Failsafe brakes engage automatically to stop machinery or vehicles in the event of power loss, ensuring safety by holding the load securely. Dynamic brakes convert kinetic energy into electrical energy dissipated as heat, providing controlled deceleration during operation without relying on mechanical clamping.
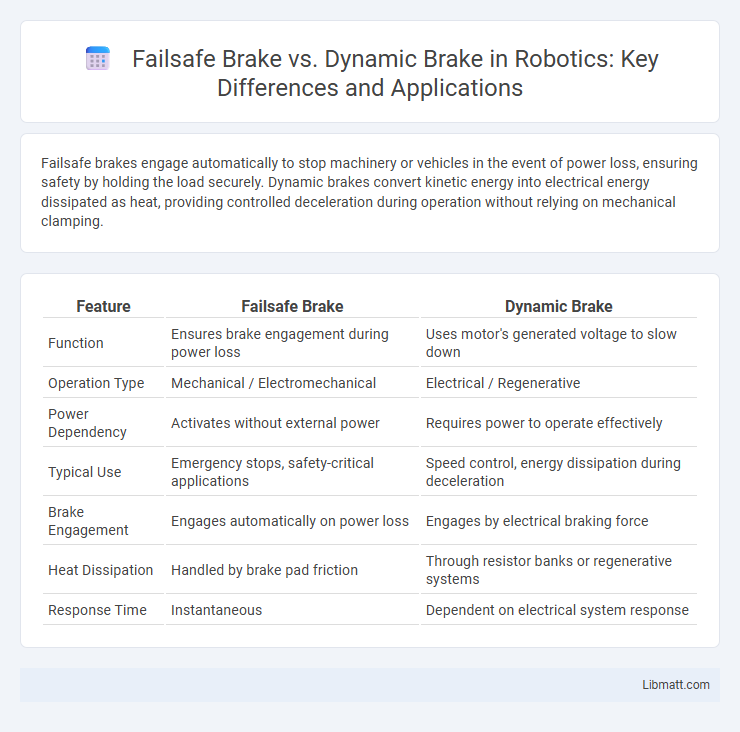
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Failsafe Brake | Dynamic Brake |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Ensures brake engagement during power loss | Uses motor's generated voltage to slow down |
| Operation Type | Mechanical / Electromechanical | Electrical / Regenerative |
| Power Dependency | Activates without external power | Requires power to operate effectively |
| Typical Use | Emergency stops, safety-critical applications | Speed control, energy dissipation during deceleration |
| Brake Engagement | Engages automatically on power loss | Engages by electrical braking force |
| Heat Dissipation | Handled by brake pad friction | Through resistor banks or regenerative systems |
| Response Time | Instantaneous | Dependent on electrical system response |
Introduction to Braking Systems
Failsafe brakes provide reliable stopping power by engaging automatically during power loss or system failure, ensuring safety in critical applications. Dynamic brakes utilize the vehicle's electric motors as generators to convert kinetic energy into electrical energy, dissipated as heat, enabling controlled deceleration without relying solely on mechanical friction. Both systems serve distinct roles in braking technology, with failsafe brakes prioritizing emergency stopping and dynamic brakes enhancing operational control and efficiency.
What is a Failsafe Brake?
A failsafe brake is a safety mechanism designed to automatically engage and stop machinery or vehicles in the event of power loss or system failure, ensuring maximum safety by preventing uncontrolled movement. Unlike dynamic brakes, which use electrical resistance to slow down motion during normal operation, failsafe brakes rely on mechanical force, such as springs, to apply braking power without external energy. Your safety is enhanced with failsafe brakes because they guarantee braking even when power is lost, making them critical in industrial and transportation applications.
What is a Dynamic Brake?
Dynamic brake is a system that uses the electric traction motors of a train as generators to convert kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is then dissipated as heat through resistors. This braking method reduces wear on mechanical brake components and improves control during deceleration. Unlike failsafe brakes, which rely on mechanical or pneumatic means to ensure safety in case of failure, dynamic brakes primarily enhance operational efficiency and energy management.
Key Differences Between Failsafe and Dynamic Brakes
Failsafe brakes engage automatically when power is lost, ensuring immediate and reliable stopping by using mechanical force or spring pressure, while dynamic brakes rely on the electric motor to slow the vehicle by converting kinetic energy into electrical energy dissipated as heat. Unlike dynamic brakes, failsafe brakes do not require electrical power to operate, providing critical safety in emergency situations or power failures. Your choice between these braking systems depends on whether you prioritize mechanical reliability or energy-efficient deceleration during operation.
How Failsafe Brakes Work
Failsafe brakes operate by using a spring mechanism that automatically applies the brake when power is lost, ensuring the vehicle stops safely without electrical input. This system relies on mechanical force to maintain braking pressure, preventing movement during power failures or emergency stops. Unlike dynamic brakes that use electrical resistance to slow the vehicle, failsafe brakes guarantee a physical hold to secure the vehicle under all conditions.
How Dynamic Brakes Operate
Dynamic brakes operate by converting the electric traction motors into generators when you apply the brakes, transforming kinetic energy into electrical energy that is dissipated as heat through resistor grids. This system provides smooth and controlled deceleration without relying solely on friction brakes, reducing wear and enhancing safety in heavy vehicles like trains and trucks. Dynamic braking is especially efficient on long descents where continuous brake application is needed to maintain speed control.
Applications of Failsafe Brakes
Failsafe brakes are primarily used in critical safety applications like elevators, cranes, and emergency stop systems in industrial machinery where maintaining brake engagement upon power loss is essential. These brakes ensure that your equipment remains securely held to prevent accidents during power failures or system malfunctions. In contrast to dynamic brakes, which rely on electrical generation to slow motion, failsafe brakes provide mechanical locking force for enhanced safety in high-risk environments.
Applications of Dynamic Brakes
Dynamic brakes are commonly used in heavy-duty applications such as trains, electric vehicles, and industrial machinery where controlled deceleration is critical. These brakes convert kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is dissipated as heat through resistor grids, making them ideal for prolonged braking on steep grades or high-speed conditions. Your system benefits from reduced wear on mechanical components and improved safety in continuous braking scenarios.
Pros and Cons: Failsafe vs Dynamic Braking
Failsafe brakes provide reliable stopping power during power loss by using mechanical force, ensuring safety but often resulting in slower response times and potential wear due to friction. Dynamic brakes convert kinetic energy into electrical energy or heat for smoother deceleration and reduced mechanical wear but rely heavily on electrical systems, which may fail under certain conditions. While failsafe braking guarantees activation without power, dynamic braking excels in energy efficiency and maintaining vehicle control during prolonged stops.
Choosing the Right Brake for Your System
Choosing the right brake for your system depends on the specific operational requirements and safety considerations of your application. Failsafe brakes engage automatically during power loss, providing reliable emergency stopping and holding capabilities, essential in critical safety scenarios. Dynamic brakes convert kinetic energy into heat via resistors, offering smooth deceleration without the need for mechanical engagement, making them suitable for applications requiring frequent speed adjustments.
Failsafe Brake vs Dynamic Brake Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com