Varnish enhances the visual appeal of printed materials by adding a glossy or matte coating that protects the surface and highlights colors without significantly increasing thickness. Lamination offers a more durable barrier against moisture, tearing, and wear by sealing the entire print with a plastic film, making your documents sturdier and longer-lasting.
Table of Comparison
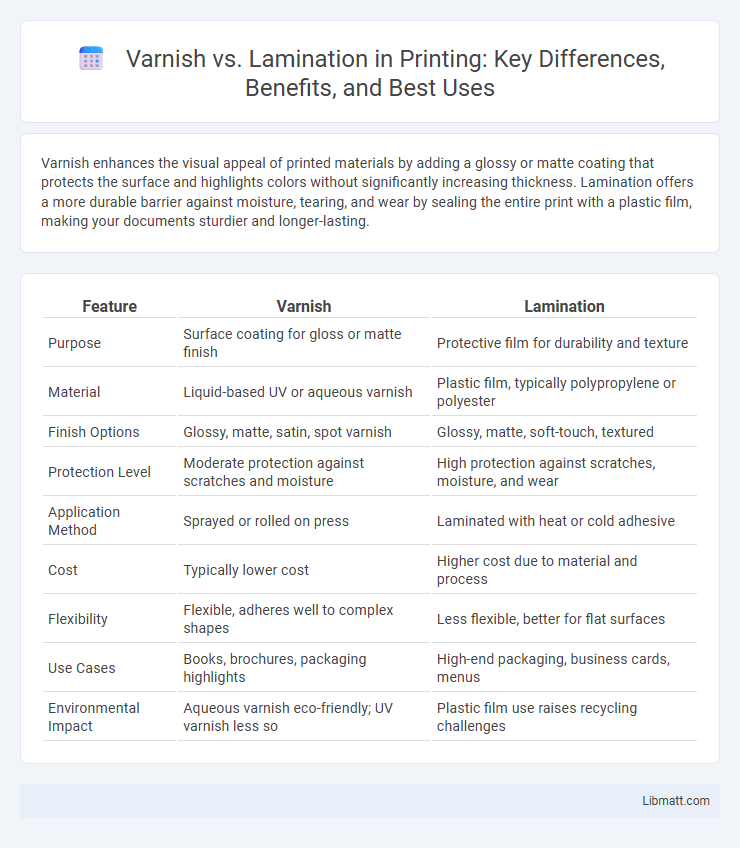
| Feature | Varnish | Lamination |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Surface coating for gloss or matte finish | Protective film for durability and texture |
| Material | Liquid-based UV or aqueous varnish | Plastic film, typically polypropylene or polyester |
| Finish Options | Glossy, matte, satin, spot varnish | Glossy, matte, soft-touch, textured |
| Protection Level | Moderate protection against scratches and moisture | High protection against scratches, moisture, and wear |
| Application Method | Sprayed or rolled on press | Laminated with heat or cold adhesive |
| Cost | Typically lower cost | Higher cost due to material and process |
| Flexibility | Flexible, adheres well to complex shapes | Less flexible, better for flat surfaces |
| Use Cases | Books, brochures, packaging highlights | High-end packaging, business cards, menus |
| Environmental Impact | Aqueous varnish eco-friendly; UV varnish less so | Plastic film use raises recycling challenges |
Introduction to Varnish and Lamination
Varnish is a clear coating applied to printed materials to enhance gloss, protect surfaces, and add durability without changing texture, while lamination involves bonding a thin plastic film to the paper for greater protection and a smooth or matte finish. Varnish typically offers cost-effective surface protection with varying sheens, whereas lamination provides superior moisture resistance and sturdiness, ideal for frequently handled items. Your choice between varnish and lamination depends on the desired finish, durability, and budget requirements for your printed project.
What is Varnish?
Varnish is a clear liquid coating applied to printed materials to enhance durability, protect against moisture, and add a subtle gloss or matte finish, depending on the type used. It penetrates the paper surface, providing a thin, protective layer without the thickness of lamination. Your printed materials benefit from varnish by attaining improved resistance to wear while maintaining a natural paper feel and vibrant colors.
What is Lamination?
Lamination is a protective process that involves applying a thin layer of plastic film over printed materials to enhance durability, water resistance, and overall appearance. This technique safeguards documents, menus, and packaging from wear, tear, and moisture damage, ensuring long-lasting quality. Your printed items benefit from a glossy or matte finish that also improves color vibrancy and surface smoothness.
Key Differences Between Varnish and Lamination
Varnish and lamination serve different purposes in protecting and enhancing printed materials, with varnish applying a liquid coating that can be glossy, matte, or satin to enhance color vibrancy and provide a subtle texture, while lamination involves bonding a thin plastic film over the surface for durable, waterproof protection. Varnish is cost-effective for short runs and adds spot effects or highlights, whereas lamination offers superior durability and resistance to tearing, scuffing, and moisture, making it ideal for high-use items. Your choice depends on the level of protection needed and the desired finish effect, with varnish focusing on aesthetic enhancement and lamination prioritizing longevity.
Advantages of Using Varnish
Varnish enhances print quality by providing a glossy or matte finish that increases visual appeal and protects against minor scratches and moisture damage. It offers cost-effective customization options, allowing selective application on specific design elements to highlight details. Varnish also improves durability and longevity of printed materials without altering the texture significantly, making it ideal for high-quality marketing collateral.
Advantages of Using Lamination
Lamination offers superior protection against moisture, scratches, and UV damage, significantly extending the lifespan and durability of printed materials. This process enhances the visual appeal by providing a smooth, glossy, or matte finish that improves color vibrancy and sharpness. Your documents or packaging benefit from a professional look and feel, making lamination an excellent choice for preserving important prints and promotional materials.
Applications of Varnish in Printing
Varnish in printing is primarily applied to enhance the visual appeal and durability of printed materials such as brochures, business cards, and packaging. It offers a protective layer that resists scratches, dirt, and moisture, ensuring longer-lasting prints. Your choice of varnish can impact glossiness and texture, making it ideal for highlighting specific design elements without altering the underlying print.
Applications of Lamination in Printing
Lamination in printing is widely used for protecting printed materials such as business cards, book covers, menus, and posters by providing a durable, water-resistant surface that enhances longevity and appearance. This process increases resistance to scratches, moisture, and UV damage, making laminated prints ideal for frequently handled or displayed items. Lamination also improves color vibrancy and can add a glossy, matte, or textured finish, contributing to both aesthetic appeal and functional durability.
Cost Comparison: Varnish vs Lamination
Varnish offers a more cost-effective solution compared to lamination, especially for short print runs and budget-conscious projects. Lamination involves higher initial expenses due to material costs and processing time but provides superior durability and a premium finish. Choosing between varnish and lamination depends on balancing budget constraints with desired product longevity and aesthetic quality.
How to Choose: Varnish or Lamination for Your Project
Choosing between varnish and lamination depends on your project's durability needs and visual appeal. Varnish provides a glossy or matte finish that enhances color vibrancy while allowing the natural texture of the paper to show through, ideal for projects requiring a subtle, elegant look. Lamination offers stronger protection against moisture, scratches, and wear, making it suitable for items handled frequently or exposed to harsh conditions; assess your project's handling and environmental factors to decide which finish best preserves your work.
Varnish vs Lamination Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com