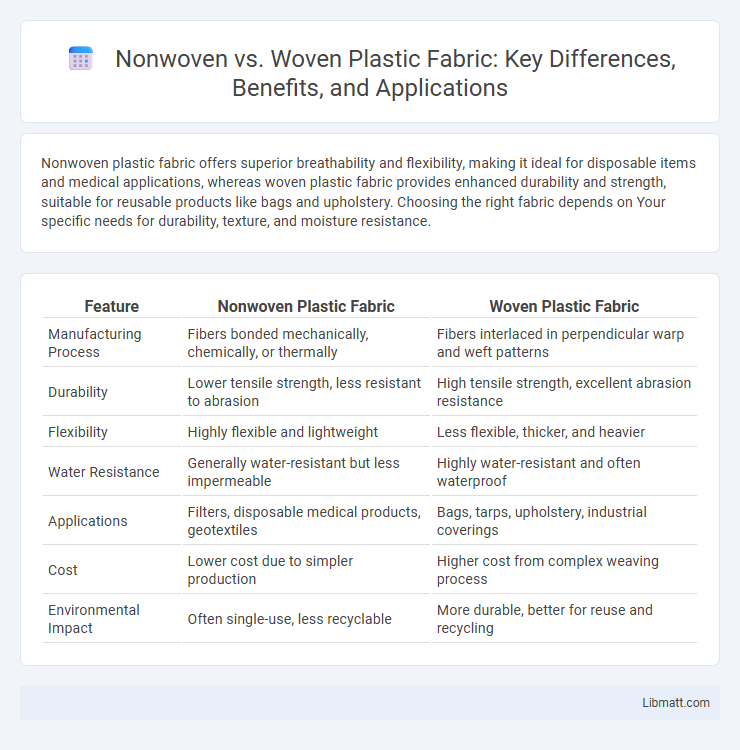
Nonwoven plastic fabric offers superior breathability and flexibility, making it ideal for disposable items and medical applications, whereas woven plastic fabric provides enhanced durability and strength, suitable for reusable products like bags and upholstery. Choosing the right fabric depends on Your specific needs for durability, texture, and moisture resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nonwoven Plastic Fabric | Woven Plastic Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Fibers bonded mechanically, chemically, or thermally | Fibers interlaced in perpendicular warp and weft patterns |
| Durability | Lower tensile strength, less resistant to abrasion | High tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and lightweight | Less flexible, thicker, and heavier |
| Water Resistance | Generally water-resistant but less impermeable | Highly water-resistant and often waterproof |
| Applications | Filters, disposable medical products, geotextiles | Bags, tarps, upholstery, industrial coverings |
| Cost | Lower cost due to simpler production | Higher cost from complex weaving process |
| Environmental Impact | Often single-use, less recyclable | More durable, better for reuse and recycling |
Introduction to Nonwoven and Woven Plastic Fabrics
Nonwoven plastic fabrics are made by bonding or felting fibers together, resulting in lightweight, breathable materials commonly used in medical masks, geotextiles, and disposable garments. Woven plastic fabrics consist of interlaced yarns or threads, offering higher strength and durability suited for applications like tarpaulins, bags, and upholstery. The manufacturing processes and structural differences influence the tensile strength, permeability, and cost-effectiveness of these materials in various industries.
Defining Nonwoven Plastic Fabric
Nonwoven plastic fabric is manufactured by bonding fibers together through mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes without weaving or knitting, creating a durable yet lightweight material. Unlike woven fabrics composed of interlaced yarns, nonwoven plastic textiles offer enhanced breathability, flexibility, and cost-effective production for applications such as medical supplies, geotextiles, and filtration systems. Their engineered fiber orientation and bonding significantly influence tensile strength, permeability, and softness, distinguishing them from traditional woven plastic fabrics.
Understanding Woven Plastic Fabric
Woven plastic fabric consists of interlaced strands of polymer threads, typically made from polypropylene or polyethylene, creating a durable and flexible material used in packaging, agriculture, and construction. This fabric's structure provides high tensile strength and resistance to tearing, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and breathability. Its ability to be easily printed on and recycled further enhances its sustainability and versatility compared to nonwoven plastic fabrics.
Key Differences: Nonwoven vs Woven Structure
Nonwoven plastic fabric consists of fibers bonded together through mechanical, chemical, or thermal processes, creating a random, web-like structure that offers flexibility and lightweight properties. Woven plastic fabric features interlaced yarns arranged in a structured, grid-like pattern, providing superior strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Understanding the key differences in these structures helps you select the appropriate fabric type based on your specific application needs and performance requirements.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Nonwoven plastic fabric is manufactured through processes such as spunbonding, meltblowing, or needle punching, which involve bonding fibers together without weaving, resulting in materials with diverse textures and strengths. Woven plastic fabric, on the other hand, is produced by interlacing plastic yarns or threads in a structured pattern using looms, providing higher tensile strength and durability. The choice between nonwoven and woven manufacturing processes significantly affects fabric properties like flexibility, breathability, and cost-efficiency for various industrial and consumer applications.
Strength and Durability: Which Is Better?
Woven plastic fabric offers superior strength and durability due to its interlaced yarn construction, providing high tensile strength and resistance to tearing, ideal for heavy-duty applications. Nonwoven plastic fabric, while less robust, excels in flexibility and lightweight use, but typically lacks the long-term durability of woven materials. Your choice depends on the required balance between strength and weight for your project's specific needs.
Cost Efficiency and Production Speed
Nonwoven plastic fabric offers superior cost efficiency due to lower raw material consumption and simplified manufacturing processes compared to woven plastic fabric. Production speed is significantly faster in nonwoven fabric fabrication as it eliminates the weaving stage, enabling rapid large-scale output. In contrast, woven plastic fabric requires intricate interlacing of fibers, resulting in higher production costs and slower manufacturing times.
Typical Applications: Where Each Excels
Nonwoven plastic fabric excels in medical disposables, filtration, geotextiles, and hygiene products due to its lightweight, breathable, and cost-effective nature. Woven plastic fabric performs best in applications requiring high tensile strength and durability, such as tarpaulins, agricultural covers, and industrial sacks. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize flexibility and disposability or strength and reusability.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Nonwoven plastic fabrics typically have a lower environmental impact due to their production process requiring less energy and water compared to woven fabrics, which involve more complex weaving machinery. Recyclability of woven plastic fabrics tends to be higher since they are generally made from pure polymer threads, making the separation and reprocessing easier, while nonwoven fabrics often combine polymers with additives or binders that complicate recycling. Both materials present challenges in waste management, but advancements in biodegradable polymers and improved recycling technologies are gradually enhancing the sustainability of plastic fabrics.
Choosing the Right Plastic Fabric for Your Needs
Nonwoven plastic fabric offers superior breathability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight filtration, medical masks, and disposable medical supplies. Woven plastic fabric provides enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear, suitable for heavy-duty uses like tarps, bags, and upholstery. Selecting the right plastic fabric depends on balancing factors such as durability requirements, environmental resistance, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance for your specific project.
Nonwoven vs woven plastic fabric Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com