Fixed automation offers high-volume, repetitive production with minimal variability, making it ideal for manufacturing standardized products efficiently. Flexible automation allows Your systems to adapt quickly to changes in product design or volume, providing versatility for diverse production needs without extensive reconfiguration.
Table of Comparison
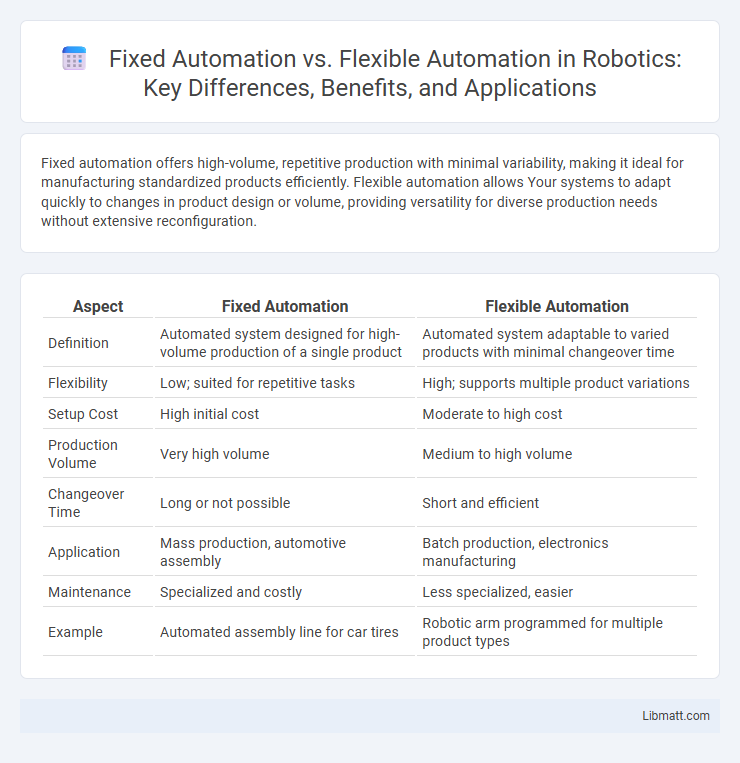
| Aspect | Fixed Automation | Flexible Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated system designed for high-volume production of a single product | Automated system adaptable to varied products with minimal changeover time |
| Flexibility | Low; suited for repetitive tasks | High; supports multiple product variations |
| Setup Cost | High initial cost | Moderate to high cost |
| Production Volume | Very high volume | Medium to high volume |
| Changeover Time | Long or not possible | Short and efficient |
| Application | Mass production, automotive assembly | Batch production, electronics manufacturing |
| Maintenance | Specialized and costly | Less specialized, easier |
| Example | Automated assembly line for car tires | Robotic arm programmed for multiple product types |
Introduction to Automation in Manufacturing
Fixed automation utilizes specialized equipment designed for high-volume production of a limited variety of products, offering high efficiency and low unit cost. Flexible automation employs programmable machines and robotic systems capable of handling multiple product types and design changes, enhancing adaptability and reducing downtime. Manufacturing automation advances productivity by integrating these systems to balance efficiency and flexibility according to production requirements.
Defining Fixed Automation
Fixed automation refers to a manufacturing process designed for high-volume production with a fixed sequence of operations controlled by specialized equipment. It features dedicated machinery and tooling tailored to produce a single product or limited range of parts, ensuring consistent output and minimal variability. This type of automation excels in efficiency and speed but lacks adaptability to product changes, making it ideal for long production runs of standardized items.
Understanding Flexible Automation
Flexible automation allows production systems to adapt quickly to changes in product design or volume without extensive reconfiguration, enhancing efficiency in customizable manufacturing. Unlike fixed automation, which is designed for high-volume, repetitive tasks with minimal variation, flexible automation integrates programmable machinery and robotics to accommodate diverse product variants. Your manufacturing process benefits from reduced downtime and improved responsiveness by implementing flexible automation techniques.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Flexible Automation
Fixed automation involves specialized equipment designed for high-volume production of a single product, offering high efficiency but low adaptability. Flexible automation uses programmable machines capable of producing multiple products with minimal changeover time, providing versatility and responsiveness to market changes. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right automation type based on production volume, product variety, and cost considerations.
Advantages of Fixed Automation
Fixed automation offers high production rates by utilizing specialized machines designed for specific tasks, ensuring consistent quality and reduced cycle time. It significantly lowers unit costs in large-scale manufacturing due to minimized labor involvement and streamlined processes. This type of automation excels in industries requiring mass production with minimal variation, such as automotive and electronics assembly.
Advantages of Flexible Automation
Flexible automation offers significant advantages, including the ability to quickly adapt to different products or changes in design without extensive retooling, which reduces downtime and increases productivity. It enables customization and small batch production while maintaining high efficiency, making it ideal for businesses facing dynamic market demands. Your manufacturing process benefits from scalability and cost-effectiveness, enhancing competitiveness in industries requiring frequent updates.
Limitations of Fixed Automation
Fixed automation offers high production speed but is limited by its inability to easily adapt to changes in product design or production volume. Its specialized machinery is costly to modify, resulting in inflexibility and significant downtime when switching tasks. Your manufacturing process may face challenges in meeting diverse or evolving market demands due to these constraints.
Limitations of Flexible Automation
Flexible automation faces limitations such as higher initial investment costs and increased system complexity compared to fixed automation. It may experience reduced throughput and efficiency when handling high-volume production runs due to its adaptability requirements. Maintenance and programming demands are also more intensive, potentially leading to greater downtime and operational challenges.
Choosing the Right Automation for Your Business
Choosing the right automation for your business depends on production volume, product variety, and cost efficiency. Fixed automation suits high-volume, low-variety manufacturing with repetitive tasks, delivering consistent quality and lower unit costs. Flexible automation adapts to changing product designs and smaller batches, offering scalability and reduced downtime for businesses needing versatility.
Future Trends in Industrial Automation
Future trends in industrial automation highlight a shift towards flexible automation systems that integrate advanced robotics, AI-driven adaptive controls, and IoT connectivity, enabling real-time customization and scalability in manufacturing processes. Fixed automation remains valuable for high-volume, repetitive tasks due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness but faces limitations in adaptability and rapid reconfiguration. The convergence of Industry 4.0 technologies fosters hybrid automation solutions, combining the precision of fixed systems with the versatility of flexible automation to meet evolving market demands and enhance operational agility.
Fixed Automation vs Flexible Automation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com