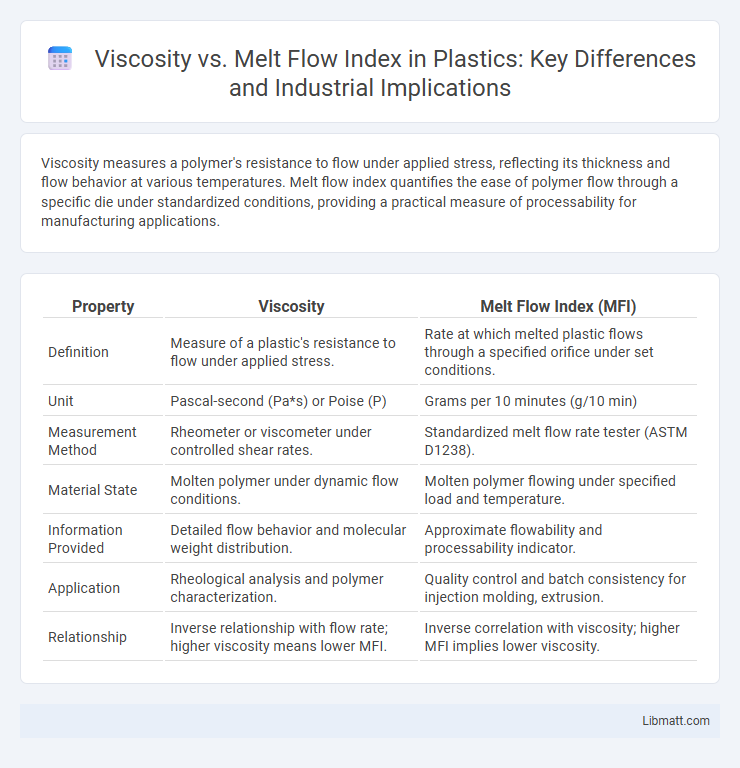
Viscosity measures a polymer's resistance to flow under applied stress, reflecting its thickness and flow behavior at various temperatures. Melt flow index quantifies the ease of polymer flow through a specific die under standardized conditions, providing a practical measure of processability for manufacturing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Viscosity | Melt Flow Index (MFI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of a plastic's resistance to flow under applied stress. | Rate at which melted plastic flows through a specified orifice under set conditions. |
| Unit | Pascal-second (Pa*s) or Poise (P) | Grams per 10 minutes (g/10 min) |
| Measurement Method | Rheometer or viscometer under controlled shear rates. | Standardized melt flow rate tester (ASTM D1238). |
| Material State | Molten polymer under dynamic flow conditions. | Molten polymer flowing under specified load and temperature. |
| Information Provided | Detailed flow behavior and molecular weight distribution. | Approximate flowability and processability indicator. |
| Application | Rheological analysis and polymer characterization. | Quality control and batch consistency for injection molding, extrusion. |
| Relationship | Inverse relationship with flow rate; higher viscosity means lower MFI. | Inverse correlation with viscosity; higher MFI implies lower viscosity. |
Introduction to Viscosity and Melt Flow Index
Viscosity measures a polymer's resistance to flow under applied force and is expressed in units such as pascal-seconds (Pa*s), reflecting molecular interactions and temperature sensitivity. Melt Flow Index (MFI) quantifies the mass of polymer extruded through a standardized die under specific conditions, given in grams per 10 minutes, providing a rapid assessment of flow characteristics during processing. Both parameters are critical in polymer engineering to predict material behavior during molding, extrusion, and quality control.
Defining Viscosity in Polymers
Viscosity in polymers measures the resistance to flow under an applied force, reflecting the internal friction between polymer chains. It is a critical parameter that influences processing behavior, mechanical properties, and final product quality. Unlike the melt flow index (MFI), which quantifies polymer flow rate under specific conditions, viscosity provides a broader understanding of molecular weight distribution and polymer chain interactions.
What is Melt Flow Index (MFI)?
Melt Flow Index (MFI) measures the ease of flow of melted thermoplastic polymers under specific conditions, indicating the material's viscosity characteristics during processing. It is quantified as the mass of polymer extruded through a standardized die in ten minutes under a set temperature and load, providing insight into the polymer's melt viscosity and processability. Understanding your polymer's MFI helps optimize manufacturing parameters for better flow behavior in extrusion or injection molding applications.
Key Differences: Viscosity vs Melt Flow Index
Viscosity measures a polymer's resistance to flow under applied stress, reflecting its molecular weight and temperature sensitivity, while the melt flow index (MFI) quantifies the amount of polymer that flows through a standardized die under specific conditions, indicating processability. Viscosity provides detailed insights into the polymer's flow behavior across various shear rates, whereas MFI offers a quick, single-point measure of melt flow rate. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate test for optimizing polymer processing parameters and quality control.
Measurement Methods for Viscosity
Viscosity measurement methods include rotational viscometers, where a spindle rotates at a controlled speed to measure resistance, and capillary rheometers that assess flow under pressure through a narrow tube. These techniques provide precise data about a polymer's flow behavior under different shear rates. Your understanding of viscosity measurement is crucial for predicting material performance in processes like injection molding.
How Melt Flow Index is Tested
Melt Flow Index (MFI) is tested by measuring the rate at which molten polymer flows through a standardized capillary under specific temperature and load conditions, providing crucial data on a material's flow properties. This process involves heating the polymer to a set temperature, applying a constant weight, and recording the mass of polymer extruded within ten minutes. Understanding your polymer's MFI through this test helps predict processing behavior and ensures quality control during manufacturing.
Applications of Viscosity and MFI in Industry
Viscosity and melt flow index (MFI) are critical parameters for polymer processing industries, guiding the selection and optimization of materials for injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding applications. Viscosity measurements provide detailed insights into a polymer's flow behavior under various shear rates, essential for formulating products with precise mechanical properties. MFI offers a rapid assessment of polymer melt flowability, enabling quality control and consistency verification in manufacturing processes such as plastic film production and fiber extrusion.
Influence of Temperature and Pressure
Viscosity and melt flow index (MFI) are critical parameters in polymer processing, heavily influenced by temperature and pressure variations. Increasing temperature typically reduces viscosity by enhancing polymer chain mobility, while MFI increases, indicating easier flow under standardized test conditions. Pressure elevations compress polymer chains, raising viscosity and lowering MFI, which impacts Your material's processability and final product quality.
Selecting the Right Parameter for Quality Control
Viscosity and melt flow index (MFI) serve distinct roles in polymer quality control, with viscosity measuring a material's resistance to deformation under shear stress and MFI quantifying the flow rate of molten polymer through a standardized die. Selecting the right parameter depends on your specific process conditions: viscosity provides detailed insight into polymer behavior under varying shear rates essential for processing optimization, whereas MFI offers a quick, standardized measure for comparing polymer grades and ensuring batch consistency. Accurate interpretation of these parameters ensures reliable quality control, helping you maintain product performance and process stability.
Conclusion: Viscosity or MFI—Which to Use?
Viscosity and melt flow index (MFI) both measure polymer melt behavior but serve different purposes; viscosity provides detailed flow resistance information under varying shear rates, while MFI offers a quick, standardized index of flowability at a specific temperature and load. For precise process control and material characterization, viscosity is preferred due to its comprehensive data on polymer melt dynamics. Your choice depends on application needs: use MFI for rapid quality checks and viscosity for in-depth rheological analysis.
Viscosity vs melt flow index Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com