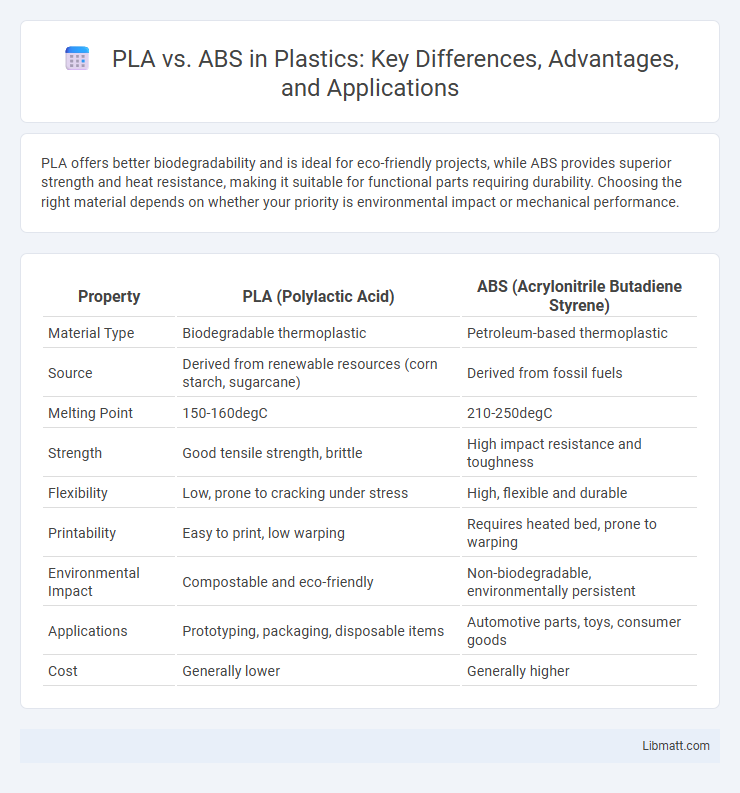
PLA offers better biodegradability and is ideal for eco-friendly projects, while ABS provides superior strength and heat resistance, making it suitable for functional parts requiring durability. Choosing the right material depends on whether your priority is environmental impact or mechanical performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | PLA (Polylactic Acid) | ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable thermoplastic | Petroleum-based thermoplastic |
| Source | Derived from renewable resources (corn starch, sugarcane) | Derived from fossil fuels |
| Melting Point | 150-160degC | 210-250degC |
| Strength | Good tensile strength, brittle | High impact resistance and toughness |
| Flexibility | Low, prone to cracking under stress | High, flexible and durable |
| Printability | Easy to print, low warping | Requires heated bed, prone to warping |
| Environmental Impact | Compostable and eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, environmentally persistent |
| Applications | Prototyping, packaging, disposable items | Automotive parts, toys, consumer goods |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Introduction to PLA and ABS
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch, known for its ease of printing and environmental friendliness. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a petroleum-based thermoplastic favored for its strength, impact resistance, and higher temperature tolerance. Both materials are widely used in 3D printing, but PLA is ideal for prototypes and environmentally conscious projects, while ABS suits functional parts requiring durability.
Chemical Composition and Structure
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch, featuring a linear aliphatic polyester structure primarily composed of lactic acid monomers. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a petroleum-based thermoplastic composed of three distinct monomers--acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene--forming a complex, high-impact resistant polymer with a branched structure. Your choice depends on the desired chemical stability and material properties, as PLA offers biodegradability while ABS provides greater durability and heat resistance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
PLA offers higher tensile strength and rigidity, making it ideal for detailed, sturdy prints, while ABS excels in impact resistance and flexibility, providing better durability for functional parts. Your choice depends on the mechanical demands of the project, as PLA is more brittle but easier to print, whereas ABS withstands higher temperatures and stress without deformation. Consider the application to balance strength, toughness, and environmental resistance between these two popular 3D printing materials.
Printability and Ease of Use
PLA offers superior printability and ease of use due to its lower melting temperature and minimal warping, making it ideal for beginners and standard 3D printers. ABS requires a heated bed and enclosed print environment to prevent warping and ensure strong layer adhesion, presenting more challenges during printing. The choice between PLA and ABS significantly impacts print success rates and post-processing needs.
Strength and Durability
PLA offers moderate strength and rigidity, making it suitable for decorative and low-stress applications, while ABS excels in durability and impact resistance, ideal for functional parts and mechanical components. ABS withstands higher temperatures and physical stress without deforming, providing longer-lasting performance in demanding environments compared to PLA. Choosing ABS enhances your project's strength and durability when toughness is a critical requirement.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, making it more environmentally friendly compared to ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), which is petroleum-based. PLA is biodegradable under industrial composting conditions, breaking down into water and carbon dioxide within months, whereas ABS is not biodegradable and can persist in landfills for hundreds of years. The lower carbon footprint of PLA and its ability to decompose in controlled environments contribute to reduced plastic pollution and resource depletion relative to ABS.
Surface Finish and Appearance
PLA offers a glossy, smooth surface finish ideal for detailed, visually appealing 3D prints, making it popular for prototypes and decorative objects. ABS typically results in a matte finish with a slightly rougher texture, favored for functional parts due to its durability and impact resistance. Post-processing techniques like sanding, vapor smoothing, or painting can significantly enhance the appearance of both PLA and ABS prints.
Temperature Resistance and Heat Tolerance
PLA (Polylactic Acid) has a lower temperature resistance, typically softening around 60degC, which makes it less suitable for high-heat applications compared to ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene). ABS exhibits superior heat tolerance with a glass transition temperature around 105degC, allowing it to maintain structural integrity under higher thermal stress. This makes ABS the preferred choice for functional parts exposed to elevated temperatures, such as automotive components or electronic housings.
Ideal Applications for PLA and ABS
PLA is ideal for prototypes, educational projects, and decorative items due to its biodegradability and ease of printing. ABS is preferred for functional parts, automotive components, and durable products requiring higher impact resistance and heat tolerance. When choosing your material, consider PLA for aesthetic or low-stress applications and ABS for strength and longevity.
Choosing the Right Filament for Your Project
Choosing between PLA and ABS depends on your project's requirements for strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance. PLA offers ease of use, biodegradability, and minimal warping, making it ideal for prototypes, cosmetic parts, and detailed models. ABS provides superior durability, impact resistance, and higher heat tolerance, suited for functional parts and mechanical components exposed to stress.
PLA vs ABS Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com