Screen printing offers bold, vibrant colors and works well on various surfaces, making it ideal for custom t-shirts and posters. Lithography excels in producing fine details and smooth gradients, perfect for high-quality art prints and commercial artwork.
Table of Comparison
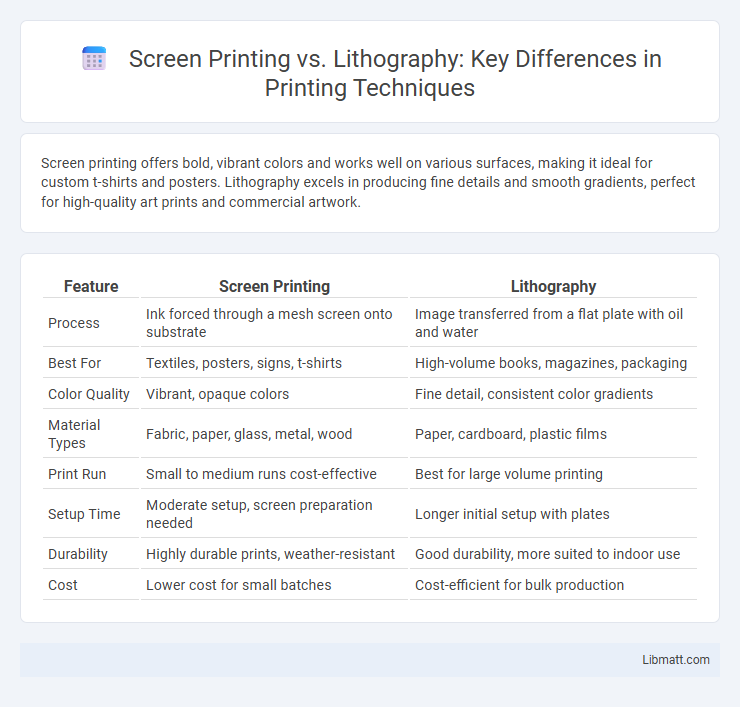
| Feature | Screen Printing | Lithography |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Ink forced through a mesh screen onto substrate | Image transferred from a flat plate with oil and water |
| Best For | Textiles, posters, signs, t-shirts | High-volume books, magazines, packaging |
| Color Quality | Vibrant, opaque colors | Fine detail, consistent color gradients |
| Material Types | Fabric, paper, glass, metal, wood | Paper, cardboard, plastic films |
| Print Run | Small to medium runs cost-effective | Best for large volume printing |
| Setup Time | Moderate setup, screen preparation needed | Longer initial setup with plates |
| Durability | Highly durable prints, weather-resistant | Good durability, more suited to indoor use |
| Cost | Lower cost for small batches | Cost-efficient for bulk production |
Introduction to Screen Printing and Lithography
Screen printing uses a mesh stencil to transfer ink onto a surface, allowing vibrant and durable prints on various materials like textiles and posters. Lithography relies on the principle of oil and water repelling each other, using a flat stone or metal plate to produce detailed, high-quality images often favored for fine art and commercial printing. Understanding these fundamental differences helps you choose the ideal printing technique for your project's texture, color intensity, and production scale.
Key Differences Between Screen Printing and Lithography
Screen printing uses a mesh screen to transfer ink onto a substrate, allowing for vibrant colors and thick ink layers, making it ideal for textiles and posters. Lithography relies on a flat printing plate where oil-based ink adheres only to the image area, producing fine detail and smooth gradients suitable for high-volume commercial printing. Your choice between screen printing and lithography depends on factors like print durability, color vibrancy, detail precision, and production scale.
Historical Background of Both Techniques
Screen printing originated in ancient China around 960 AD, evolving over centuries before gaining widespread commercial use in the early 20th century. Lithography was invented in 1796 by Alois Senefelder and revolutionized printing by using a chemical process on limestone, becoming essential for mass production of images and texts in the 19th century. Understanding the historical development of these techniques helps you appreciate their unique applications and technological advancements in modern printing.
Materials and Equipment Used
Screen printing relies on a mesh screen, squeegee, and stencil to transfer ink onto substrates like fabric, paper, or glass, while lithography uses a flat stone or metal plate treated with chemicals to create images based on the repulsion of oil and water. The materials for screen printing are typically thicker, opaque inks suited for textiles and promotional items, whereas lithography uses finer, oil-based inks ideal for high-resolution prints on paper. Your choice between these printing techniques depends on the specific materials and equipment available, as screen printing excels in versatility and durability and lithography shines in detailed, high-volume print production.
Print Quality and Image Detail
Screen printing excels in producing vibrant colors and thick ink layers, making it ideal for bold designs but often lacks the fine image detail achievable with lithography. Lithography offers superior print quality with precise, sharp details and smooth gradients due to its ability to reproduce images with high resolution and subtle tonal variations. The choice between the two methods depends on whether the priority is vivid, durable prints or intricate, detailed imagery.
Cost Comparison: Screen Printing vs Lithography
Screen printing typically incurs higher initial setup costs due to stencil creation and specialized equipment, making it more cost-effective for small to medium production runs. Lithography, or offset printing, involves significant upfront expenses for plate preparation but offers lower per-unit costs with large volume prints, making it economical for high-volume projects. Choosing between screen printing and lithography depends largely on budget constraints, project scale, and desired print quality.
Ideal Applications for Each Printing Method
Screen printing excels in producing vibrant, durable designs on textiles, posters, and promotional materials, making it ideal for apparel, signage, and large-format prints where bold colors and longevity are essential. Lithography is best suited for high-volume printing of detailed images, such as brochures, magazines, and packaging, due to its precision and cost-efficiency in reproducing fine details and gradients. Your choice between screen printing and lithography should depend on the intended application, desired print quality, and production scale.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Screen printing typically consumes more water and produces higher amounts of chemical waste compared to lithography, which uses oil-based inks more efficiently and generates less hazardous runoff. Your choice of lithography can reduce environmental impact due to its reliance on recyclable plates and minimized waste production. Prioritizing sustainable printing methods supports eco-friendly practices by lowering energy use and promoting responsible resource management.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Screen printing offers vibrant colors and durability, making it ideal for bold designs and apparel customization, but it can be less cost-effective for small runs due to setup time. Lithography provides high-definition detail and smooth gradients, great for fine art and commercial printing, though it may lack the texture and durability of screen prints. Understanding your project's scale and design complexity will help you choose the best printing method for your needs.
Choosing the Right Printing Method for Your Project
Screen printing offers vibrant colors and durability, ideal for textiles, posters, and promotional materials requiring bold designs and long-lasting prints. Lithography excels in producing high-volume, detailed images with smooth color gradients, making it perfect for fine art reproductions and commercial printing jobs. Consider your project's scale, complexity, and material to select the printing method that balances cost, quality, and purpose effectively.
Screen printing vs lithography Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com