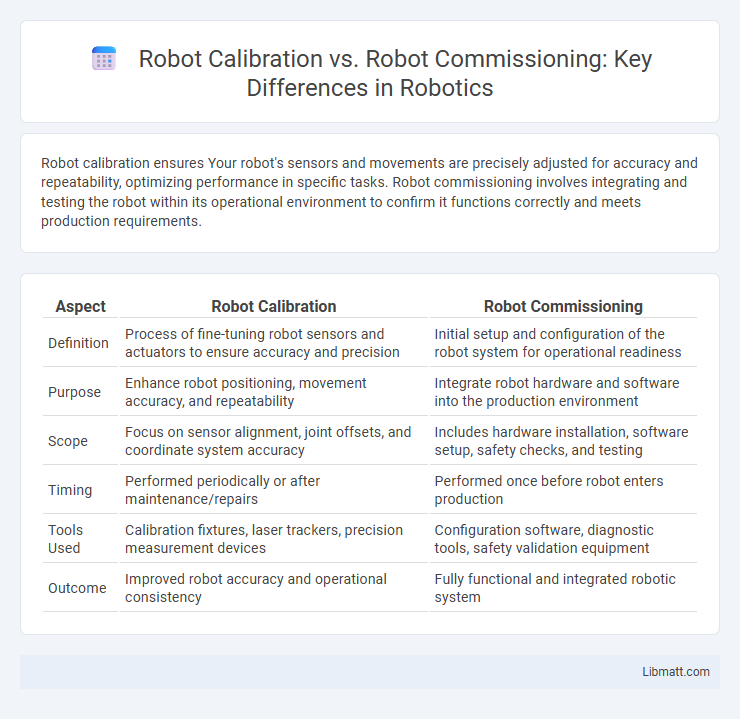
Robot calibration ensures Your robot's sensors and movements are precisely adjusted for accuracy and repeatability, optimizing performance in specific tasks. Robot commissioning involves integrating and testing the robot within its operational environment to confirm it functions correctly and meets production requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Robot Calibration | Robot Commissioning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of fine-tuning robot sensors and actuators to ensure accuracy and precision | Initial setup and configuration of the robot system for operational readiness |
| Purpose | Enhance robot positioning, movement accuracy, and repeatability | Integrate robot hardware and software into the production environment |
| Scope | Focus on sensor alignment, joint offsets, and coordinate system accuracy | Includes hardware installation, software setup, safety checks, and testing |
| Timing | Performed periodically or after maintenance/repairs | Performed once before robot enters production |
| Tools Used | Calibration fixtures, laser trackers, precision measurement devices | Configuration software, diagnostic tools, safety validation equipment |
| Outcome | Improved robot accuracy and operational consistency | Fully functional and integrated robotic system |
Introduction to Robot Calibration and Commissioning
Robot calibration ensures precise alignment of a robotic arm's sensors and joints, enhancing accuracy and repeatability during tasks. Commissioning involves the comprehensive setup and testing of the robot system, including software configuration and safety validation, to prepare it for production. Your robotic system's efficiency and performance depend heavily on thorough calibration followed by meticulous commissioning.
Defining Robot Calibration
Robot calibration involves precisely measuring and adjusting a robot's parameters to enhance accuracy and repeatability in its movements and tasks. This process ensures that the robot's control system aligns with its physical configuration, correcting any discrepancies caused by mechanical wear or assembly tolerances. Effective calibration significantly improves robot performance in applications such as manufacturing, automation, and quality control.
Defining Robot Commissioning
Robot commissioning involves the systematic process of integrating a new robot into an existing automation system by configuring its software, verifying hardware functionality, and performing initial testing to ensure operational readiness. This phase follows robot calibration, which focuses on adjusting the robot's parameters for precise movement and accuracy. Proper robot commissioning ensures that your robotic system operates efficiently, safely, and according to the intended performance specifications.
Key Differences Between Calibration and Commissioning
Robot calibration fine-tunes a robot's sensors and actuators to ensure precise measurements and accurate movements, improving overall performance and reliability. Robot commissioning involves the initial setup, testing, and verification of the robot system to confirm it operates correctly within its intended environment. Understanding these key differences helps you streamline the integration and maintenance processes, enhancing your robotic system's efficiency.
Importance of Robot Calibration in Automation
Robot calibration ensures precise alignment of sensors and actuators, directly impacting the accuracy and repeatability of automated tasks. It reduces errors, minimizes downtime, and enhances the overall efficiency of your robotic systems. Proper calibration is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and extending the lifespan of automation equipment.
Role of Robot Commissioning in System Integration
Robot commissioning plays a crucial role in system integration by ensuring that all robotic components and subsystems function seamlessly within the broader automation environment. It involves configuring, testing, and validating the robot's performance alongside sensors, conveyors, and control systems to achieve optimal operational efficiency. Effective commissioning minimizes downtime and facilitates smoother communication between the robot and other integrated manufacturing systems.
Step-by-Step Robot Calibration Process
Robot calibration involves precise measurement and adjustment of a robot's joint angles and spatial positioning to enhance accuracy and repeatability. The step-by-step robot calibration process typically starts with collecting kinematic data using specialized sensors, followed by analyzing deviations from expected positions, adjusting joint parameters, and verifying improvements through repeated testing. Your successful calibration ensures optimal robot performance, setting it apart from robot commissioning, which encompasses the broader task of installing, testing, and integrating the robot system into production workflows.
Step-by-Step Robot Commissioning Procedure
Robot commissioning involves a step-by-step procedure that ensures your robot operates accurately and reliably within its intended environment. This process typically includes mechanical setup, electrical connections, software installation, calibration, testing, and validation of all robot functions. Proper commissioning guarantees optimized performance, safety compliance, and seamless integration with existing systems, distinguishing it from the broader calibration phase focused solely on sensor and motion accuracy.
Common Challenges in Calibration and Commissioning
Common challenges in robot calibration include achieving precise sensor alignment and compensating for mechanical tolerances that affect accuracy. During robot commissioning, integrating diverse subsystems and validating control parameters often present significant obstacles. Both processes require meticulous testing to ensure optimal performance and minimize operational errors.
Best Practices for Effective Robot Deployment
Robot calibration ensures precise alignment and accurate sensor feedback, directly impacting your robot's performance and task reliability. Robot commissioning involves integrating hardware, software, and control systems to validate operational readiness and safety protocols. Implementing best practices such as thorough sensor calibration, real-time system diagnostics, and iterative testing guarantees effective robot deployment and maximized productivity.
Robot Calibration vs Robot Commissioning Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com