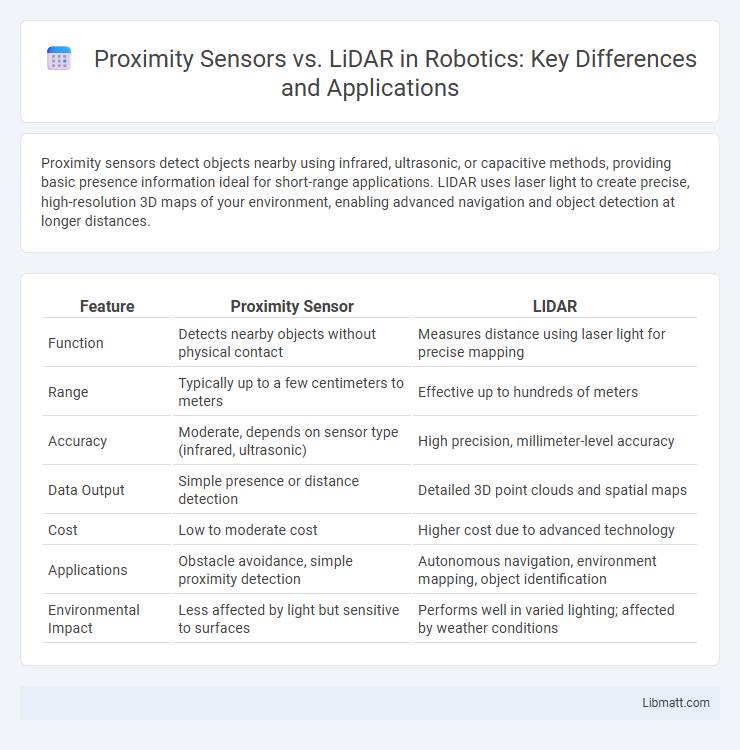
Proximity sensors detect objects nearby using infrared, ultrasonic, or capacitive methods, providing basic presence information ideal for short-range applications. LIDAR uses laser light to create precise, high-resolution 3D maps of your environment, enabling advanced navigation and object detection at longer distances.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Proximity Sensor | LIDAR |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Detects nearby objects without physical contact | Measures distance using laser light for precise mapping |
| Range | Typically up to a few centimeters to meters | Effective up to hundreds of meters |
| Accuracy | Moderate, depends on sensor type (infrared, ultrasonic) | High precision, millimeter-level accuracy |
| Data Output | Simple presence or distance detection | Detailed 3D point clouds and spatial maps |
| Cost | Low to moderate cost | Higher cost due to advanced technology |
| Applications | Obstacle avoidance, simple proximity detection | Autonomous navigation, environment mapping, object identification |
| Environmental Impact | Less affected by light but sensitive to surfaces | Performs well in varied lighting; affected by weather conditions |
Introduction to Proximity Sensors and LIDAR
Proximity sensors detect objects or obstacles within a short range using technologies like infrared, ultrasonic, or capacitive sensing, making them ideal for simple presence detection and close-range applications. LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) uses laser pulses to generate precise 3D maps of an environment, offering high-resolution spatial data crucial for advanced navigation and object recognition. Both technologies enhance Your system's ability to perceive surroundings but differ significantly in range, accuracy, and complexity of data output.
How Proximity Sensors Work
Proximity sensors detect the presence of nearby objects without physical contact by emitting electromagnetic waves or ultrasonic signals and measuring the reflection or interruption of these waves. They often use technologies such as infrared, capacitive, inductive, or ultrasonic sensing to determine distance and proximity. Your device relies on the quick response and accuracy of proximity sensors for applications like obstacle detection, object counting, or touchless control.
Understanding LIDAR Technology
LIDAR technology uses laser light pulses to measure distances by calculating the time it takes for the light to reflect back from objects, enabling high-resolution 3D mapping and precise spatial awareness. Unlike proximity sensors that typically detect the presence or absence of objects within a short range using infrared or ultrasonic signals, LIDAR provides detailed depth information over greater distances. This makes LIDAR essential for applications requiring accurate environmental mapping, such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, and surveying.
Key Differences Between Proximity Sensors and LIDAR
Proximity sensors detect objects within a limited range using methods like infrared, ultrasonic, or capacitive sensing, providing basic on/off presence information suitable for short-distance applications. LIDAR uses laser pulses to create detailed, high-resolution 3D maps of the environment, enabling precise distance measurement and object detection over longer ranges. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right technology based on factors like accuracy, range, and application complexity.
Accuracy and Precision Comparison
Proximity sensors typically offer lower accuracy and precision, detecting objects at short ranges with general presence rather than exact distance measurement, whereas LIDAR provides high-resolution 3D mapping and precise distance data capable of detecting minute variations. LIDAR's advanced laser-based technology delivers accuracy within millimeters, making it ideal for applications requiring detailed spatial awareness, while proximity sensors are better suited for simple obstacle detection where precision is less critical. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the right sensor based on the accuracy and precision demands of your specific project.
Range and Detection Capabilities
Proximity sensors typically operate within short ranges of a few centimeters to a few meters, making them ideal for close object detection in industrial automation and mobile devices. LIDAR systems offer significantly longer detection ranges, often exceeding hundreds of meters, with high-resolution 3D spatial mapping capabilities essential for autonomous vehicles and robotics. The advanced sensing technology of LIDAR provides precise distance measurements and detailed environmental awareness compared to the limited range and simpler detection zones of proximity sensors.
Applications of Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors are widely used in industrial automation for object detection and positioning, enhancing robotic precision and safety. They are integral in smartphones and automotive systems for features like gesture recognition, obstacle detection, and parking assistance. Their cost-effectiveness and reliability make them suitable for packaging, manufacturing, and consumer electronics, where quick detection without physical contact is essential.
Use Cases for LIDAR
LIDAR excels in detailed 3D mapping and autonomous vehicle navigation, providing precise distance measurements over large areas with high resolution. It is widely used in agriculture for crop monitoring, in forestry for canopy analysis, and in urban planning for creating accurate topographic maps. Unlike proximity sensors, LIDAR enables complex environmental modeling and obstacle detection in dynamic, outdoor settings.
Cost and Implementation Factors
Proximity sensors generally offer a lower-cost and simpler implementation compared to LIDAR systems, making them ideal for basic object detection in consumer electronics and robotics. LIDAR provides higher accuracy and longer detection ranges but requires more complex integration and higher initial investment, often suited for autonomous vehicles and advanced mapping. Your choice depends on budget constraints and the precision level needed for the application.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
Proximity sensors offer cost-effective, short-range object detection ideal for simple applications like obstacle avoidance and presence detection, while LIDAR provides high-resolution, long-range 3D mapping suitable for autonomous vehicles and advanced robotics. Selecting the right technology depends on factors such as detection range, environmental conditions, required accuracy, and budget constraints. Integrating sensors with complementary strengths can optimize performance for complex projects requiring both precise localization and obstacle proximity awareness.
Proximity sensor vs LIDAR Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com