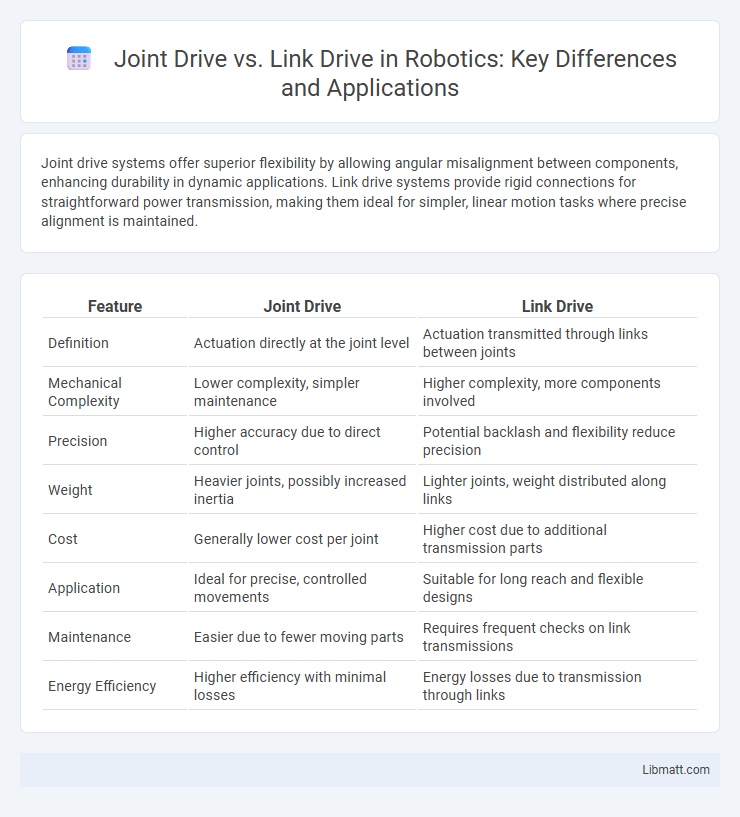
Joint drive systems offer superior flexibility by allowing angular misalignment between components, enhancing durability in dynamic applications. Link drive systems provide rigid connections for straightforward power transmission, making them ideal for simpler, linear motion tasks where precise alignment is maintained.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Joint Drive | Link Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actuation directly at the joint level | Actuation transmitted through links between joints |
| Mechanical Complexity | Lower complexity, simpler maintenance | Higher complexity, more components involved |
| Precision | Higher accuracy due to direct control | Potential backlash and flexibility reduce precision |
| Weight | Heavier joints, possibly increased inertia | Lighter joints, weight distributed along links |
| Cost | Generally lower cost per joint | Higher cost due to additional transmission parts |
| Application | Ideal for precise, controlled movements | Suitable for long reach and flexible designs |
| Maintenance | Easier due to fewer moving parts | Requires frequent checks on link transmissions |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher efficiency with minimal losses | Energy losses due to transmission through links |
Introduction to Joint Drive and Link Drive
Joint Drive systems transmit torque through interlocking components, providing precise movement and high efficiency in mechanical applications. Link Drive utilizes interconnected links to transfer motion and force, allowing flexibility in movement paths and load distribution. Understanding the differences between Joint Drive and Link Drive helps optimize your machinery's performance and durability based on specific operational needs.
Key Differences Between Joint Drive and Link Drive
Joint Drive features interconnected components that transfer power through articulated joints, offering precise movement and flexibility ideal for robotics and automated machinery. Link Drive relies on rigid links connected via pivots, providing straightforward mechanical transmission suited for applications requiring consistent torque and simplicity. Your choice between Joint Drive and Link Drive depends on the specific demands for motion complexity and mechanical robustness in your project.
How Joint Drive Works
Joint Drive operates by integrating multiple motorized joints connected through a series of linkages or gears, allowing coordinated movement across complex machinery platforms. This method enhances precision and power distribution by synchronizing rotational forces at each joint, which is critical for robotics, industrial automation, and prosthetics applications. Your systems benefit from smoother motion and improved load handling due to this interconnected joint mechanism.
How Link Drive Operates
Link Drive operates by mechanically connecting the motor and the driven component through a system of interlocking links, enabling direct power transfer with minimal backlash and increased efficiency. This method ensures precise torque transmission and reduced wear compared to traditional joint drive systems. Your machinery benefits from smoother operation and easier maintenance due to the simplified linkage mechanism inherent in Link Drive designs.
Performance Comparison: Joint Drive vs Link Drive
Joint Drive systems offer higher torque transmission and improved precision for heavy-duty applications, making them ideal for industrial machinery requiring robust performance. Link Drive mechanisms provide smoother operation and reduced backlash, enhancing efficiency in moderate load scenarios with faster response times. Your choice between Joint Drive and Link Drive should consider the balance between load capacity and operational smoothness to optimize system performance.
Advantages of Joint Drive Systems
Joint drive systems offer precise control and enhanced torque transmission, improving overall machinery efficiency and performance. Their modular design allows for easy maintenance and adaptability across various industrial applications. You benefit from reduced wear and increased reliability, leading to lower downtime and operational costs.
Benefits of Link Drive Mechanisms
Link drive mechanisms offer enhanced flexibility and precise motion control compared to joint drive systems, making them ideal for complex robotic applications. They reduce mechanical backlash and improve load distribution, resulting in higher efficiency and durability. These mechanisms also enable more compact designs and smoother transmission of power, optimizing performance in automation and manufacturing processes.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Joint drive systems are widely utilized in robotics, automation, and aerospace for precise rotational motion control, enabling complex joint articulation in robotic arms and aircraft control surfaces. Link drive mechanisms find extensive application in manufacturing and automotive industries, offering linear or oscillating motion transfer in conveyor systems, engine valve trains, and mechanical linkages. Both drives cater to specific motion requirements: joint drives excel in tasks needing rotational accuracy, while link drives are preferred for straightforward linear or pivoting movements in assembly lines and mechanical systems.
Cost Analysis: Joint Drive vs Link Drive
Joint Drive systems typically incur higher initial costs due to complex components and precise alignment requirements, impacting overall budget considerations. Link Drive configurations offer cost-efficient installation and maintenance, leveraging simpler mechanical linkages that reduce both parts and labor expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals Link Drive systems often provide superior economic value for applications demanding reliable performance with minimal upfront investment.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Selecting between a Joint Drive and Link Drive hinges on application requirements such as torque capacity, alignment flexibility, and maintenance preferences. Joint Drives excel in handling misalignment and absorbing shock loads, making them ideal for industrial machinery with variable positions. Link Drives offer simpler installation and cost-effectiveness for straightforward, low-torque applications demanding precision and minimal maintenance.
Joint Drive vs Link Drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com