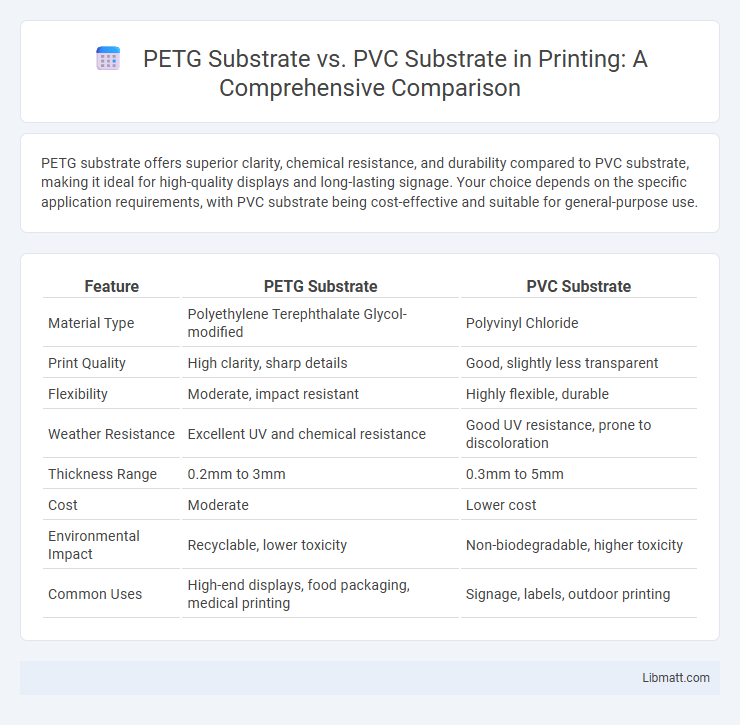
PETG substrate offers superior clarity, chemical resistance, and durability compared to PVC substrate, making it ideal for high-quality displays and long-lasting signage. Your choice depends on the specific application requirements, with PVC substrate being cost-effective and suitable for general-purpose use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | PETG Substrate | PVC Substrate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified | Polyvinyl Chloride |
| Print Quality | High clarity, sharp details | Good, slightly less transparent |
| Flexibility | Moderate, impact resistant | Highly flexible, durable |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent UV and chemical resistance | Good UV resistance, prone to discoloration |
| Thickness Range | 0.2mm to 3mm | 0.3mm to 5mm |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower cost |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, lower toxicity | Non-biodegradable, higher toxicity |
| Common Uses | High-end displays, food packaging, medical printing | Signage, labels, outdoor printing |
Introduction to PETG and PVC Substrates
PETG substrate is a glycol-modified polyester known for its excellent clarity, impact resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for high-quality printing and packaging applications. PVC substrate, or polyvinyl chloride, offers superior durability, weather resistance, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in signage, labels, and construction materials. Both substrates provide versatile solutions, with PETG favored for its optical properties and PVC preferred for robust, outdoor applications.
Material Composition: PETG vs PVC
PETG substrate is a copolyester known for its clarity, flexibility, and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and transparency. PVC substrate, composed of polyvinyl chloride, is more rigid and chemical-resistant but tends to be less flexible and heavier than PETG. Your choice between PETG and PVC depends on whether you prioritize lightweight flexibility and clarity or rigidity and chemical resistance.
Manufacturing Processes of PETG and PVC Substrates
PETG substrates are manufactured through extrusion, where polyethylene terephthalate glycol is melted and formed into sheets, offering high clarity and chemical resistance. PVC substrates are produced via calendering or extrusion, involving the melting and forming of polyvinyl chloride, which provides strong durability and flexibility. Both processes require precise temperature and control parameters to ensure consistent thickness and surface quality for printing and lamination applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
PETG substrate offers higher impact resistance and greater flexibility compared to PVC substrate, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and formability. PVC substrate tends to be more rigid and exhibits better chemical resistance but is prone to brittleness under low temperatures. Both materials have similar moisture resistance, yet PETG provides superior clarity and is easier to thermoform than PVC.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
PETG substrate offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to PVC substrate due to its recyclability and lower release of harmful chemicals during production and disposal. PVC substrates contribute significantly to environmental pollution through the emission of dioxins and other toxic substances, making them less sustainable. Choosing PETG for Your projects supports sustainability efforts by reducing ecological footprint and promoting circular economy principles in material usage.
Durability and Longevity
PETG substrate offers superior durability and longevity compared to PVC substrate due to its enhanced impact resistance and chemical stability. PETG resists cracking and yellowing over time, maintaining clarity and structural integrity in harsh environments. PVC substrate tends to degrade faster under UV exposure, becoming brittle and prone to warping, which limits its lifespan in outdoor applications.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
PETG substrate offers superior chemical resistance and clarity, making it ideal for food packaging, medical devices, and retail displays where hygiene and transparency are critical. PVC substrate is widely used in construction, signage, and automotive industries due to its durability, weather resistance, and ease of printing. Your choice depends on the application requirements for flexibility, environmental exposure, and regulatory compliance.
Printability and Visual Quality
PETG substrates offer superior printability due to their excellent ink adhesion and smooth surface, resulting in vibrant, high-resolution prints with enhanced color accuracy. PVC substrates also provide good printability but may exhibit slight ink absorption variations, which can affect overall image sharpness and consistency. Visually, PETG substrates deliver a glossy, clear finish that enhances brightness and contrast, while PVC substrates typically present a matte or satin finish, offering durability but less vivid visual impact.
Cost Analysis: PETG vs PVC
PETG substrate typically incurs higher material costs compared to PVC substrate due to its enhanced durability and chemical resistance. PVC substrate offers a more budget-friendly option with widespread availability, making it suitable for large-scale productions with cost sensitivity. Cost analysis should also consider PETG's longer lifespan and recyclability, which may offset upfront expenses in long-term applications.
Choosing the Right Substrate: Key Considerations
PETG substrate offers superior durability, clarity, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting and impact-resistant materials. PVC substrate provides excellent affordability, flexibility, and ease of printing, suited for cost-sensitive projects with moderate durability needs. When choosing the right substrate, factors such as environmental exposure, expected lifespan, budget constraints, and print quality requirements play crucial roles in determining whether PETG or PVC best meets the project's demands.
PETG substrate vs PVC substrate Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com