Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making, which is crucial for robotics operating in dynamic environments. Cloud robotics leverages centralized cloud resources for heavy computation and data storage, enabling robots to access vast information and collaborate over networks, complementing the low-latency benefits of edge computing in your robotics applications.
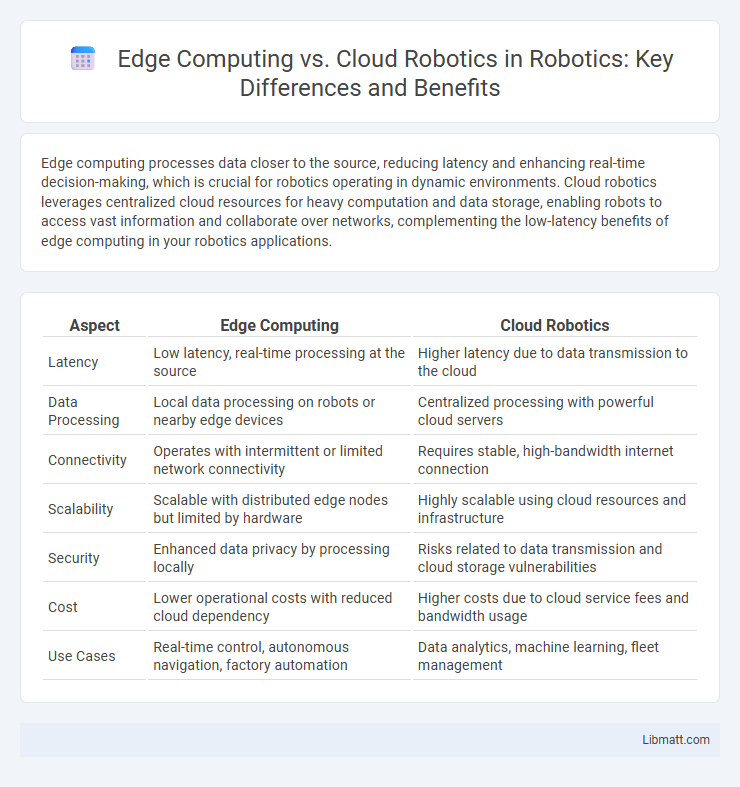
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Edge Computing | Cloud Robotics |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Low latency, real-time processing at the source | Higher latency due to data transmission to the cloud |
| Data Processing | Local data processing on robots or nearby edge devices | Centralized processing with powerful cloud servers |
| Connectivity | Operates with intermittent or limited network connectivity | Requires stable, high-bandwidth internet connection |
| Scalability | Scalable with distributed edge nodes but limited by hardware | Highly scalable using cloud resources and infrastructure |
| Security | Enhanced data privacy by processing locally | Risks related to data transmission and cloud storage vulnerabilities |
| Cost | Lower operational costs with reduced cloud dependency | Higher costs due to cloud service fees and bandwidth usage |
| Use Cases | Real-time control, autonomous navigation, factory automation | Data analytics, machine learning, fleet management |
Introduction to Edge Computing and Cloud Robotics
Edge computing processes data near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth use, essential for real-time robotic applications. Cloud robotics leverages centralized cloud servers to provide robots with extensive computational power and data storage for complex tasks. Your choice between these technologies depends on the need for speed, data processing capacity, and connectivity in robot operations.
Core Concepts: Defining Edge Computing
Edge computing processes data near the source, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making in robotics applications. Cloud robotics relies on centralized servers to handle computation and data storage, often leading to higher communication delay. You benefit from edge computing by enabling robots to perform faster, autonomous tasks with minimal dependency on cloud connectivity.
Core Concepts: Understanding Cloud Robotics
Cloud robotics integrates cloud computing with robotic systems, enabling robots to leverage centralized data storage, powerful processing, and shared knowledge bases over the internet. Edge computing processes data locally on or near the robot, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making by minimizing reliance on remote servers. Your choice between edge and cloud robotics depends on the balance you need between immediate responsiveness and scalability through extensive cloud resources.
Architecture Differences: Edge vs Cloud Approaches
Edge computing architecture processes data locally on devices or nearby edge servers, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by minimizing data transfer to centralized cloud servers. Cloud robotics relies on robust cloud infrastructure to handle heavy computational tasks, data storage, and coordination, enabling robots to access vast resources and shared knowledge remotely. The key architectural difference lies in edge computing's distributed, real-time processing focus versus cloud robotics' centralized, scalable data management and complex algorithm execution.
Latency and Real-Time Processing Comparison
Edge computing offers significantly lower latency than cloud robotics by processing data locally on devices or nearby edge servers, minimizing the delay caused by data transmission to distant cloud centers. Real-time processing in edge computing enables immediate response crucial for time-sensitive robotic applications such as autonomous navigation and collision avoidance. Your robotic systems benefit from enhanced responsiveness and reduced network dependency when utilizing edge computing over traditional cloud robotics for latency-sensitive tasks.
Scalability and Resource Allocation
Edge computing enables localized processing, reducing latency and optimizing resource allocation by handling data near the source, which enhances scalability for real-time robotic applications. Cloud robotics leverages vast centralized computational power and storage, offering virtually unlimited scalability but can face challenges with latency and bandwidth constraints. Your choice between the two depends on balancing immediate processing needs with the ability to scale resources dynamically across distributed or centralized systems.
Security and Privacy Implications
Edge computing enhances security and privacy in robotics by processing sensitive data locally on devices, reducing exposure to external cyber threats and minimizing data transmission risks inherent in cloud-based systems. Cloud robotics, while offering scalability and centralized updates, introduces vulnerabilities through reliance on distant servers that can be targeted for data breaches or unauthorized access. Implementing robust encryption and access controls is critical in both paradigms to safeguard robotic operations and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Application Scenarios: Best Use Cases
Edge computing excels in real-time, latency-sensitive applications such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and smart surveillance, where immediate data processing near the source is critical. Cloud robotics is ideal for complex tasks requiring extensive data analysis, machine learning, and collaboration across multiple robots, such as remote surgery, fleet management, and large-scale agricultural monitoring. Hybrid approaches leverage edge computing for fast response and cloud robotics for computational power and centralized data storage, optimizing performance in smart manufacturing and connected logistics.
Challenges and Limitations
Edge computing faces challenges such as limited processing power, storage capacity, and energy constraints compared to centralized cloud systems. Cloud robotics depends heavily on unreliable network connectivity and latency issues, which can hinder real-time decision-making and responsiveness in robotic applications. Balancing these limitations is crucial to optimize your system's performance while ensuring scalability and low-latency operation.
Future Trends and Industry Outlook
Edge computing enhances cloud robotics by enabling real-time data processing closer to sensors and robots, reducing latency and improving autonomy. Future trends indicate widespread adoption of hybrid architectures combining edge and cloud capabilities to optimize performance, scalability, and security in industrial automation and smart manufacturing. Your investment in these technologies will drive more efficient robotic workflows and responsive control systems in next-generation robotic applications.
Edge computing vs Cloud robotics Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com