Offset printing delivers high-quality, cost-effective results for large print runs by transferring ink from plates to paper, making it ideal for bulk production. Digital printing offers quicker turnaround and customization options, allowing you to print smaller quantities with variable data efficiently and without the need for plates.
Table of Comparison
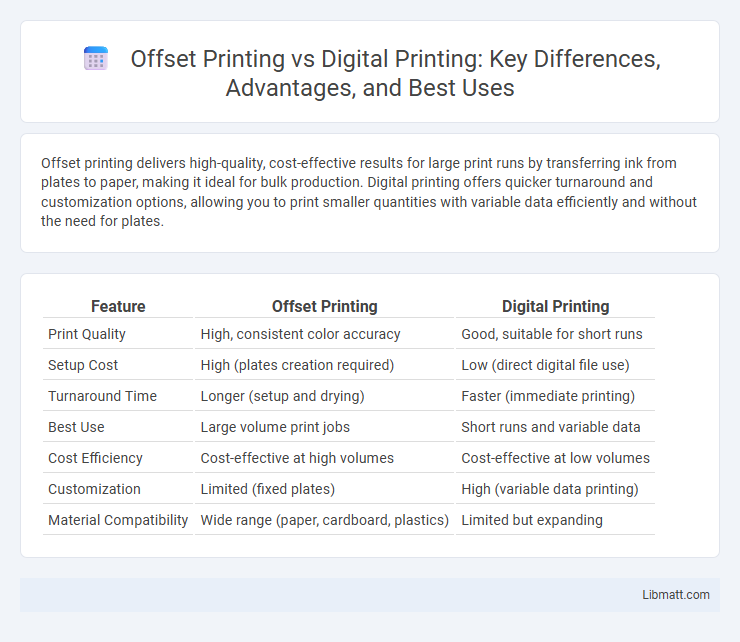
| Feature | Offset Printing | Digital Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Print Quality | High, consistent color accuracy | Good, suitable for short runs |
| Setup Cost | High (plates creation required) | Low (direct digital file use) |
| Turnaround Time | Longer (setup and drying) | Faster (immediate printing) |
| Best Use | Large volume print jobs | Short runs and variable data |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective at high volumes | Cost-effective at low volumes |
| Customization | Limited (fixed plates) | High (variable data printing) |
| Material Compatibility | Wide range (paper, cardboard, plastics) | Limited but expanding |
Introduction to Printing Technologies
Offset printing utilizes metal plates to transfer ink onto paper, providing high-quality, consistent results ideal for large print runs, while digital printing directly prints images from digital files, offering flexibility and faster turnaround for smaller quantities. Your choice depends on factors like order size, budget, and desired print quality, with offset excelling in cost-efficiency for bulk jobs and digital catering to customization and quick production. Understanding these fundamental differences helps optimize printing strategies for varied business needs.
What is Offset Printing?
Offset printing is a traditional printing technique that transfers ink from a metal plate to a rubber blanket before applying it to the printing surface, typically paper. This method excels in producing high-quality, consistent images and is ideal for large print runs due to its cost-effectiveness and fast output. Offset printing supports a wide range of substrates and offers superior color accuracy and detail compared to digital printing.
What is Digital Printing?
Digital printing is a modern printing method that directly transfers digital images onto various substrates using laser or inkjet technology, eliminating the need for printing plates. This process enables high-quality, on-demand prints with rapid turnaround times and cost efficiency for short runs. It is ideal for producing variable data printing, personalized materials, and small batch orders with consistent color accuracy.
Key Differences Between Offset and Digital Printing
Offset printing offers high-quality color consistency and is cost-effective for large print runs, using plates to transfer ink onto paper. Digital printing provides faster turnaround times and is ideal for small print volumes, printing directly from digital files without the need for plates. The key differences involve setup complexity, cost efficiency based on quantity, and image precision.
Print Quality Comparison
Offset printing delivers superior print quality with crisp, sharp images and consistent color reproduction ideal for large-volume projects. Digital printing offers excellent quality for short runs, with improvements in color accuracy and detail but may show slight variations compared to offset. Your choice depends on balancing quality needs with project size and budget constraints.
Cost Analysis: Offset vs Digital Printing
Offset printing offers lower unit costs for large print runs due to economies of scale, making it more cost-effective for high-volume projects. Digital printing has higher per-unit costs but eliminates setup fees and allows economical small runs with quick turnaround times. Businesses must consider volume, budget, and turnaround when choosing between offset and digital printing methods.
Speed and Turnaround Time
Offset printing offers faster turnaround times for large volume orders due to its high-speed press capabilities and efficient setup for mass production. Digital printing excels in quick, short-run jobs, allowing you to receive prints almost immediately without the need for lengthy setup processes. Evaluating your project size helps determine whether offset or digital printing best suits your speed and delivery requirements.
Best Applications for Offset Printing
Offset printing excels in producing high-quality, consistent images on large-volume projects such as books, magazines, brochures, and newspapers. It is ideal for jobs requiring precise color matching, long print runs, and various paper types, including textured and thick stocks. Businesses seeking cost-effective solutions for bulk print orders often choose offset printing for its superior plate-based process and lower unit cost at scale.
Best Applications for Digital Printing
Digital printing excels in producing short runs, customized products, and quick turnaround projects, making it ideal for personalized marketing materials, photo books, and small batch packaging. Its ability to handle variable data printing allows You to create targeted campaigns with unique elements for each recipient. High-quality color consistency and minimal setup time make digital printing the best choice for on-demand prints and rapid prototyping.
Choosing the Right Printing Method for Your Project
Offset printing offers high-quality, cost-effective results for large-volume projects, delivering precise color accuracy and consistency with each print run. Digital printing excels in short runs and quick turnaround times, allowing for easy customization and minimal setup costs, ideal for personalized or time-sensitive materials. Your choice depends on project size, budget, and detail requirements to ensure optimal printing performance and cost efficiency.
Offset vs Digital Printing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com