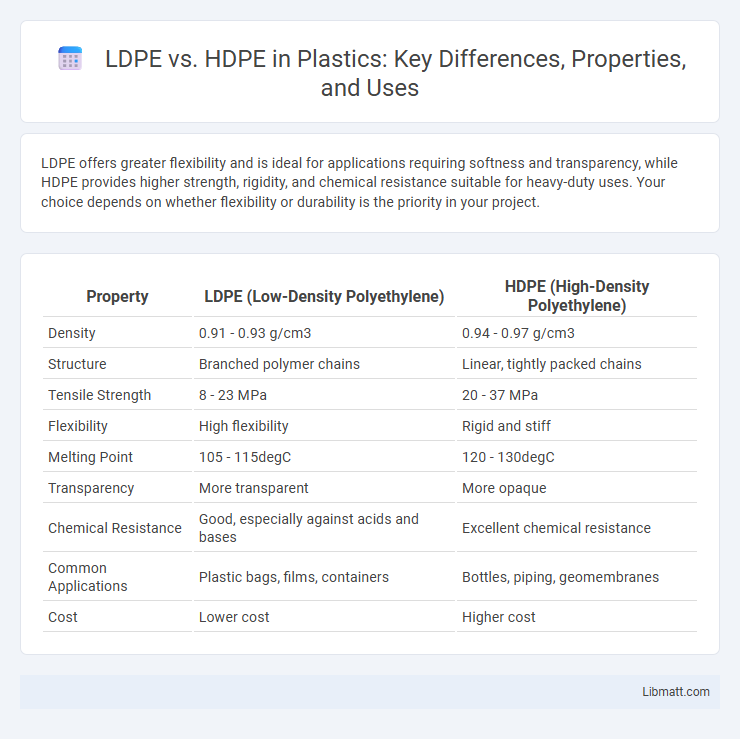
LDPE offers greater flexibility and is ideal for applications requiring softness and transparency, while HDPE provides higher strength, rigidity, and chemical resistance suitable for heavy-duty uses. Your choice depends on whether flexibility or durability is the priority in your project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) | HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.91 - 0.93 g/cm3 | 0.94 - 0.97 g/cm3 |
| Structure | Branched polymer chains | Linear, tightly packed chains |
| Tensile Strength | 8 - 23 MPa | 20 - 37 MPa |
| Flexibility | High flexibility | Rigid and stiff |
| Melting Point | 105 - 115degC | 120 - 130degC |
| Transparency | More transparent | More opaque |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, especially against acids and bases | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Common Applications | Plastic bags, films, containers | Bottles, piping, geomembranes |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to LDPE and HDPE
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) features a highly branched polymer structure, resulting in a flexible, translucent material ideal for packaging films and squeeze bottles. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) has a linear structure with minimal branching, producing a dense, strong, and rigid plastic widely used in containers, pipes, and plastic lumber. Both LDPE and HDPE are cost-effective, recyclable thermoplastics derived from ethylene, but they differ significantly in density, strength, and typical applications.
Chemical Structure Differences
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) features a highly branched polymer chain structure, resulting in less tightly packed molecules and lower crystallinity compared to high-density polyethylene (HDPE). HDPE has a linear polymer chain with minimal branching, allowing for higher density and increased crystallinity, which contributes to its greater tensile strength and rigidity. The differences in branching directly impact their melting points, mechanical properties, and chemical resistance, with HDPE exhibiting superior thermal and chemical stability.
Physical Properties Comparison
LDPE features a lower density of around 0.91-0.93 g/cm3 and exhibits greater flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring pliability. HDPE has a higher density of about 0.94-0.97 g/cm3, resulting in superior tensile strength, rigidity, and chemical resistance, suitable for heavy-duty containers and piping. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize flexibility and ease of sealing (LDPE) or strength and durability (HDPE).
Manufacturing Processes
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) is produced through high-pressure polymerization using free radical initiators, resulting in a branched polymer structure with lower density. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is manufactured via low-pressure polymerization using Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysts, creating a linear polymer chain with minimal branching and higher crystallinity. These distinct manufacturing processes directly influence the materials' density, strength, and application suitability.
Common Applications of LDPE
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) is widely used in packaging materials such as plastic bags, film wrap, and containers due to its flexibility and transparency. Its applications extend to squeeze bottles, toys, and wire insulation, benefiting from its impact resistance and low-temperature toughness. You will find LDPE prevalent in industries requiring lightweight, durable, and moisture-resistant solutions.
Common Applications of HDPE
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is widely used in manufacturing containers such as milk jugs, detergent bottles, and water pipes due to its high strength-to-density ratio and excellent chemical resistance. It is also common in geomembranes, plastic lumber, and corrosion-resistant piping systems in industrial applications. HDPE's durability and flexibility make it ideal for packaging, toys, and agricultural films.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has a lower melting point and is less dense than high-density polyethylene (HDPE), making it more flexible but harder to recycle due to contamination and degradation issues. HDPE is more widely recycled because of its higher strength and purity, resulting in a more efficient recycling process and lower environmental impact over its lifecycle. Both materials pose challenges for waste management, but HDPE's recyclability and resistance to environmental stress contribute to a reduced ecological footprint compared to LDPE.
Cost and Economic Factors
HDPE generally costs more than LDPE due to its higher density and stronger molecular structure, which requires more raw material and energy during production. LDPE offers a more economical option for applications requiring flexibility and lower strength, making it ideal for packaging and disposable products where cost efficiency is critical. Your choice between LDPE and HDPE should consider both the initial material cost and the projected durability and performance requirements to maximize economic value.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each
LDPE offers superior flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for packaging films and containers but has lower tensile strength and chemical resistance compared to HDPE. HDPE boasts high tensile strength, excellent chemical resistance, and rigidity, making it suitable for heavy-duty containers and pipes, but it is less flexible and more prone to stress cracking. Your choice depends on whether flexibility or strength is more critical for your application.
Choosing Between LDPE and HDPE
Choosing between LDPE and HDPE depends on your specific application requirements, as LDPE offers greater flexibility and impact resistance while HDPE provides superior strength and chemical resistance. LDPE's lower density makes it ideal for lightweight, flexible packaging, whereas HDPE's higher density suits heavy-duty containers and piping. Understanding these differences ensures you select the optimal material for durability and performance in your project.
LDPE vs HDPE Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com