A hot runner system maintains molten plastic flow within heated channels, reducing waste and cycle times, while a cold runner system allows the plastic to solidify in the runner before ejection, often increasing material waste but simplifying mold design. Your choice between hot runner and cold runner systems depends on factors like production volume, material type, and cost efficiency.
Table of Comparison
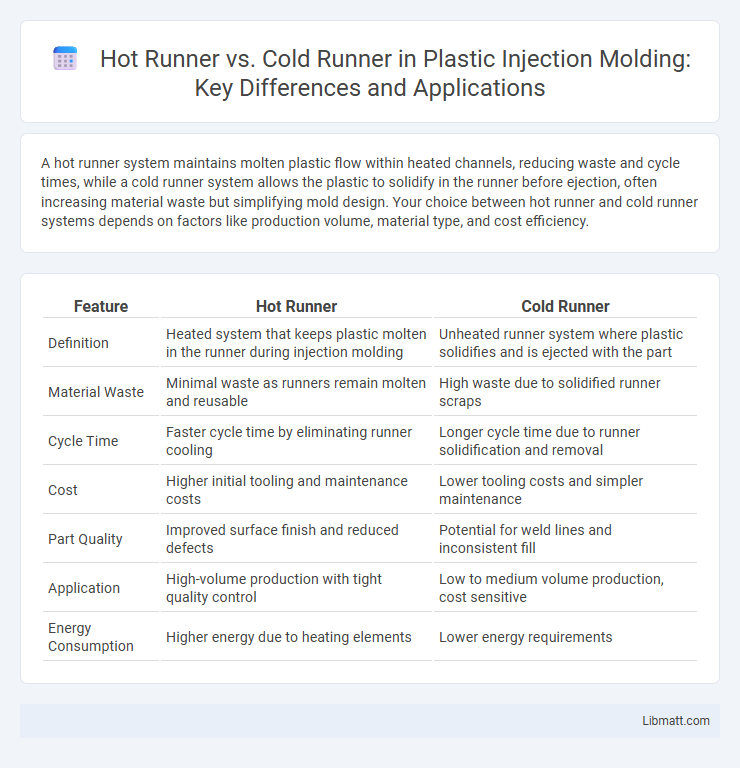
| Feature | Hot Runner | Cold Runner |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heated system that keeps plastic molten in the runner during injection molding | Unheated runner system where plastic solidifies and is ejected with the part |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste as runners remain molten and reusable | High waste due to solidified runner scraps |
| Cycle Time | Faster cycle time by eliminating runner cooling | Longer cycle time due to runner solidification and removal |
| Cost | Higher initial tooling and maintenance costs | Lower tooling costs and simpler maintenance |
| Part Quality | Improved surface finish and reduced defects | Potential for weld lines and inconsistent fill |
| Application | High-volume production with tight quality control | Low to medium volume production, cost sensitive |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy due to heating elements | Lower energy requirements |
Introduction to Injection Molding Runners
Injection molding runners channel molten plastic from the injection molding machine nozzle into the mold cavities, either through hot or cold runner systems. Hot runner systems maintain the plastic in a molten state within heated channels, reducing waste and cycle time, while cold runner systems rely on unheated channels that solidify the plastic, often leading to higher material waste. Understanding the differences between hot runner vs cold runner systems helps optimize Your manufacturing efficiency and product quality.
What is a Hot Runner System?
A Hot Runner System is an advanced injection molding technology that uses heated components to keep the plastic molten as it flows through the system, minimizing material waste and cycle times. Unlike cold runner systems where the plastic solidifies in the runner channels, hot runners maintain consistent temperature control to improve product quality and reduce post-production trimming. Your manufacturing efficiency can benefit from the precise temperature management and reduced runner scrap associated with hot runner systems.
What is a Cold Runner System?
A cold runner system in injection molding refers to a setup where the plastic material flows through unheated channels before reaching the mold cavities, resulting in solidified runners that are ejected along with the finished parts. This system reduces initial tooling costs and simplifies maintenance but generates more material waste due to the need to trim the runners after molding. Cold runner molds are commonly used for smaller production runs and materials sensitive to heat degradation.
Key Differences Between Hot and Cold Runners
Hot runners maintain plastic in a molten state through heated components, enabling faster cycle times and reduced material waste by eliminating runner scrap. Cold runners use unheated channels, where the plastic solidifies and must be ejected as scrap, resulting in higher material usage and longer cooling cycles. The decision between hot and cold runner systems significantly impacts manufacturing efficiency, cost, and part quality in injection molding processes.
Advantages of Hot Runner Systems
Hot runner systems provide precise temperature control and reduce material waste by eliminating runner scrap, leading to increased manufacturing efficiency. These systems enable faster cycle times and improved part quality by maintaining consistent melt flow and reducing signs of defects like knit lines or cold shuts. Your production process benefits from lower operational costs and greater design flexibility, making hot runners ideal for high-volume injection molding.
Benefits of Cold Runner Systems
Cold runner systems offer significant advantages such as lower initial tooling costs and reduced maintenance complexity compared to hot runner systems. They provide greater flexibility for running multiple materials and colors, minimizing contamination risks during production. Additionally, cold runners improve part quality by eliminating issues related to residual heat, ensuring consistent cooling and dimensional stability.
Drawbacks of Hot Runner Systems
Hot runner systems can present challenges such as higher initial costs due to complex components and maintenance requirements. They may experience thermal degradation of the material if temperature control is not precise, impacting product quality. Your manufacturing process might also face issues with system clogging and more complicated troubleshooting compared to cold runner systems.
Limitations of Cold Runner Systems
Cold runner systems have limitations including slower cycle times due to the need to eject solidified runners after each injection, leading to increased material waste and additional post-processing costs. The solidified runners can cause inconsistent part quality and higher scrap rates, especially when manufacturing complex or multi-cavity molds. Your production efficiency may decrease as cold runner systems require more frequent maintenance and slower cooling compared to hot runner systems, which maintain molten plastic flow continuously.
Choosing Between Hot and Cold Runner Systems
Choosing between hot and cold runner systems depends on factors such as production volume, material type, and cost efficiency. Hot runner systems reduce waste and cycle time by keeping the plastic molten, ideal for high-volume runs and complex molds, while cold runner systems offer lower upfront costs and simpler maintenance suited for low to medium production. Evaluating factors like part quality, mold complexity, and budget constraints helps determine the most suitable system for injection molding projects.
Conclusion: Which Runner System is Right for You?
Choosing between a hot runner and cold runner system depends on your production goals, budget, and material considerations. Hot runners reduce waste and cycle times, ideal for high-volume manufacturing and complex parts, while cold runners offer lower upfront costs, better for small runs or budget-sensitive projects. Your decision should balance efficiency, cost, and product quality to optimize molding performance.
Hot Runner vs Cold Runner Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com