High speed injection delivers fluids rapidly to maximize efficiency in applications like automotive fuel systems, while high pressure injection focuses on forcefully delivering fluids to penetrate tough surfaces or materials. Your choice depends on whether speed or force is more critical for the desired outcome.
Table of Comparison
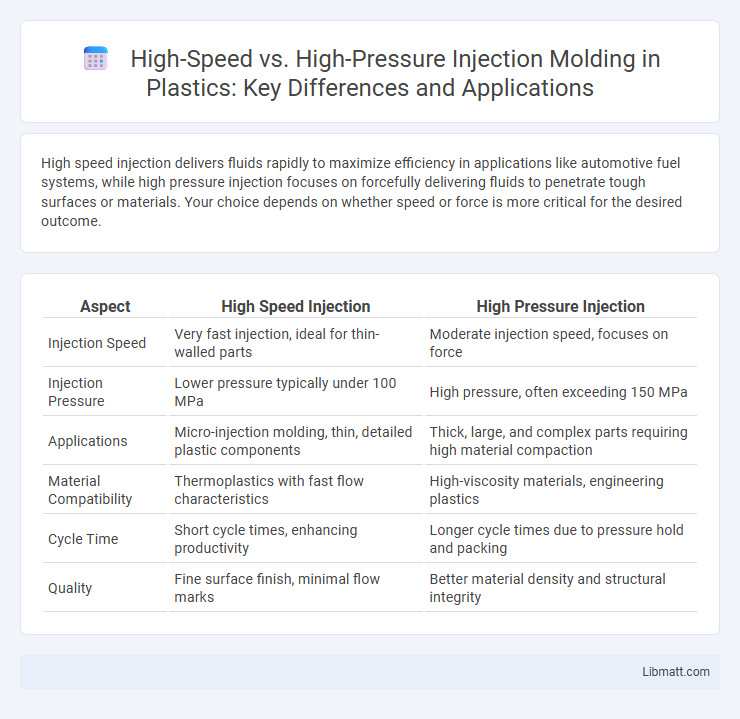
| Aspect | High Speed Injection | High Pressure Injection |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Speed | Very fast injection, ideal for thin-walled parts | Moderate injection speed, focuses on force |
| Injection Pressure | Lower pressure typically under 100 MPa | High pressure, often exceeding 150 MPa |
| Applications | Micro-injection molding, thin, detailed plastic components | Thick, large, and complex parts requiring high material compaction |
| Material Compatibility | Thermoplastics with fast flow characteristics | High-viscosity materials, engineering plastics |
| Cycle Time | Short cycle times, enhancing productivity | Longer cycle times due to pressure hold and packing |
| Quality | Fine surface finish, minimal flow marks | Better material density and structural integrity |
Introduction to Injection Molding Dynamics
Injection molding dynamics involves understanding the critical differences between high-speed and high-pressure injection processes, which directly impact part quality and cycle time. High-speed injection ensures rapid cavity filling, reducing the risk of premature cooling and minimizing weld lines, while high-pressure injection focuses on packing the mold to maintain dimensional accuracy and prevent sink marks. Your choice between these methods depends on material properties, mold design, and the desired balance between efficiency and precision.
Defining High Speed Injection
High speed injection refers to the rapid delivery of fluid or material into a system, emphasizing velocity to achieve quick distribution and penetration. This method is critical in applications such as fuel injection in engines or medical injections where timing and penetration depth affect performance and outcome. Understanding your system's tolerance for velocity versus pressure ensures optimized results in high-speed injection scenarios.
Defining High Pressure Injection
High pressure injection involves delivering fluids at extremely high pressures, typically exceeding 1,000 psi, to penetrate materials or surfaces with intense force. This method is commonly used in industrial cleaning, fuel injection systems, and hydraulic applications where precise and powerful fluid delivery is essential. Understanding high pressure injection helps you choose the right technique based on the required penetration depth and fluid dynamics compared to high speed injection.
Core Differences: Speed vs. Pressure
High-speed injection prioritizes rapid fluid delivery, enhancing efficiency by minimizing injection time, while high-pressure injection emphasizes applying greater force to penetrate dense or resistant materials. The core difference lies in how these methods optimize performance: speed maximizes throughput, and pressure ensures deeper, more effective infusion. Selecting the right approach depends on your specific application needs, balancing speed with the required injection force.
Material Compatibility and Selection
High speed injection prioritizes materials with excellent flow characteristics and thermal stability, such as certain thermoplastics like polypropylene and polycarbonate, ensuring consistent mold filling under rapid conditions. High pressure injection requires materials that can withstand intense stress and potential shear forces, often favoring engineering plastics like nylon and polyamide blends for their superior mechanical strength and durability. Selecting compatible materials reduces defects like warping or cracking, optimizing product quality across varying injection parameters.
Impact on Product Quality
High-speed injections often ensure precise dosing and consistent product fill, reducing variability in manufacturing processes, which enhances the overall quality and reliability of the final product. High-pressure injections improve material density and reduce voids or air pockets, resulting in stronger, more durable products with superior surface finishes. The choice between high speed and high pressure directly influences product integrity, dimensional stability, and defect rates in injection molding or pharmaceutical delivery systems.
Cycle Time and Efficiency Considerations
High speed injection offers shorter cycle times by rapidly filling molds, which enhances production efficiency for high-volume manufacturing. In contrast, high pressure injection improves part quality and precision but may increase cycle time due to longer cooling and packing phases. Balancing injection speed and pressure is crucial to optimize Your process for both efficiency and product performance.
Equipment and Technological Requirements
High speed injection systems require advanced pumps and precision nozzles capable of delivering fluid at rapid rates, ensuring consistent flow without causing cavitation or mechanical wear. High pressure injection demands robust equipment designed to withstand extreme pressures, such as reinforced pipelines, pressure-resistant seals, and high-strength materials to prevent leaks or ruptures. Your choice between high speed and high pressure injection should consider the technological capabilities of the equipment to maintain safety, efficiency, and process integrity.
Cost Implications of Each Method
High speed injection systems typically incur higher initial equipment costs due to advanced technology requirements and precision components, but offer lower operating expenses through reduced cycle times and energy efficiency. High pressure injection may demand more robust machinery and maintenance, resulting in increased long-term operational costs despite potentially lower upfront investment. Evaluating your production volume and material characteristics helps determine which method optimizes cost-effectiveness in the context of your specific manufacturing needs.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Application
High speed injection is ideal for applications requiring rapid filling and minimized cycle times, such as mass production of small, intricate parts. High pressure injection suits materials with higher viscosity or applications demanding superior detail and strength, ensuring complete mold fill and structural integrity. Selecting the right process depends on factors like material properties, part complexity, production volume, and desired surface finish to achieve optimal results.
High speed vs high pressure injection Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com