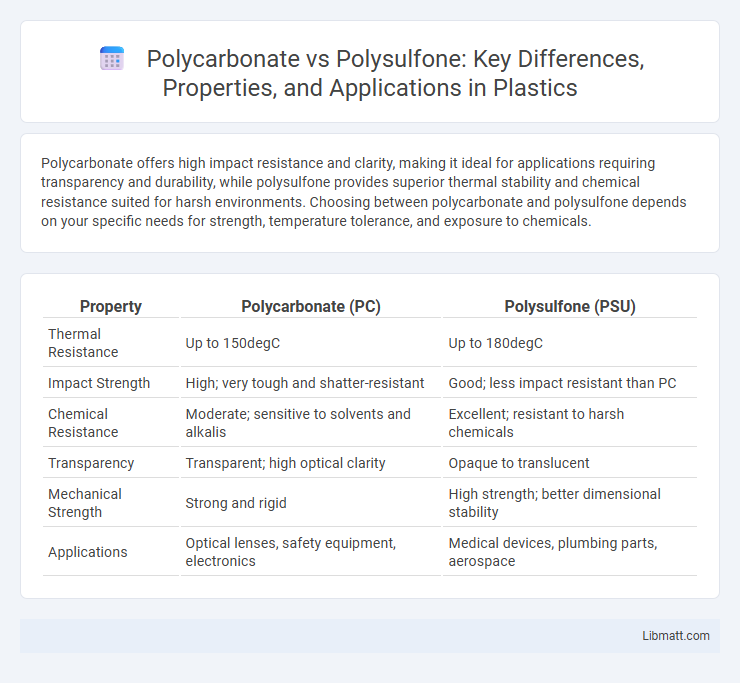
Polycarbonate offers high impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and durability, while polysulfone provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance suited for harsh environments. Choosing between polycarbonate and polysulfone depends on your specific needs for strength, temperature tolerance, and exposure to chemicals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polysulfone (PSU) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 150degC | Up to 180degC |
| Impact Strength | High; very tough and shatter-resistant | Good; less impact resistant than PC |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; sensitive to solvents and alkalis | Excellent; resistant to harsh chemicals |
| Transparency | Transparent; high optical clarity | Opaque to translucent |
| Mechanical Strength | Strong and rigid | High strength; better dimensional stability |
| Applications | Optical lenses, safety equipment, electronics | Medical devices, plumbing parts, aerospace |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Polysulfone
Polycarbonate is a highly durable, transparent thermoplastic known for its impact resistance and optical clarity, widely used in lenses, bulletproof glass, and electronic components. Polysulfone is a high-performance polymer valued for its thermal stability, chemical resistance, and toughness, commonly applied in medical devices, membranes, and aerospace parts. Both materials offer distinct advantages in engineering and manufacturing where strength, durability, and specific environmental resistances are critical.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic polymer consisting of bisphenol A and phosgene units, characterized by carbonate groups (-O-(C=O)-O-) in its backbone that provide transparency and impact resistance. Polysulfone is an aromatic polymer composed of sulfone groups (-SO2-) linked to aromatic rings, which confer high thermal stability and chemical resistance. The presence of carbonate linkages in polycarbonate results in greater flexibility, while the sulfone groups in polysulfone contribute to its rigidity and superior performance under heat and chemical exposure.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polycarbonate offers high impact resistance and excellent toughness, making it ideal for applications requiring strong mechanical durability. Polysulfone, while less impact-resistant, provides superior heat resistance and dimensional stability under mechanical stress. You can select polycarbonate for flexibility and impact absorption or polysulfone when mechanical strength must be maintained at elevated temperatures.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Polycarbonate offers moderate thermal resistance with a glass transition temperature around 147degC, making it suitable for many everyday applications but less ideal for high-heat environments. Polysulfone exhibits superior thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity up to 180-190degC and excellent resistance to repeated sterilization cycles, ideal for demanding thermal applications. Your choice depends on whether moderate heat tolerance or high thermal resilience is critical for the specific use case.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Polycarbonate offers exceptional optical clarity with a light transmittance of around 88-90%, making it ideal for applications requiring high transparency and impact resistance. Polysulfone, while durable and heat-resistant, has a lower light transmittance of approximately 85%, resulting in slightly reduced transparency compared to polycarbonate. Your choice between these materials should consider the importance of maximum optical clarity alongside other performance characteristics.
Chemical and UV Resistance
Polycarbonate offers moderate chemical resistance but is prone to degradation when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, making it less suitable for prolonged outdoor applications without protective coatings. Polysulfone exhibits superior chemical resistance, particularly against acids, bases, and organic solvents, combined with excellent inherent UV stability, allowing it to maintain structural integrity and clarity under harsh environmental conditions. These properties make polysulfone preferable in high-performance environments requiring long-term exposure to aggressive chemicals and UV radiation.
Applications in Industry
Polycarbonate is extensively used in industries requiring high impact resistance and optical clarity, such as automotive components, eyewear lenses, and medical devices. Polysulfone excels in high-temperature environments and chemical resistance, making it ideal for aerospace, food processing, and filtration applications. Your choice between polycarbonate and polysulfone depends on the specific industrial requirements for durability and thermal performance.
Safety and Biocompatibility
Polycarbonate offers excellent safety with high impact resistance and clarity, but it may release bisphenol A (BPA) under certain conditions, which raises biocompatibility concerns. Polysulfone exhibits superior biocompatibility due to its chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it suitable for medical devices and sterilization processes. Your choice should consider the intended application's exposure to chemicals and temperature to ensure optimal safety and compatibility.
Cost and Availability
Polycarbonate typically costs less than polysulfone, making it a more budget-friendly option for various applications. Polycarbonate is widely available due to its extensive use in consumer goods, automotive parts, and electronics. Polysulfone is less common and generally more expensive, primarily used in specialized industrial and medical components where higher heat and chemical resistance are required.
Choosing the Right Material
Selecting between polycarbonate and polysulfone depends on specific application requirements such as thermal resistance, impact strength, and chemical stability. Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for safety equipment and optical applications. Polysulfone excels in high-temperature environments and chemical exposure, preferred for medical devices and aerospace components requiring sterilization durability.
Polycarbonate vs Polysulfone Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com