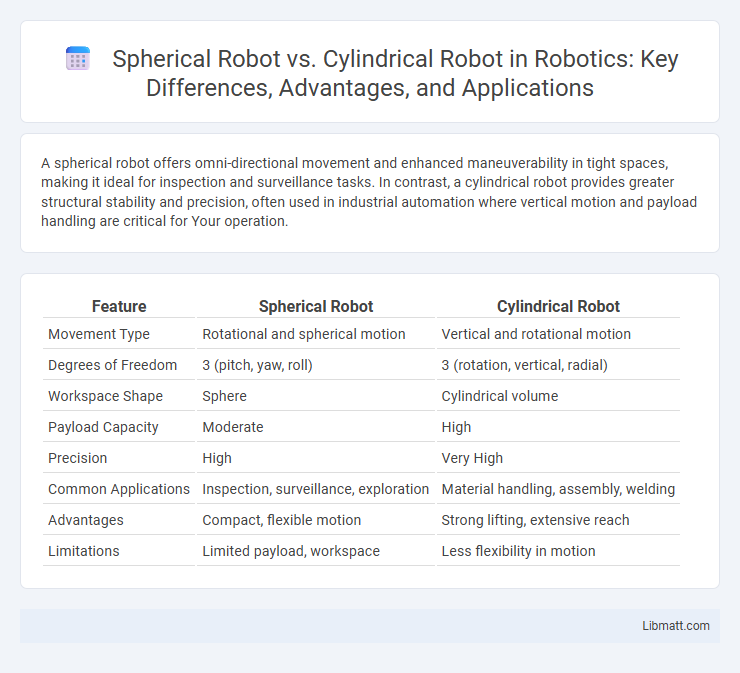
A spherical robot offers omni-directional movement and enhanced maneuverability in tight spaces, making it ideal for inspection and surveillance tasks. In contrast, a cylindrical robot provides greater structural stability and precision, often used in industrial automation where vertical motion and payload handling are critical for Your operation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spherical Robot | Cylindrical Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Movement Type | Rotational and spherical motion | Vertical and rotational motion |
| Degrees of Freedom | 3 (pitch, yaw, roll) | 3 (rotation, vertical, radial) |
| Workspace Shape | Sphere | Cylindrical volume |
| Payload Capacity | Moderate | High |
| Precision | High | Very High |
| Common Applications | Inspection, surveillance, exploration | Material handling, assembly, welding |
| Advantages | Compact, flexible motion | Strong lifting, extensive reach |
| Limitations | Limited payload, workspace | Less flexibility in motion |
Introduction to Spherical and Cylindrical Robots
Spherical robots feature a round, ball-like structure that allows for rotational and translational movement within a spherical coordinate system, optimizing flexibility and reach in confined spaces. Cylindrical robots operate with a jointed arm moving within a cylindrical coordinate system, enabling precise vertical and radial motions ideal for assembly and material handling tasks. Both robot types offer distinct kinematic advantages tailored to specific industrial applications, with spherical robots excelling in compact maneuverability and cylindrical robots providing stable, linear reach.
Structural Design Comparison
Spherical robots feature a compact, ball-shaped structure that enables omnidirectional movement and enhances maneuverability in confined spaces. Cylindrical robots, characterized by a vertical column and a rotating arm, offer precise vertical and radial motion suited for tasks requiring stability and controlled reach. Your choice depends on whether flexibility and multi-directional navigation or stability and linear motion are prioritized in the robotic application.
Degrees of Freedom: Movement Capabilities
Spherical robots typically have three degrees of freedom, allowing rotational movement around multiple axes, which enables them to maneuver in confined spaces with high precision. Cylindrical robots possess two to three degrees of freedom, mainly allowing vertical and rotational movements around a fixed base, making them ideal for tasks such as assembly and packaging. The enhanced rotational capabilities of spherical robots provide superior flexibility for complex tasks, while cylindrical robots offer stability and straightforward reach within a cylindrical work envelope.
Work Envelope and Reach Analysis
Spherical robots offer a compact work envelope characterized by a rotational base and an arm that operates within a spherical sector, providing excellent reach in all directions within that hemisphere, ideal for tasks requiring multidirectional access. Cylindrical robots generate a work envelope shaped like a cylindrical volume, combining rotational base movement with linear vertical and radial arm motions, allowing for efficient reach along linear and vertical planes but limited reach at extreme horizontal angles. Analysis shows spherical robots maximize volumetric reach in a confined space, while cylindrical robots excel in applications requiring consistent vertical reach and workspace height adaptability.
Precision and Accuracy Differences
Spherical robots excel in precision due to their ability to achieve multi-axis movement with fewer mechanical components, resulting in smoother and more consistent motion paths. Cylindrical robots offer higher positional accuracy in linear tasks, as their design allows for straightforward control along vertical and rotational axes. The choice between spherical and cylindrical robots depends on the application's need for rotational flexibility versus linear positional accuracy.
Typical Applications and Industries
Spherical robots excel in applications requiring agile, omnidirectional movement such as surveillance, exploration, and entertainment industries, thanks to their compact and versatile design. Cylindrical robots are commonly used in manufacturing and assembly lines, especially in automotive and electronics sectors, due to their precise vertical and rotational movements. Your choice depends on whether you need flexible navigation or specialized, repetitive tasks in heavy industries.
Ease of Programming and Integration
Spherical robots feature simplified kinematics that streamline programming through fewer degrees of freedom, allowing for more intuitive control algorithms compared to cylindrical robots. Cylindrical robots often require complex inverse kinematics calculations due to their linear and rotational joint configurations, increasing programming complexity and integration time. Integration of spherical robots tends to be more straightforward in compact workspaces, while cylindrical robots offer better adaptability in applications demanding precise linear motion but may require advanced software customization.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Spherical robots generally incur higher initial costs due to complex design and advanced sensors, while cylindrical robots offer more affordable pricing with simpler mechanical structures. Maintenance for spherical robots can be more challenging and costly because of intricate moving parts and calibration requirements. Cylindrical robots benefit from easier access to components and lower upkeep expenses, making them suitable for budget-conscious industrial applications.
Pros and Cons of Each Robot Type
Spherical robots offer enhanced maneuverability and omnidirectional movement due to their round shape, making them ideal for navigating complex environments, but they often face challenges with stability and precise control. Cylindrical robots provide greater rigidity and strength, enabling them to handle heavier payloads with accurate vertical and rotational movements, yet their limited degrees of freedom restrict flexibility compared to spherical robots. Understanding the trade-offs between your application's need for agility versus load capacity will help determine the most suitable robot type.
Future Trends in Spherical and Cylindrical Robotics
Spherical robots are advancing with enhanced mobility and agility, driven by developments in omnidirectional wheel technology and compact sensor integration, enabling applications in complex terrains and dynamic environments. Cylindrical robots continue to evolve with improvements in precision and payload capacity, benefiting industries such as manufacturing and healthcare through modular design and AI-driven control systems. Emerging trends include the convergence of AI and IoT in both robot types, promoting smarter, more autonomous operation and real-time adaptive responses across diverse sectors.
Spherical robot vs Cylindrical robot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com