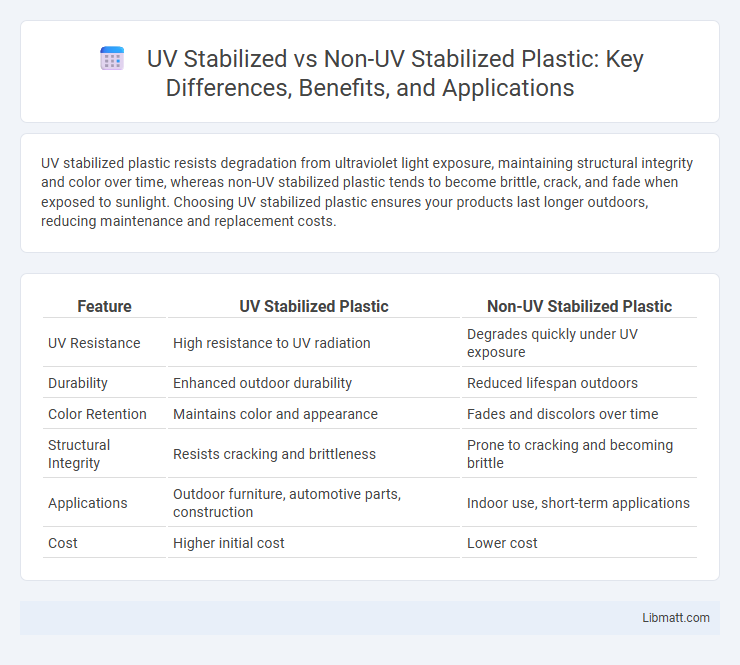
Table of Comparison
| Feature | UV Stabilized Plastic | Non-UV Stabilized Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| UV Resistance | High resistance to UV radiation | Degrades quickly under UV exposure |
| Durability | Enhanced outdoor durability | Reduced lifespan outdoors |
| Color Retention | Maintains color and appearance | Fades and discolors over time |
| Structural Integrity | Resists cracking and brittleness | Prone to cracking and becoming brittle |
| Applications | Outdoor furniture, automotive parts, construction | Indoor use, short-term applications |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to UV Stabilized and Non-UV Stabilized Plastics
UV stabilized plastics contain additives that protect polymer chains from degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation, extending material lifespan and maintaining structural integrity. Non-UV stabilized plastics lack these protective agents, making them susceptible to brittleness, discoloration, and surface cracking when exposed to prolonged sunlight. This fundamental difference impacts applications where long-term UV exposure is a critical factor in material selection.
Understanding UV Degradation in Plastics
UV-stabilized plastic incorporates additives that absorb or block harmful ultraviolet rays, significantly slowing the UV degradation process that causes brittleness, discoloration, and loss of mechanical strength in non-UV stabilized plastics. Non-UV stabilized plastics break down rapidly when exposed to sunlight, leading to surface cracking and reduced lifespan, which can compromise the durability of outdoor applications. To protect your products and extend their functional life, selecting UV-stabilized materials is essential for environments with prolonged sun exposure.
Key Differences Between UV Stabilized and Non-UV Stabilized Plastics
UV stabilized plastics contain additives that absorb or block harmful ultraviolet rays, significantly enhancing durability and preventing degradation such as cracking and color fading. Non-UV stabilized plastics lack these protective compounds, making them prone to brittleness, discoloration, and structural failure when exposed to prolonged sunlight. Choosing UV stabilized plastic ensures your materials maintain strength and appearance in outdoor applications, extending the lifespan and performance of your products.
Chemical Additives for UV Stabilization
UV stabilized plastics contain chemical additives such as UV absorbers, hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS), and UV quenchers that protect the polymer chains from degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation. Non-UV stabilized plastics lack these additives, resulting in faster discoloration, brittleness, and reduced mechanical strength when exposed to sunlight. Ensuring your plastic products have the appropriate UV stabilizers extends their lifespan and maintains their structural integrity under prolonged UV exposure.
Advantages of UV Stabilized Plastics
UV stabilized plastics exhibit enhanced durability and resistance to degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation, extending the lifespan of outdoor products significantly. These plastics maintain their color, mechanical strength, and flexibility under prolonged sun exposure, reducing maintenance and replacement costs. Their superior performance in harsh sunlight environments makes them ideal for applications like automotive parts, outdoor furniture, and construction materials.
Drawbacks of Non-UV Stabilized Plastics
Non-UV stabilized plastics degrade rapidly when exposed to sunlight, resulting in brittleness, discoloration, and loss of mechanical strength. Your outdoor applications risk premature failure and increased maintenance costs due to these materials' susceptibility to UV-induced cracking and fading. The absence of UV inhibitors accelerates polymer breakdown, significantly shortening the plastic's lifespan compared to UV stabilized alternatives.
Common Applications of UV Stabilized Plastics
UV stabilized plastics are widely used in outdoor applications such as garden furniture, roofing sheets, agricultural films, and automotive components to prevent degradation from prolonged sun exposure. These plastics contain additives that absorb or block harmful UV rays, ensuring longer durability and maintaining mechanical properties in harsh environmental conditions. Your choice of UV stabilized plastic enhances product longevity and reduces maintenance costs in environments exposed to direct sunlight.
Cost Implications: UV Stabilized vs. Non-UV Stabilized
UV stabilized plastic generally incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized additives that protect against sun damage, prolonging material lifespan and reducing replacement frequency. Non-UV stabilized plastic tends to be cheaper initially, but its susceptibility to degradation under sunlight often leads to increased maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Choosing UV stabilized plastic can offer better long-term cost-efficiency, especially for outdoor applications where durability is critical to Your investment.
Environmental Impact and Longevity
UV stabilized plastic resists degradation from sunlight exposure, significantly extending its lifespan and reducing the frequency of replacements, which minimizes plastic waste accumulation in the environment. Non-UV stabilized plastic breaks down faster under UV radiation, releasing harmful microplastics and chemicals that contribute to environmental pollution. Choosing UV stabilized plastic ensures your products last longer and have a lower environmental footprint over time.
How to Choose the Right Plastic for Outdoor Use
Selecting UV stabilized plastic for outdoor use ensures enhanced resistance to sun damage, preventing discoloration, brittleness, and structural degradation caused by prolonged UV exposure. Non-UV stabilized plastics may deteriorate quickly under sunlight, reducing the lifespan and performance of outdoor products. For applications requiring long-term durability and aesthetic retention, prioritizing UV stabilized materials is essential to maintain integrity and appearance in harsh outdoor environments.
UV Stabilized Plastic vs Non-UV Stabilized Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com