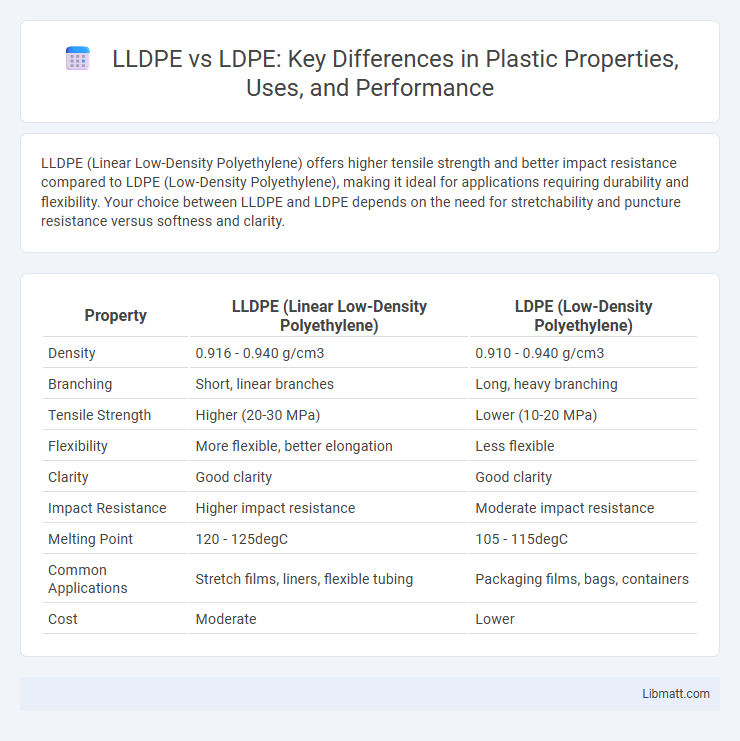
LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) offers higher tensile strength and better impact resistance compared to LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene), making it ideal for applications requiring durability and flexibility. Your choice between LLDPE and LDPE depends on the need for stretchability and puncture resistance versus softness and clarity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) | LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.916 - 0.940 g/cm3 | 0.910 - 0.940 g/cm3 |
| Branching | Short, linear branches | Long, heavy branching |
| Tensile Strength | Higher (20-30 MPa) | Lower (10-20 MPa) |
| Flexibility | More flexible, better elongation | Less flexible |
| Clarity | Good clarity | Good clarity |
| Impact Resistance | Higher impact resistance | Moderate impact resistance |
| Melting Point | 120 - 125degC | 105 - 115degC |
| Common Applications | Stretch films, liners, flexible tubing | Packaging films, bags, containers |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower |
Introduction to LLDPE and LDPE
LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) and LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) are versatile thermoplastics used extensively in packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods. LLDPE offers higher tensile strength and flexibility due to its linear polymer chains with short branches, while LDPE has a more branched structure resulting in greater transparency and impact resistance. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right material for your specific application needs.
Chemical Structure Differences
LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) features a linear polymer chain with short, controlled branching, enhancing its tensile strength and flexibility. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) contains a highly branched polymer structure, resulting in lower density and increased softness. Understanding these chemical structure differences helps you select the right polyethylene type for durability or pliability in manufacturing applications.
Manufacturing Processes
LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) is produced through copolymerization of ethylene with alpha-olefins using techniques like solution, gas-phase, or slurry polymerization, resulting in a linear structure with short branches. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) is manufactured by high-pressure radical polymerization of ethylene, producing highly branched polymer chains with a less dense molecular structure. Understanding these distinct manufacturing processes helps you select the right polyethylene type based on flexibility, strength, and application requirements.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) exhibits higher tensile strength and superior impact resistance compared to LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene), making it more suitable for applications requiring durability. LLDPE has greater flexibility and puncture resistance due to its linear molecular structure with short branches, whereas LDPE's highly branched structure results in lower density and softer, more elastic properties. Both materials offer good chemical resistance, but LLDPE demonstrates improved stress crack resistance and better performance under mechanical stress.
Flexibility and Strength Comparison
LLDPE offers greater tensile strength and puncture resistance compared to LDPE, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and impact resistance. LDPE provides superior flexibility and softness, which benefits products needing easy stretch and pliability. For your projects, choosing LLDPE enhances structural integrity, while LDPE ensures more flexibility and stretchability.
Applications and Uses
LLDPE is extensively used in packaging films, stretch wraps, and agricultural mulch films due to its high tensile strength and puncture resistance. LDPE finds applications in grocery bags, squeeze bottles, and food packaging where flexibility and clarity are essential. Both materials are preferred in different sectors based on their mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness.
Cost Analysis
LLDPE typically offers a lower cost per pound compared to LDPE due to its efficient production process and higher raw material utilization. While LDPE has a higher price point attributed to its branched polymer structure and specialized applications, LLDPE's cost-effectiveness makes it preferable for large-scale packaging and film extrusion. The overall cost analysis highlights LLDPE as a more economical choice for manufacturers prioritizing durability and flexibility without significantly increasing expenses.
Environmental Impact
LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) and LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) differ in environmental impact due to their production processes and recyclability rates. LLDPE typically uses less raw material for the same strength, resulting in reduced resource consumption and lower carbon emissions during manufacturing. You can improve sustainability by choosing LLDPE products, as they are often more recyclable and have a smaller ecological footprint compared to LDPE.
Market Availability
LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) and LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) both have strong market presence but differ in availability due to production methods and application demand. LLDPE is more widely available in bulk for industrial uses such as packaging films and stretch wraps because of its superior tensile strength and flexibility. Your choice depends on specific application needs, but LLDPE generally offers greater accessibility in various grades and formulations compared to LDPE.
Choosing the Right Material
Choosing the right material between LLDPE and LDPE depends on your application's flexibility and strength requirements. LLDPE offers superior tensile strength and puncture resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging and stretch films. LDPE provides excellent clarity and flexibility, better suited for applications needing softness and high transparency, such as plastic bags and food packaging.
LLDPE vs LDPE Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com