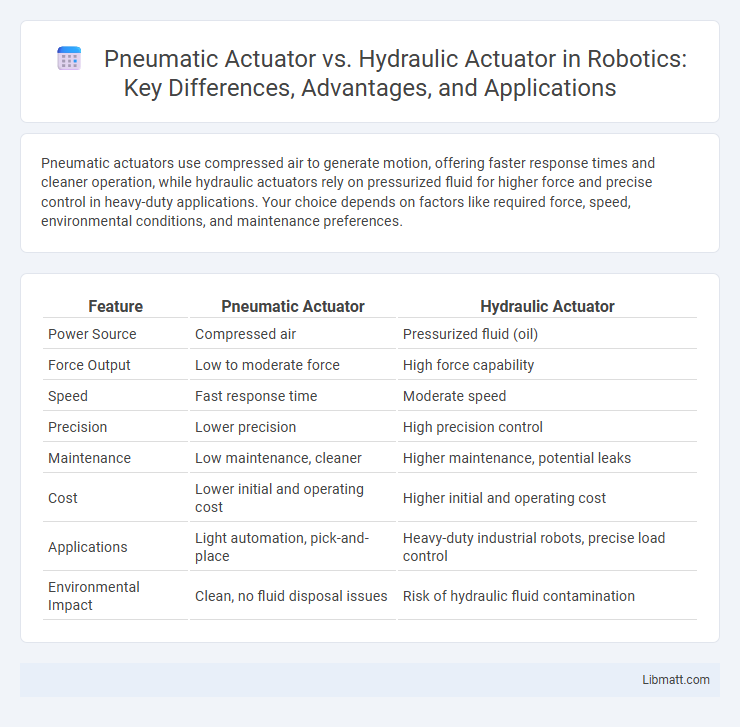
Pneumatic actuators use compressed air to generate motion, offering faster response times and cleaner operation, while hydraulic actuators rely on pressurized fluid for higher force and precise control in heavy-duty applications. Your choice depends on factors like required force, speed, environmental conditions, and maintenance preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pneumatic Actuator | Hydraulic Actuator |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Compressed air | Pressurized fluid (oil) |
| Force Output | Low to moderate force | High force capability |
| Speed | Fast response time | Moderate speed |
| Precision | Lower precision | High precision control |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, cleaner | Higher maintenance, potential leaks |
| Cost | Lower initial and operating cost | Higher initial and operating cost |
| Applications | Light automation, pick-and-place | Heavy-duty industrial robots, precise load control |
| Environmental Impact | Clean, no fluid disposal issues | Risk of hydraulic fluid contamination |
Introduction to Pneumatic and Hydraulic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators utilize compressed air to generate mechanical motion, offering rapid response times and clean operation, making them ideal for lightweight and high-speed applications. Hydraulic actuators rely on pressurized fluid to produce high force and precise control, suitable for heavy-duty industrial machinery requiring substantial power. Both actuator types convert energy into mechanical motion but differ significantly in power density, control accuracy, and maintenance demands.
Working Principles of Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators operate by converting compressed air into mechanical motion, using the pressure difference between air chambers to create linear or rotary movement. These actuators typically consist of a piston or diaphragm sealed within a cylinder, where compressed air enters one side, pushing the piston to generate force. The simplicity, quick response time, and clean operation make pneumatic actuators ideal for applications requiring fast, repetitive motion with moderate force.
Operating Mechanism of Hydraulic Actuators
Hydraulic actuators operate by converting fluid pressure into mechanical force through the movement of pistons within a cylinder, utilizing incompressible hydraulic fluid to generate precise and powerful motion. The actuator's performance depends on the hydraulic pump, valves, and fluid dynamics, allowing for high force output and smooth control in heavy-duty industrial applications. Compared to pneumatic actuators, hydraulic systems provide superior force density and consistent power, especially in environments requiring robust and precise actuation under significant load conditions.
Key Differences Between Pneumatic and Hydraulic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators use compressed air to generate motion, offering faster response times and cleaner operation, while hydraulic actuators rely on pressurized fluid for higher force output and precision control. Pneumatic systems are ideal for lightweight, low-force applications and environments requiring minimal contamination, whereas hydraulic systems excel in heavy-duty, high-load scenarios demanding robust power and durability. Maintenance and operational costs differ as pneumatic actuators tend to have lower complexity and cost, but hydraulic actuators provide superior torque and are better suited for applications involving significant mechanical stress.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Force, and Precision
Pneumatic actuators deliver rapid response and high-speed operation ideal for applications requiring quick cycling, while hydraulic actuators excel in generating significantly higher force and handling heavy loads with precision. Your choice depends on the required balance between speed and power: pneumatic systems provide lightweight, energy-efficient motion with moderate force, whereas hydraulic systems offer superior force control and precision in slower, heavy-duty tasks. Precision in hydraulic actuators generally surpasses pneumatic ones due to their ability to maintain consistent pressure and smooth movement under varying loads.
Applications of Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators are widely used in automation systems for packaging, material handling, and assembly operations due to their fast response times and clean operation. Industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and automotive manufacturing rely on pneumatic actuators for repetitive motion tasks requiring reliability and low maintenance. Their suitability for environments requiring explosion-proof or sterile conditions makes them ideal for use in chemical plants and medical equipment.
Applications of Hydraulic Actuators
Hydraulic actuators are widely used in heavy machinery such as construction equipment, industrial presses, and aircraft control systems due to their high force output and precise control capabilities. Their ability to handle large loads and provide smooth, consistent movement makes them ideal for applications requiring strong, reliable actuation in harsh environments. Industries like automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and marine engineering frequently rely on hydraulic actuators to perform critical functions that demand durability and robustness.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators offer advantages such as fast response times, high speed operation, and simplicity in design, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid movement and frequent cycling. They also provide cleaner and safer operation compared to hydraulic actuators due to the use of compressed air, reducing risks of fluid leaks and contamination. However, pneumatic actuators generally produce lower force output and less precise control than hydraulic systems, which may limit their use in high-load or highly accurate positioning tasks.
Pros and Cons of Hydraulic Actuators
Hydraulic actuators offer high power density and precise control, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring substantial force. They are highly reliable in harsh environments due to their robust construction and ability to operate under extreme temperatures and pressures. However, hydraulic systems can suffer from fluid leaks, maintenance complexity, and potential environmental concerns due to hydraulic fluid handling.
Selecting the Right Actuator: Factors to Consider
When selecting the right actuator, consider factors such as operating environment, force requirements, and response speed. Pneumatic actuators are ideal for clean, fast, and lightweight applications with moderate force, while hydraulic actuators excel in high-force, heavy-load environments requiring precise control. Your choice should align with system efficiency, maintenance capabilities, and safety standards to ensure optimal performance.
Pneumatic Actuator vs Hydraulic Actuator Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com