Differential drive robots use two independently powered wheels allowing precise control over speed and direction, making them ideal for navigating tight spaces and executing sharp turns. Omni drive systems feature multiple wheels with rollers enabling seamless movement in any direction, enhancing your robot's maneuverability and agility in complex environments.
Table of Comparison
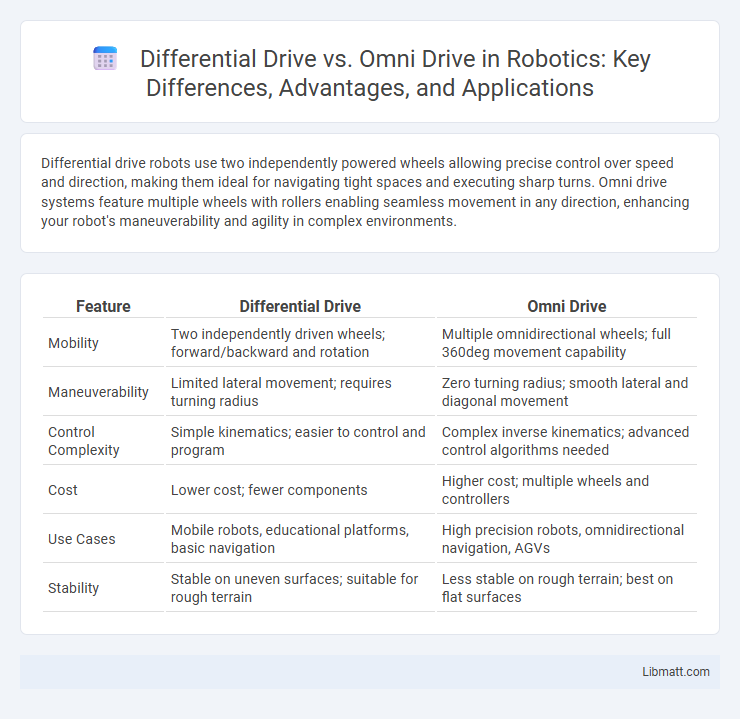
| Feature | Differential Drive | Omni Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | Two independently driven wheels; forward/backward and rotation | Multiple omnidirectional wheels; full 360deg movement capability |
| Maneuverability | Limited lateral movement; requires turning radius | Zero turning radius; smooth lateral and diagonal movement |
| Control Complexity | Simple kinematics; easier to control and program | Complex inverse kinematics; advanced control algorithms needed |
| Cost | Lower cost; fewer components | Higher cost; multiple wheels and controllers |
| Use Cases | Mobile robots, educational platforms, basic navigation | High precision robots, omnidirectional navigation, AGVs |
| Stability | Stable on uneven surfaces; suitable for rough terrain | Less stable on rough terrain; best on flat surfaces |
Introduction to Mobile Robot Drive Systems
Differential drive and omni drive are foundational mobile robot drive systems used for maneuverability and control. Differential drive features two independently driven wheels on either side, enabling robots to pivot and move with precision on flat surfaces. Omni drive incorporates multiple omni-directional wheels allowing robots to move instantly in any direction, offering superior agility in complex environments.
Overview of Differential Drive Mechanisms
Differential drive mechanisms use two independently controlled wheels on either side of the robot, allowing it to move forward, backward, and rotate by varying the speed and direction of each wheel. This design provides simplicity, robustness, and efficient maneuverability, especially in navigating tight spaces or curved paths. Your choice of differential drive enhances precise control and energy efficiency for many mobile robotics applications.
Understanding Omni Drive Technology
Omni drive technology utilizes omnidirectional wheels equipped with rollers arranged at specific angles, enabling movement in any direction without changing the robot's orientation. This design contrasts with differential drive systems, which rely on two independently driven wheels for forward, backward, and rotational movement but lack lateral mobility. The omnidirectional capabilities of omni drive robots enhance maneuverability in tight spaces and improve navigation efficiency in complex environments.
Key Differences Between Differential and Omni Drive
Differential drive systems use two fixed, independently driven wheels to control movement and steering, providing precise control over direction but limited lateral mobility. Omni drive employs multiple omnidirectional wheels, enabling seamless movement in any direction without changing orientation, which enhances maneuverability in tight or dynamic environments. The key difference lies in differential drive's reliance on wheel speed variation for steering versus omni drive's inherent ability to move omnidirectionally through coordinated wheel motion.
Maneuverability and Motion Capabilities
Differential Drive robots offer precise control in forward and rotational movements, making them highly maneuverable in narrow spaces but limited in lateral motion. Omni Drive systems excel in omnidirectional movement, allowing seamless lateral, diagonal, and rotational maneuvers without reorienting the robot. The enhanced motion capabilities of Omni Drives enable superior agility in dynamic environments compared to the more constrained motion patterns of Differential Drives.
Hardware Complexity and Design Considerations
Differential drive systems feature two independently driven wheels on a single axis, resulting in simpler mechanical design and fewer components, which reduces hardware complexity and maintenance requirements. Omni drive systems incorporate multiple omni-directional wheels arranged in configurations such as the three-wheel or four-wheel setup, increasing hardware complexity due to additional motors, encoders, and intricate control algorithms needed for precise multi-directional movement. Design considerations for differential drives prioritize simplicity and robustness on flat surfaces, whereas omni drives demand precise calibration and sensor integration to handle complex maneuvers and environments requiring lateral mobility.
Applications Best Suited for Differential Drive
Differential drive systems are best suited for applications requiring precise control and maneuverability in tight spaces, such as indoor robots, warehouse automation, and mobile service robots. Their simple design with two independently driven wheels offers efficient navigation on flat surfaces and reliable performance in environments with obstacles. Common use cases include differential drive robots in research, education, and autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) where accurate path following is critical.
Applications Ideal for Omni Drive
Omni drive systems excel in environments requiring precise and highly maneuverable movement, such as indoor robotics, automated warehouses, and service robots navigating tight spaces. Their ability to move holonomically--allowing translation in any direction without changing orientation--makes them ideal for applications like floor-cleaning robots, medical assistance devices, and interactive kiosks. Unlike differential drive, omni drive enables smoother lateral movements and quicker response times, enhancing performance in dynamic, obstacle-rich settings.
Cost and Maintenance Comparison
Differential drive systems typically have lower initial costs and simpler maintenance due to fewer motors and mechanical components compared to omni drive systems, which require multiple independent motors and complex wheel assemblies. Omni drives, although more expensive upfront, offer enhanced maneuverability but often demand higher upkeep, including frequent wheel replacements and calibration. The choice depends on balancing budget constraints against desired mobility and maintenance capacity.
Choosing the Right Drive System for Your Robot
Differential drive systems offer simplicity and precise control, making them ideal for robots requiring straightforward navigation on flat surfaces. Omni drive systems provide enhanced maneuverability with multi-directional movement, enabling your robot to navigate complex environments and tight spaces effortlessly. Selecting the right drive system depends on your robot's operational needs, balancing ease of control against the flexibility of movement.
Differential Drive vs Omni Drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com