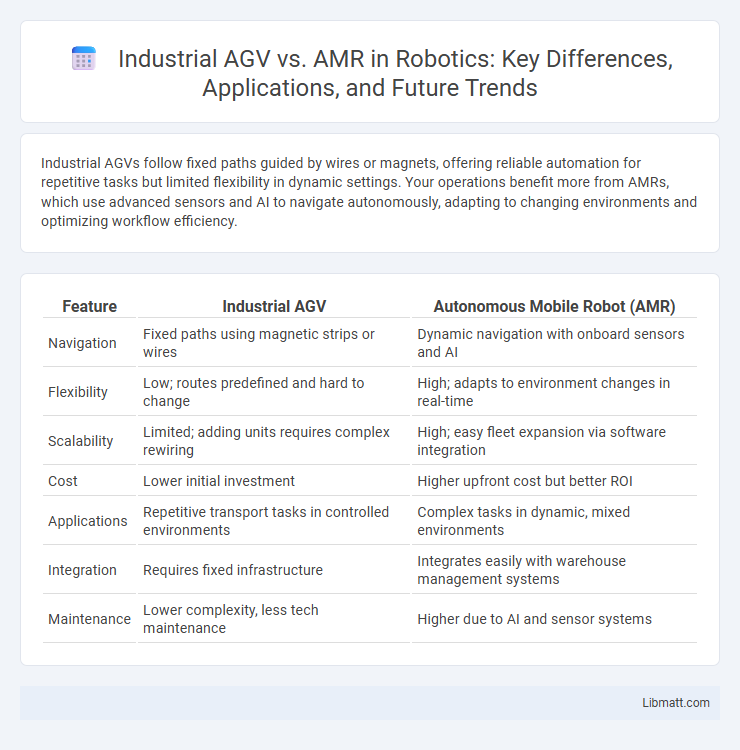
Industrial AGVs follow fixed paths guided by wires or magnets, offering reliable automation for repetitive tasks but limited flexibility in dynamic settings. Your operations benefit more from AMRs, which use advanced sensors and AI to navigate autonomously, adapting to changing environments and optimizing workflow efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Industrial AGV | Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) |
|---|---|---|
| Navigation | Fixed paths using magnetic strips or wires | Dynamic navigation with onboard sensors and AI |
| Flexibility | Low; routes predefined and hard to change | High; adapts to environment changes in real-time |
| Scalability | Limited; adding units requires complex rewiring | High; easy fleet expansion via software integration |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher upfront cost but better ROI |
| Applications | Repetitive transport tasks in controlled environments | Complex tasks in dynamic, mixed environments |
| Integration | Requires fixed infrastructure | Integrates easily with warehouse management systems |
| Maintenance | Lower complexity, less tech maintenance | Higher due to AI and sensor systems |
Introduction to Industrial AGV and AMR
Industrial Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are pre-programmed machines designed to follow fixed routes using sensors and markers for material transport in warehouses and factories. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) navigate dynamically using advanced sensors, cameras, and AI algorithms to adapt to changing environments without the need for physical guides. Both AGVs and AMRs optimize intralogistics by automating repetitive tasks, but AMRs offer enhanced flexibility and scalability in complex industrial settings.
Key Differences Between AGV and AMR
Industrial Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) follow fixed paths using sensors or magnetic tape, while Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) utilize advanced navigation systems and AI to dynamically map and navigate complex environments. AGVs excel in repetitive, structured tasks with defined routes, whereas AMRs offer greater flexibility and adaptability for varied, changing workflows. Your choice depends on the need for either consistent path automation or intelligent, real-time route optimization.
Technology Overview: AGV vs AMR
Industrial Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) operate using fixed paths and magnetic or optical sensors to follow predetermined routes, ensuring efficient material transport in controlled environments. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) utilize advanced sensors, machine learning, and real-time mapping to navigate dynamic spaces with adaptive decision-making capabilities. The key technological difference lies in AGVs' reliance on external guidance systems versus AMRs' integrated onboard intelligence for flexible, autonomous navigation.
Navigation and Guidance Systems
Industrial AGVs primarily use fixed-path navigation systems such as magnetic tape, wires, or reflectors embedded in the floor, which limit their flexibility but provide consistent guidance along predefined routes. AMRs employ advanced navigation and guidance technologies including LiDAR, computer vision, and simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), enabling dynamic path planning and obstacle avoidance in complex, changing environments. This technological difference results in AMRs offering greater operational adaptability and reduced infrastructure modification costs compared to traditional AGVs.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Operations
Industrial AGVs follow fixed paths guided by magnetic strips or wires, offering limited flexibility and requiring manual reprogramming for layout changes. In contrast, AMRs use advanced sensors and AI to navigate dynamically around obstacles, adapting in real-time to evolving warehouse environments. Your operations benefit from greater adaptability with AMRs, enabling seamless adjustments to workflow without costly downtime.
Safety Features and Risk Management
Industrial AGVs are equipped with fixed safety features such as emergency stop buttons, laser scanners, and bumpers to prevent collisions in predefined routes. AMRs utilize advanced AI-driven sensors, real-time environment mapping, and dynamic obstacle avoidance to enhance safety and adapt to changing conditions on the factory floor. Risk management in AMRs emphasizes continuous learning and predictive analytics to minimize accidents, while Industrial AGVs rely more on structured environments and manual configuration for hazard prevention.
Implementation and Integration in Industry
Industrial AGVs require fixed infrastructure such as magnetic strips or QR codes for navigation, making their implementation in manufacturing environments more rigid but reliable for repetitive tasks. AMRs utilize advanced sensors, cameras, and AI-driven software to dynamically map and navigate complex industrial layouts, enabling easier integration with existing systems and greater adaptability to changing production workflows. Both systems can be integrated with warehouse management and enterprise resource planning software, but AMRs offer higher scalability and flexibility, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency during fleet expansion or layout modifications.
Cost Analysis: AGV vs AMR
Industrial AGVs typically have lower upfront costs but incur higher long-term expenses due to fixed pathways and limited scalability. AMRs involve higher initial investment but offer cost savings over time through flexible navigation, reduced infrastructure requirements, and improved productivity. Your choice should weigh immediate budget constraints against potential operational efficiencies and future adaptability.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Industrial AGVs are commonly deployed in manufacturing plants and warehouses for repetitive material transport tasks, such as moving pallets and raw materials across fixed routes. AMRs offer greater flexibility and adaptability, making them ideal for dynamic environments like e-commerce fulfillment centers and pharmaceutical facilities where they navigate complex layouts and collaborate with human workers. Your choice depends on whether you need a robust solution for predictable workflows or an intelligent system that supports real-time route adjustments and scalable automation.
Future Trends in Automated Material Handling
Industrial AGVs and AMRs are evolving with advancements in AI, IoT integration, and adaptable navigation systems, enhancing precision and operational efficiency in automated material handling. Future trends emphasize scalable fleet management, real-time data analytics, and improved human-robot collaboration to optimize supply chain workflows. These innovations aim to reduce downtime, increase flexibility in dynamic environments, and support smart factory initiatives.
Industrial AGV vs AMR Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com