LiDAR sensors provide precise distance measurements using laser light, making them ideal for high-resolution mapping and object detection in autonomous vehicles and robotics. Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to measure proximity, offering cost-effective solutions for short-range obstacle avoidance but with lower accuracy and resolution compared to LiDAR.
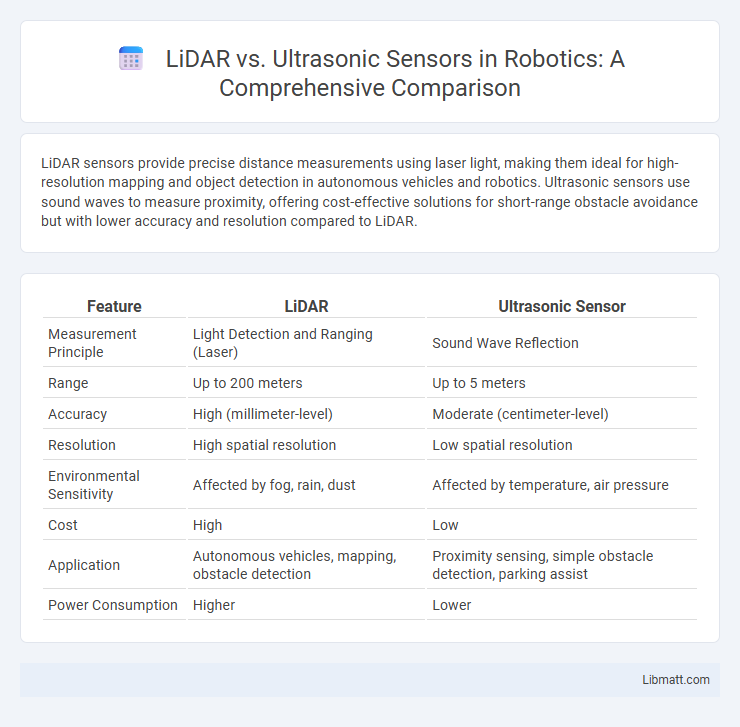
Table of Comparison
| Feature | LiDAR | Ultrasonic Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Light Detection and Ranging (Laser) | Sound Wave Reflection |
| Range | Up to 200 meters | Up to 5 meters |
| Accuracy | High (millimeter-level) | Moderate (centimeter-level) |
| Resolution | High spatial resolution | Low spatial resolution |
| Environmental Sensitivity | Affected by fog, rain, dust | Affected by temperature, air pressure |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Application | Autonomous vehicles, mapping, obstacle detection | Proximity sensing, simple obstacle detection, parking assist |
| Power Consumption | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to LiDAR and Ultrasonic Sensors
LiDAR sensors use laser light to measure distances by calculating the time it takes for the emitted light to reflect off objects and return, providing high-resolution 3D maps, while ultrasonic sensors emit sound waves to detect nearby objects by measuring the echo time, excelling in short-range obstacle detection. LiDAR offers superior accuracy and detail for applications like autonomous vehicles and mapping, whereas ultrasonic sensors are cost-effective solutions ideal for parking assistance and simple proximity sensing. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the right sensor technology based on your project's range, accuracy, and environmental requirements.
Working Principles: LiDAR vs Ultrasonic Sensors
LiDAR operates by emitting laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for the light to reflect back from objects, enabling precise distance calculation and detailed 3D mapping. Ultrasonic sensors use high-frequency sound waves, transmitting pulses that bounce off surfaces, with distance determined by the echo return time. While LiDAR excels in long-range accuracy and fine resolution, ultrasonic sensors are cost-effective for short-range object detection in various applications like robotics and automotive parking assistance.
Key Differences Between LiDAR and Ultrasonic Sensors
LiDAR sensors use laser light to measure distance with high precision and long range capabilities, making them ideal for detailed mapping and autonomous navigation. Ultrasonic sensors emit sound waves to detect objects, offering cost-effective, close-range measurements but with lower accuracy and resolution compared to LiDAR. Your choice depends on the application's need for accuracy, range, and environmental conditions.
Accuracy and Resolution Comparison
LiDAR sensors provide significantly higher accuracy and resolution compared to ultrasonic sensors, with centimeter-level precision enabling detailed 3D mapping and object detection. Ultrasonic sensors typically offer lower resolution and accuracy, often limited to a few centimeters, making them suitable for basic proximity detection rather than precise measurements. The advanced optical technology in LiDAR allows for finer spatial discrimination, critical in applications like autonomous vehicles and robotics.
Range and Sensing Capabilities
LiDAR sensors typically offer a longer range, often exceeding 100 meters, with high-resolution 3D mapping capabilities, making them ideal for detailed environmental scanning. Ultrasonic sensors operate effectively at shorter distances, usually up to 5 meters, and are primarily used for detecting object proximity with lower spatial resolution. Your choice between LiDAR and ultrasonic sensors should consider the necessity for precise range detection and the complexity of the sensing environment.
Applications of LiDAR Sensors
LiDAR sensors are widely used in autonomous vehicles for precise mapping and obstacle detection, enabling safer navigation. In agriculture, LiDAR technology assists in crop monitoring and terrain modeling, enhancing yield management. Your robotics projects can benefit from LiDAR sensors' high-resolution 3D scanning capabilities for accurate environment perception and object recognition.
Applications of Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors are widely used in applications such as obstacle detection in automotive parking systems, liquid level measurement in tanks, and proximity sensing in robotics. These sensors emit high-frequency sound waves to detect object distance and are favored in environments where LiDAR may be less effective due to environmental conditions like fog or dust. Your choice of sensor depends on factors like range, resolution, and operational environment, with ultrasonic sensors offering cost-effective solutions for short-range detection tasks.
Advantages and Limitations of LiDAR
LiDAR offers high-resolution 3D mapping and accurate distance measurements with a longer sensor range compared to ultrasonic sensors, making it ideal for autonomous vehicles and advanced robotics. However, LiDAR systems are generally more expensive and sensitive to weather conditions such as heavy rain or fog, which can degrade their performance. Ultrasonic sensors, while cost-effective and reliable in close-range detection, lack the precision and range capabilities of LiDAR technology.
Advantages and Limitations of Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors provide reliable distance measurement by emitting high-frequency sound waves, excelling in detecting solid objects and performing well in conditions with low visibility such as dust or darkness. Their cost-effectiveness and wide beam angle make them suitable for short-range applications, including obstacle detection and parking assistance in automotive systems. Limitations include reduced accuracy over longer distances, susceptibility to interference from soft or angled surfaces, and lower resolution compared to LiDAR technology.
Which Sensor is Better: LiDAR or Ultrasonic?
LiDAR sensors provide higher accuracy and longer detection ranges compared to ultrasonic sensors, making them ideal for applications requiring precise distance measurements and detailed mapping. Ultrasonic sensors are cost-effective and perform well in short-range obstacle detection, especially in automotive parking systems and simple object avoidance tasks. If your project demands advanced spatial resolution and longer-distance sensing, LiDAR is the better choice, whereas ultrasonic sensors suit budget-conscious or close-range applications.
LiDAR vs Ultrasonic Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com