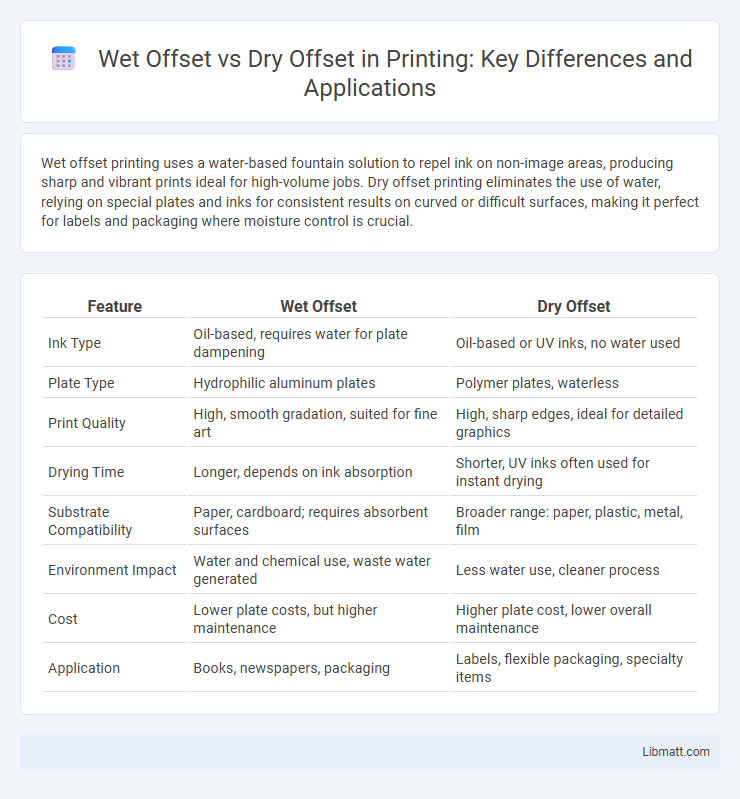
Wet offset printing uses a water-based fountain solution to repel ink on non-image areas, producing sharp and vibrant prints ideal for high-volume jobs. Dry offset printing eliminates the use of water, relying on special plates and inks for consistent results on curved or difficult surfaces, making it perfect for labels and packaging where moisture control is crucial.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wet Offset | Dry Offset |
|---|---|---|
| Ink Type | Oil-based, requires water for plate dampening | Oil-based or UV inks, no water used |
| Plate Type | Hydrophilic aluminum plates | Polymer plates, waterless |
| Print Quality | High, smooth gradation, suited for fine art | High, sharp edges, ideal for detailed graphics |
| Drying Time | Longer, depends on ink absorption | Shorter, UV inks often used for instant drying |
| Substrate Compatibility | Paper, cardboard; requires absorbent surfaces | Broader range: paper, plastic, metal, film |
| Environment Impact | Water and chemical use, waste water generated | Less water use, cleaner process |
| Cost | Lower plate costs, but higher maintenance | Higher plate cost, lower overall maintenance |
| Application | Books, newspapers, packaging | Labels, flexible packaging, specialty items |
Introduction to Offset Printing Techniques
Wet offset printing utilizes a water-based fountain solution to repel ink from non-image areas, ensuring precise ink transfer and high-quality prints on paper. Dry offset printing, also known as letterset, uses a rubber blanket to transfer ink directly onto substrates without the need for dampening, ideal for printing on rough or uneven surfaces like metal cans. Both techniques are essential in offset printing, offering distinct advantages for different materials and project requirements.
What is Wet Offset Printing?
Wet offset printing uses a water-based dampening system to repel ink from non-image areas, ensuring sharp and high-quality prints on paper and other substrates. This method excels in producing vibrant colors and precise details, especially for high-volume commercial printing like magazines and brochures. Your choice of wet offset printing guarantees consistent results with smooth color transitions and excellent image clarity.
What is Dry Offset Printing?
Dry offset printing is a technique that combines elements of letterpress and offset printing, where the image is transferred from a plate to a rubber blanket and then directly onto the substrate without using any water or dampening solution. This method is ideal for printing on non-porous surfaces such as metal, plastic, glass, and foil, offering sharp, high-quality images with excellent ink adhesion. Dry offset presses are commonly used in packaging industries for products like tin cans, capsules, and glass bottles, providing durable and vibrant prints resistant to smudging and fading.
Key Differences Between Wet and Dry Offset Printing
Wet offset printing uses a water-based fountain solution to repel ink from non-image areas, resulting in high-quality, sharp images with excellent color fidelity. Dry offset printing eliminates the water fountain solution, relying on silicone-coated plates to prevent ink from adhering to non-image areas, making it ideal for printing on non-absorbent surfaces like metal and plastic. Key differences include substrate compatibility, ink drying methods, and environmental impact, with wet offset suited for porous papers and dry offset for specialized materials.
Advantages of Wet Offset Printing
Wet offset printing offers superior ink adhesion and vibrancy, enhancing image quality on a wide range of paper types. The water-based process reduces ink dot gain, resulting in sharper details and more accurate color reproduction. This method supports faster production speeds and greater consistency, making it ideal for high-volume commercial printing.
Benefits of Dry Offset Printing
Dry offset printing offers advantages such as faster setup times and reduced waste, making it cost-effective for short to medium print runs. It eliminates the need for water in the process, preventing paper deformation and enhancing image sharpness and color vibrancy. Your projects benefit from consistent high-quality prints with less environmental impact compared to wet offset methods.
Common Applications of Wet Offset Printing
Wet offset printing excels in high-quality packaging and labels, where vibrant colors and sharp details are essential. This technique is commonly used for printing brochures, magazines, and product packaging that require precise color reproduction and consistency. Your printed materials benefit from wet offset's ability to handle large volume runs efficiently while maintaining excellent image clarity.
Typical Uses for Dry Offset Printing
Dry offset printing is typically used for printing on non-porous surfaces such as metal cans, glass bottles, and plastic containers due to its oil-based ink compatibility and fast drying time. It excels in producing sharp, high-quality images on curved or irregular surfaces, making it popular in the packaging industry for items like beverage cans and food containers. This method is favored for its efficiency in high-volume production runs where precise ink application and durability are essential.
Cost and Efficiency Comparison
Wet offset printing generally incurs higher costs due to the use of water and ink balance control, leading to increased maintenance and setup time. Dry offset printing offers greater efficiency with faster setup, reduced waste, and lower solvent usage, making it more cost-effective for short to medium runs. Your choice between wet and dry offset should consider production volume and budget constraints to maximize cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Offset Printing Method
Selecting between wet offset and dry offset printing hinges on your project's material type and print quality needs. Wet offset excels with absorbent surfaces like paper due to its use of water-based inks, ensuring sharp and vibrant results. Dry offset is ideal for non-porous substrates like plastic or metal, as it employs an oil-based ink that adheres better without smudging, making your printed materials durable and visually appealing.
Wet offset vs dry offset Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com