Glass-filled nylon offers enhanced strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability compared to unfilled nylon, making it ideal for high-performance applications where durability is critical. Your choice between these materials depends on whether you prioritize toughness and resistance to wear or flexibility and ease of machining.
Table of Comparison
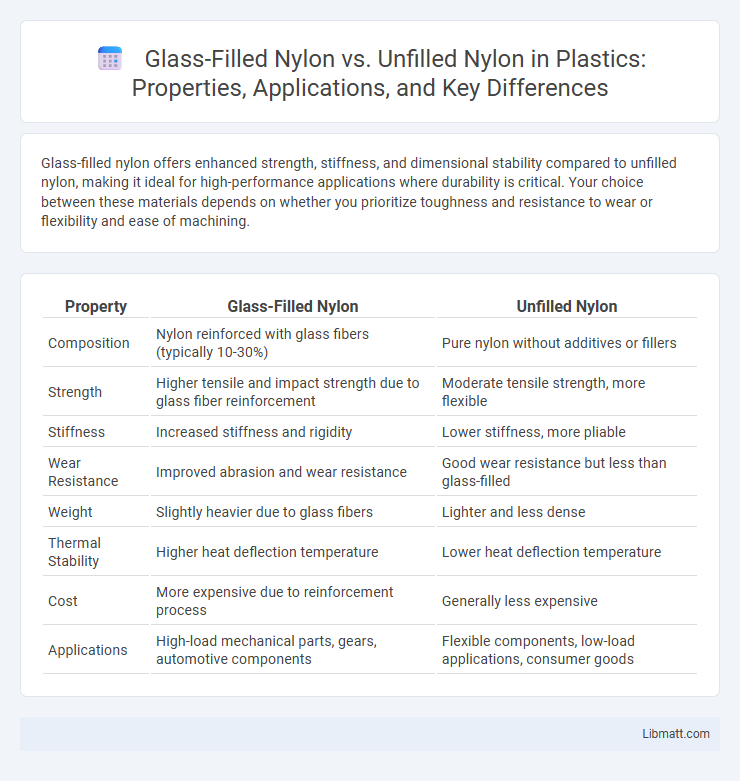
| Property | Glass-Filled Nylon | Unfilled Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Nylon reinforced with glass fibers (typically 10-30%) | Pure nylon without additives or fillers |
| Strength | Higher tensile and impact strength due to glass fiber reinforcement | Moderate tensile strength, more flexible |
| Stiffness | Increased stiffness and rigidity | Lower stiffness, more pliable |
| Wear Resistance | Improved abrasion and wear resistance | Good wear resistance but less than glass-filled |
| Weight | Slightly heavier due to glass fibers | Lighter and less dense |
| Thermal Stability | Higher heat deflection temperature | Lower heat deflection temperature |
| Cost | More expensive due to reinforcement process | Generally less expensive |
| Applications | High-load mechanical parts, gears, automotive components | Flexible components, low-load applications, consumer goods |
Introduction to Nylon Plastics
Glass-filled nylon exhibits significantly enhanced mechanical strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability compared to unfilled nylon, making it suitable for high-performance industrial applications. Unfilled nylon offers excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and ease of processing, which suits applications requiring moderate strength and toughness. Both materials maintain nylon's inherent resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and heat, but glass-filled variants deliver superior load-bearing capabilities due to the reinforcing glass fibers embedded within the polymer matrix.
What is Glass-Filled Nylon?
Glass-filled nylon is a composite material made by reinforcing nylon with glass fibers, typically ranging from 10% to 50% by weight. This reinforcement enhances the mechanical properties of nylon, including increased tensile strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability compared to unfilled nylon. Glass-filled nylon is widely used in automotive, electrical, and industrial applications where higher strength and heat resistance are required.
What is Unfilled Nylon?
Unfilled nylon is a type of polyamide polymer that contains no reinforcing fillers, resulting in a material with high flexibility, excellent impact resistance, and good chemical resistance. It offers superior toughness and wear resistance compared to glass-filled nylon but has lower stiffness and tensile strength. Unfilled nylon is widely used in applications requiring durability and flexibility, such as gears, bushings, and consumer goods.
Material Composition Differences
Glass-filled nylon contains reinforcing glass fibers, typically 10-50%, which enhance its mechanical strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability compared to unfilled nylon, which is composed solely of pure polyamide polymer chains. The addition of glass fibers alters the thermal properties, increasing heat resistance and reducing moisture absorption, whereas unfilled nylon exhibits higher flexibility and impact resistance due to its homogeneous polymer structure. These compositional differences directly influence performance characteristics, making glass-filled nylon suitable for structural applications and unfilled nylon preferable for parts requiring flexibility.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Glass-filled nylon exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to unfilled nylon, boasting increased tensile strength, stiffness, and impact resistance due to the reinforcement provided by glass fibers. This enhancement makes glass-filled nylon ideal for structural components requiring durability and rigidity, while unfilled nylon remains more flexible and less brittle. The fiber content typically ranges from 10% to 50%, directly influencing the improved mechanical properties in glass-filled variants.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Glass-filled nylon exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to unfilled nylon, maintaining structural integrity at higher temperatures up to 260degC, whereas unfilled nylon typically withstands temperatures around 120degC to 180degC. Chemical resistance also varies significantly; glass-filled nylon resists solvents, oils, and chemicals better due to its reinforced structure, making it ideal for demanding environments. Your choice between these materials depends on the application's thermal and chemical exposure requirements, with glass-filled nylon providing enhanced durability and performance.
Weight and Density Analysis
Glass-filled nylon exhibits significantly higher density, typically around 1.3 to 1.5 g/cm3, compared to unfilled nylon's density of approximately 1.02 g/cm3, resulting in increased weight for equivalent volumes. The inclusion of glass fibers enhances mechanical strength but also contributes to a denser and heavier composite. Engineers must balance the trade-off between improved structural performance and added weight when selecting between glass-filled and unfilled nylon for lightweight applications.
Applications in Industry
Glass-filled nylon offers superior strength, rigidity, and thermal stability, making it ideal for automotive parts, electrical components, and industrial machinery where durability under stress is critical. Unfilled nylon provides excellent flexibility and wear resistance, commonly used in packaging, textiles, and consumer goods requiring lightweight and impact absorption. Your choice between glass-filled and unfilled nylon depends on whether your application demands enhanced mechanical performance or greater flexibility and cost-efficiency.
Cost Considerations
Glass-filled nylon typically costs more than unfilled nylon due to the added expense of reinforcing fibers and the enhanced mechanical properties that improve durability and strength. While unfilled nylon offers a more budget-friendly option for applications with less demanding structural requirements, glass-filled nylon's longer lifespan and greater resistance to wear can reduce replacement costs over time. Your choice should balance initial material expense against performance needs, especially in high-stress environments where glass-filled nylon provides better value.
Choosing Between Glass-Filled and Unfilled Nylon
Choosing between glass-filled nylon and unfilled nylon depends on application requirements like strength, durability, and weight. Glass-filled nylon contains glass fibers that enhance tensile strength, stiffness, and thermal resistance, making it ideal for load-bearing parts and high-stress environments. Unfilled nylon offers greater flexibility, chemical resistance, and is lighter, suitable for applications where impact resistance and machinability are prioritized.
Glass-Filled Nylon vs Unfilled Nylon Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com