2D vision captures flat images representing height and width, limiting depth perception and spatial understanding. Your ability to interpret scenes improves significantly with 3D vision, which adds depth, enabling more accurate object recognition and interaction within an environment.
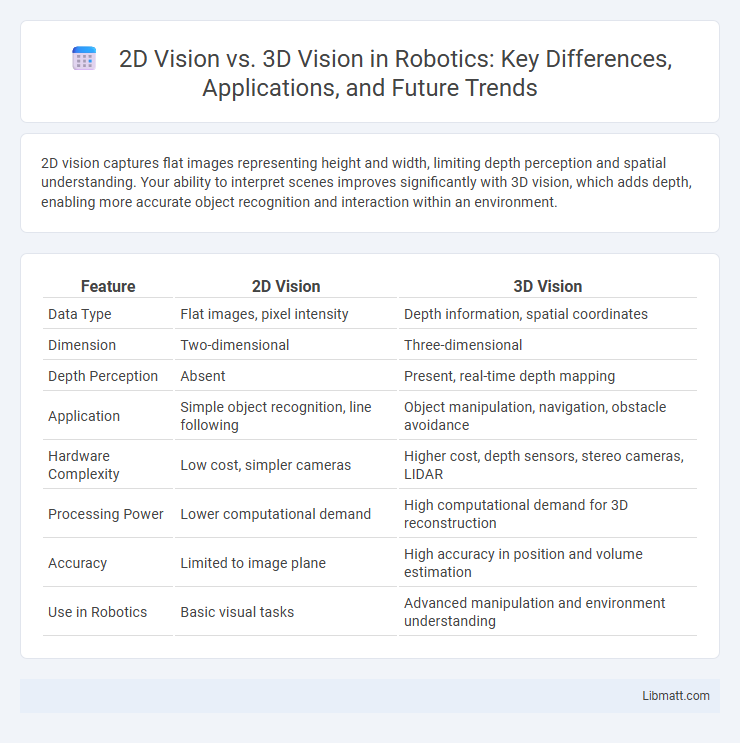
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 2D Vision | 3D Vision |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Flat images, pixel intensity | Depth information, spatial coordinates |
| Dimension | Two-dimensional | Three-dimensional |
| Depth Perception | Absent | Present, real-time depth mapping |
| Application | Simple object recognition, line following | Object manipulation, navigation, obstacle avoidance |
| Hardware Complexity | Low cost, simpler cameras | Higher cost, depth sensors, stereo cameras, LIDAR |
| Processing Power | Lower computational demand | High computational demand for 3D reconstruction |
| Accuracy | Limited to image plane | High accuracy in position and volume estimation |
| Use in Robotics | Basic visual tasks | Advanced manipulation and environment understanding |
Introduction to 2D and 3D Vision
2D vision captures flat images representing width and height, primarily used in photography, computer vision, and screen displays. 3D vision extends perception by adding depth, enabling spatial understanding crucial for robotics, augmented reality, and medical imaging. Your choice between 2D and 3D vision impacts the accuracy and complexity of visual data interpretation in various applications.
Key Differences Between 2D and 3D Vision
2D vision captures flat images representing width and height, making it ideal for tasks like object recognition and pattern analysis, whereas 3D vision includes depth information, enabling spatial understanding and accurate measurement of objects in a three-dimensional space. While 2D vision relies on single-plane image data, 3D vision often uses stereoscopic cameras, LiDAR, or structured light to reconstruct depth maps and volumetric models. Your choice between 2D and 3D vision depends on the application's need for depth perception, with 3D vision excelling in robotics, navigation, and augmented reality.
How 2D Vision Works
2D vision relies on detecting and interpreting light intensity and color from a flat image plane captured by a camera sensor, processing pixel data to identify shapes, edges, and textures. It uses algorithms such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for object recognition and feature extraction within two-dimensional image frames. Unlike 3D vision, 2D vision lacks depth perception, limiting its ability to determine spatial relationships and object distances.
How 3D Vision Works
3D vision works by capturing depth information from multiple viewpoints, using techniques like stereoscopy, structured light, or time-of-flight sensors to create a three-dimensional representation of the environment. Unlike 2D vision, which only processes flat images, 3D vision reconstructs spatial geometry by analyzing disparities or depth cues between images or light patterns. Your applications benefit from enhanced object detection and spatial awareness, improving accuracy in robotics, augmented reality, and autonomous navigation.
Applications of 2D Vision
2D vision is extensively applied in image recognition, barcode scanning, quality inspection, and facial recognition systems due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Industries such as manufacturing leverage 2D vision for defect detection and assembly verification, enhancing production accuracy and speed. In retail and security, 2D vision supports real-time monitoring and access control, making it essential for automated processes and surveillance.
Applications of 3D Vision
3D vision technology enables accurate depth perception and spatial understanding, crucial for applications such as autonomous vehicles, robotic navigation, and augmented reality. In industrial automation, 3D vision systems enhance quality control and precise object manipulation. Medical imaging and virtual reality also benefit from 3D vision, providing detailed anatomical models and immersive user experiences.
Advantages of 2D Vision
2D vision systems offer advantages such as simplicity, lower cost, and faster processing times compared to 3D vision. These systems excel in applications requiring high-speed inspection, pattern recognition, and object identification on flat surfaces. Your choice of 2D vision can optimize efficiency and reduce expenses in environments where depth information is not critical.
Advantages of 3D Vision
3D vision offers enhanced depth perception, enabling accurate measurements and spatial understanding critical for applications like robotics, autonomous vehicles, and medical imaging. It provides more detailed object recognition and scene analysis compared to 2D vision, improving precision in tasks that require dimensional data. The ability to capture volumetric information reduces ambiguity and increases reliability in complex environments, leading to better decision-making and operational efficiency.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Approach
2D vision systems struggle with depth perception and object occlusion, resulting in limited spatial understanding and difficulty in accurately interpreting complex scenes. 3D vision overcomes some depth-related issues but faces challenges such as higher computational costs, sensor calibration complexities, and sensitivity to environmental factors like lighting and surface texture. You must consider these limitations when selecting the appropriate vision approach for applications like robotics, augmented reality, or autonomous navigation.
Future Trends in Vision Technology
Future trends in vision technology emphasize the integration of 3D vision systems, which offer enhanced depth perception and spatial awareness compared to traditional 2D vision. Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are driving the development of more accurate 3D imaging techniques for applications in autonomous vehicles, robotics, and augmented reality. Your ability to leverage these cutting-edge 3D vision innovations will significantly improve object recognition and environmental interaction in complex scenarios.
2D vision vs 3D vision Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com