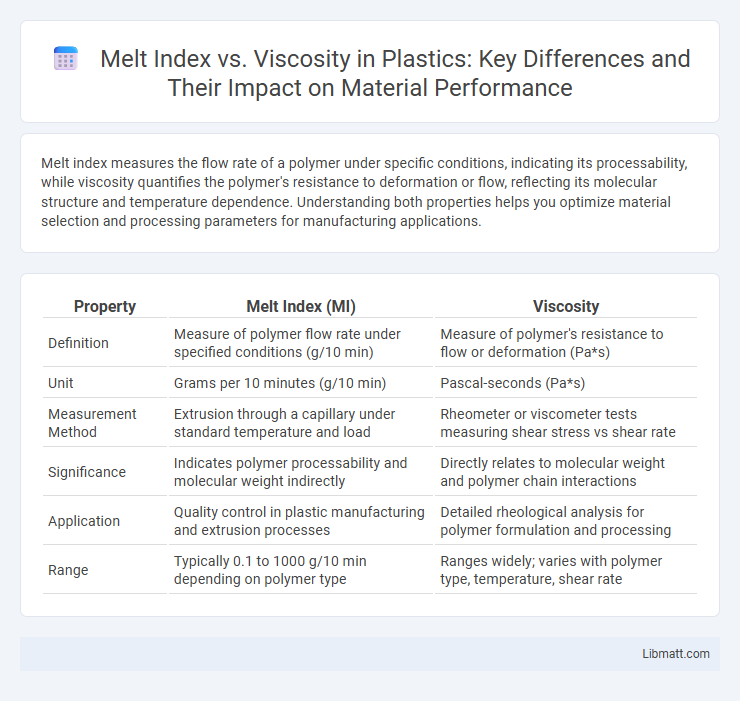
Melt index measures the flow rate of a polymer under specific conditions, indicating its processability, while viscosity quantifies the polymer's resistance to deformation or flow, reflecting its molecular structure and temperature dependence. Understanding both properties helps you optimize material selection and processing parameters for manufacturing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Melt Index (MI) | Viscosity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of polymer flow rate under specified conditions (g/10 min) | Measure of polymer's resistance to flow or deformation (Pa*s) |
| Unit | Grams per 10 minutes (g/10 min) | Pascal-seconds (Pa*s) |
| Measurement Method | Extrusion through a capillary under standard temperature and load | Rheometer or viscometer tests measuring shear stress vs shear rate |
| Significance | Indicates polymer processability and molecular weight indirectly | Directly relates to molecular weight and polymer chain interactions |
| Application | Quality control in plastic manufacturing and extrusion processes | Detailed rheological analysis for polymer formulation and processing |
| Range | Typically 0.1 to 1000 g/10 min depending on polymer type | Ranges widely; varies with polymer type, temperature, shear rate |
Introduction to Melt Index and Viscosity
Melt Index measures the flow rate of melted thermoplastic polymers, indicating their ease of processing under specific conditions. Viscosity quantifies a fluid's resistance to flow, reflecting how a polymer material responds to applied stress during manufacturing. Understanding these properties helps you select the appropriate polymer grade for efficient extrusion or molding processes.
Understanding Melt Index: Definition and Importance
Melt Index (MI) measures the flow rate of a thermoplastic polymer under specific temperature and pressure conditions, indicating its processability during extrusion or molding. This value helps predict how easily a polymer melts and flows, directly impacting the quality and efficiency of manufacturing processes. Understanding your material's melt index is crucial for selecting the right polymer grade to achieve optimal performance in your application.
Explaining Viscosity in Polymer Processing
Viscosity in polymer processing measures the material's resistance to flow, significantly influencing the ease of molding and shaping polymers. It directly affects the melt index, which quantifies the flow rate of a polymer melt under specific conditions. Understanding the relationship between viscosity and melt index ensures optimal process parameters for consistent product quality and efficient manufacturing.
Key Differences Between Melt Index and Viscosity
Melt index measures the flow rate of thermoplastic polymers under specific temperature and pressure conditions, indicating how easily a material can be processed. Viscosity quantifies a polymer's resistance to flow, reflecting molecular weight and structural properties affecting material behavior in both solid and molten states. The key difference lies in melt index being a standardized, empirical value primarily used for processing control, while viscosity provides a fundamental rheological property essential for understanding polymer performance in various applications.
Measurement Methods for Melt Index
Melt Index is measured using a standardized melt flow indexer, which evaluates the flow rate of thermoplastic polymers under specific temperature and load conditions, expressed in grams per 10 minutes. This method involves extruding the polymer through a calibrated die and recording the mass of material extruded, reflecting the polymer's molecular weight and flow characteristics. Understanding the melt index measurement helps you predict processing behavior and optimize material selection for injection molding or extrusion applications.
Techniques for Measuring Viscosity
Techniques for measuring viscosity include capillary rheometry, rotational viscometry, and oscillatory rheometry, each providing distinct insights into polymer flow behavior under varying shear rates and temperatures. Capillary rheometry measures the melt flow by forcing the polymer melt through a narrow die, closely correlating with the melt index, while rotational viscometers determine viscosity by applying controlled shear in a controlled environment. Oscillatory rheometry assesses the polymer's viscoelastic properties, offering detailed analysis beyond simple viscosity that is crucial for understanding processing characteristics.
Influence on Polymer Properties and Performance
Melt index and viscosity are critical parameters influencing polymer properties and performance, determining processability and end-use functionality. Melt index reflects the flow rate of a polymer melt under specific conditions, affecting ease of molding and extrusion, while viscosity measures resistance to flow and correlates with molecular weight and polymer chain entanglement. Your material selection benefits from balancing these factors, optimizing strength, flexibility, and durability for targeted applications.
Applications: When to Use Melt Index vs. Viscosity
Melt index is ideal for quick assessment of polymer flow under standardized conditions, commonly used in quality control and production of thermoplastics for injection molding and extrusion applications. Viscosity provides detailed insights into a polymer's molecular weight distribution and flow behavior across a range of temperatures and shear rates, essential for formulating materials for films, coatings, and adhesives. Selecting melt index or viscosity depends on the need for rapid processing evaluation versus comprehensive rheological analysis to optimize polymer performance in specific manufacturing processes.
Factors Affecting Melt Index and Viscosity
Melt index and viscosity are influenced by polymer molecular weight, temperature, and shear rate, with higher molecular weights typically decreasing melt index and increasing viscosity. Temperature elevation reduces viscosity by enhancing polymer chain mobility while increasing melt index due to easier flow under load. Your ability to control these factors during processing ensures optimal polymer performance and product quality.
Choosing the Right Parameter for Quality Control
Melt index and viscosity are critical parameters in polymer quality control, with melt index measuring the flow rate of molten polymer and viscosity indicating resistance to flow. Selecting the appropriate parameter depends on the polymer type and processing conditions; melt index suits thermoplastics with rapid flow characterization, while viscosity provides detailed insight for complex formulations and temperature-dependent behavior. Accurate control of these parameters ensures consistent product performance and processing efficiency in manufacturing environments.
Melt Index vs Viscosity Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com