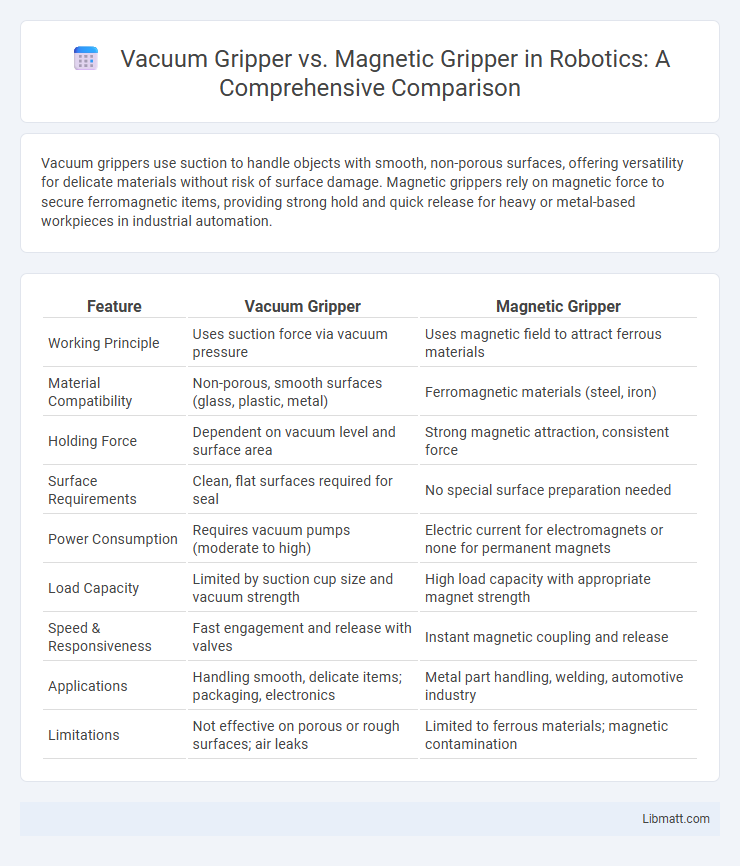
Vacuum grippers use suction to handle objects with smooth, non-porous surfaces, offering versatility for delicate materials without risk of surface damage. Magnetic grippers rely on magnetic force to secure ferromagnetic items, providing strong hold and quick release for heavy or metal-based workpieces in industrial automation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Gripper | Magnetic Gripper |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Uses suction force via vacuum pressure | Uses magnetic field to attract ferrous materials |
| Material Compatibility | Non-porous, smooth surfaces (glass, plastic, metal) | Ferromagnetic materials (steel, iron) |
| Holding Force | Dependent on vacuum level and surface area | Strong magnetic attraction, consistent force |
| Surface Requirements | Clean, flat surfaces required for seal | No special surface preparation needed |
| Power Consumption | Requires vacuum pumps (moderate to high) | Electric current for electromagnets or none for permanent magnets |
| Load Capacity | Limited by suction cup size and vacuum strength | High load capacity with appropriate magnet strength |
| Speed & Responsiveness | Fast engagement and release with valves | Instant magnetic coupling and release |
| Applications | Handling smooth, delicate items; packaging, electronics | Metal part handling, welding, automotive industry |
| Limitations | Not effective on porous or rough surfaces; air leaks | Limited to ferrous materials; magnetic contamination |
Introduction to Industrial Grippers
Industrial grippers, essential for automated material handling, come in various types including vacuum grippers and magnetic grippers, each suited for specific applications. Vacuum grippers use suction to lift and transport objects, ideal for smooth, non-porous surfaces, while magnetic grippers rely on magnetic force to handle ferrous materials securely. Understanding your product's surface and weight can help determine whether a vacuum or magnetic gripper will optimize efficiency and reliability in your industrial automation processes.
How Vacuum Grippers Work
Vacuum grippers operate by creating a pressure differential between the vacuum cup and the object surface, using a vacuum pump or venturi system to evacuate air and generate suction. This suction force securely holds objects made of various materials, especially non-porous surfaces like glass, metal, or plastic. Their adaptability to irregular shapes and delicate handling makes vacuum grippers ideal for automation in industries such as packaging, electronics, and automotive manufacturing.
How Magnetic Grippers Work
Magnetic grippers operate using magnetic fields generated by permanent magnets or electromagnets to securely hold ferromagnetic materials during handling or robotic automation. The magnetic force attracts and clamps the metal object without requiring physical contact or pressure, making them ideal for lifting and positioning heavy steel parts. These grippers excel in applications where non-contact gripping reduces wear and contamination, providing reliable, efficient, and energy-saving material handling solutions.
Key Differences Between Vacuum and Magnetic Grippers
Vacuum grippers rely on suction force created by a vacuum pump to hold objects, making them ideal for handling smooth, non-porous surfaces like glass or plastic sheets. Magnetic grippers use magnetic fields to lift ferromagnetic materials efficiently, providing strong grip without requiring surface contact. Your choice between vacuum and magnetic grippers depends on the material properties and application requirements, such as the need for grip strength or surface compatibility.
Advantages of Vacuum Grippers
Vacuum grippers offer exceptional adaptability for handling delicate or irregularly shaped objects without causing surface damage, making them ideal for industries like electronics and food packaging. Their ability to create a strong suction force enables secure lifting of non-metallic and porous materials, which magnetic grippers cannot manage effectively. You benefit from lower energy consumption and quieter operation, enhancing efficiency in automated systems where precision and gentle handling are crucial.
Advantages of Magnetic Grippers
Magnetic grippers offer a strong, reliable hold on ferrous materials without requiring surface contact, enabling precise and damage-free handling. They consume less energy compared to vacuum grippers, especially in permanent magnet designs, which maintain grip without continuous power. Magnetic grippers also perform well in dusty or oily environments where vacuum grippers may lose suction efficiency.
Limitations of Vacuum Grippers
Vacuum grippers have limitations when handling porous or irregularly shaped materials because they require a smooth, non-porous surface to create an effective seal. They also struggle with heavy objects due to reduced suction power and are less effective in dusty or oily environments, which can compromise the vacuum system's reliability. Your choice of gripper should consider these factors to ensure optimal performance in your specific application.
Limitations of Magnetic Grippers
Magnetic grippers are limited by their inability to handle non-ferrous materials such as aluminum, plastic, or glass, restricting their use to ferromagnetic objects only. Their gripping force can also be affected by surface conditions like rust, dirt, or paint, which reduce magnetic attraction and compromise stability. Unlike vacuum grippers, magnetic grippers are less effective for delicate or unevenly shaped items, limiting their versatility in diverse industrial applications.
Application Scenarios: Choosing the Right Gripper
Vacuum grippers excel in handling smooth, non-porous surfaces such as glass, plastics, and sheet metal, making them ideal for packaging, electronics, and automotive industries. Magnetic grippers are better suited for ferrous metals and rough surfaces, commonly used in steel manufacturing, material handling, and heavy engineering sectors. Selecting the right gripper depends on factors like material type, surface texture, payload weight, and precision requirements.
Future Trends in Gripping Technology
Future trends in gripping technology emphasize enhanced adaptability and efficiency, with vacuum grippers evolving to incorporate smart sensors for precise control and energy optimization. Magnetic grippers are advancing through the use of lightweight, high-strength rare-earth magnets and programmable magnetic fields to handle diverse materials without physical contact. Integration of AI and IoT in both vacuum and magnetic grippers is driving predictive maintenance and real-time process adjustments, significantly improving automation in manufacturing.
Vacuum Gripper vs Magnetic Gripper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com