Polyolefin offers excellent moisture resistance and lightweight durability, making it ideal for environments requiring water repellency and chemical stability. Polyester provides superior strength and UV resistance, ensuring long-lasting performance in applications exposed to sunlight and mechanical stress.
Table of Comparison
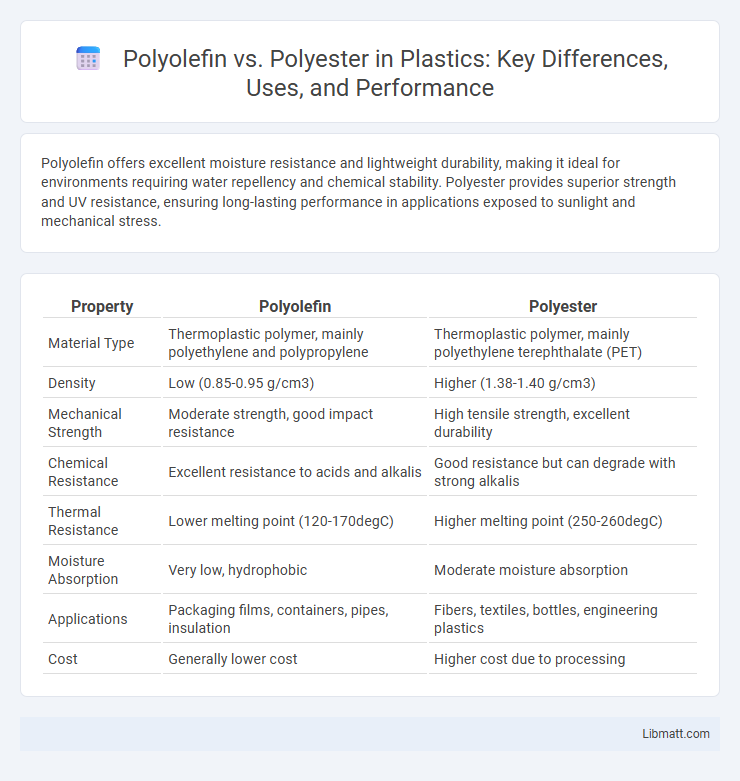
| Property | Polyolefin | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer, mainly polyethylene and polypropylene | Thermoplastic polymer, mainly polyethylene terephthalate (PET) |
| Density | Low (0.85-0.95 g/cm3) | Higher (1.38-1.40 g/cm3) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate strength, good impact resistance | High tensile strength, excellent durability |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids and alkalis | Good resistance but can degrade with strong alkalis |
| Thermal Resistance | Lower melting point (120-170degC) | Higher melting point (250-260degC) |
| Moisture Absorption | Very low, hydrophobic | Moderate moisture absorption |
| Applications | Packaging films, containers, pipes, insulation | Fibers, textiles, bottles, engineering plastics |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to processing |
Introduction to Polyolefin and Polyester
Polyolefin is a category of thermoplastic polymers derived from olefins such as polyethylene and polypropylene, known for their chemical resistance, low density, and flexibility. Polyester, primarily polyethylene terephthalate (PET), is a synthetic polymer recognized for its high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to shrinking and stretching. Both materials serve diverse applications in packaging, textiles, and automotive industries due to their distinct physical and chemical properties.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyolefins, including polyethylene and polypropylene, are composed of long hydrocarbon chains derived from olefin monomers, featuring a simple, non-polar chemical structure primarily made of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Polyester fibers, such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), consist of ester functional groups in their backbone formed by the polycondensation of diols and dicarboxylic acids, resulting in a more polar, aromatic chemical structure. The presence of ester linkages in polyester imparts higher thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to the chemically inert, saturated hydrocarbon backbone of polyolefins.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Polyolefin exhibits excellent tensile strength and impact resistance, making it highly durable for applications requiring flexibility and toughness. Polyester offers superior mechanical strength and dimensional stability, maintaining its form under stress and temperature variations. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize lightweight resilience with polyolefin or long-lasting rigidity with polyester.
Applications in Industry
Polyolefin fibers, such as polypropylene and polyethylene, are widely used in packaging, automotive components, and geotextiles due to their lightweight, chemical resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. Polyester finds extensive applications in textile manufacturing, industrial ropes, conveyor belts, and tire reinforcements because of its strength, durability, and UV resistance. Your choice between polyolefin and polyester depends on the specific requirements of wind, moisture exposure, and mechanical stress in your industry.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyolefin fibers, such as polypropylene and polyethylene, are often favored for their recyclability and lower carbon footprint compared to polyester, which is derived from petroleum and contributes significantly to microplastic pollution. Polyester production consumes more energy and releases higher greenhouse gas emissions, whereas polyolefin materials are gaining traction in sustainable packaging and textile applications due to their potential for closed-loop recycling. Your choice of polyolefin over polyester can reduce environmental impact by supporting lower emissions and enhanced material recovery efforts.
Cost Analysis: Polyolefin vs Polyester
Polyolefin materials generally offer a lower production cost compared to polyester due to their simpler polymer structure and less energy-intensive manufacturing process. Polyester, while more expensive, provides enhanced durability and better resistance to environmental factors, often justifying its higher price in applications requiring long-term performance. Cost analysis must consider not only raw material prices but also lifecycle expenses, including maintenance and replacement frequency, where polyolefins may offer savings despite shorter service life.
Moisture Resistance and Absorbency
Polyolefin offers superior moisture resistance compared to polyester, making it ideal for applications requiring low water absorption and quick-drying properties. Polyester absorbs slightly more moisture but maintains strength and durability when wet, offering balanced performance in both dry and damp conditions. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize water repellency or moderate absorbency for comfort and function.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Polyolefin exhibits superior chemical resistance, particularly against acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments. Polyester offers higher thermal stability withstanding continuous use temperatures up to 150degC, whereas polyolefin typically degrades above 100degC. Both materials resist moisture well, but polyester's enhanced thermal resistance supports applications requiring prolonged heat exposure.
Recycling and End-of-Life Options
Polyolefin fibers, primarily polypropylene and polyethylene, offer excellent recyclability through mechanical and chemical processes, enabling their conversion into pellets for reuse in textiles and packaging. Polyester, mostly polyethylene terephthalate (PET), is widely recycled via both mechanical reprocessing and advanced chemical recycling methods, such as depolymerization, facilitating closed-loop recycling and reducing environmental impact. End-of-life options for polyolefins often include energy recovery due to their high calorific value, while polyester benefits from established recycling infrastructure, making it a preferred choice for sustainable textile production.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Polyolefin offers exceptional chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and excellent electrical insulation, making it ideal for packaging and insulation applications. Polyester provides superior mechanical strength, UV resistance, and durability, suitable for textiles and outdoor gear. Selecting between polyolefin and polyester depends on the specific requirements for flexibility, environmental exposure, and mechanical performance in your project.
Polyolefin vs Polyester Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com