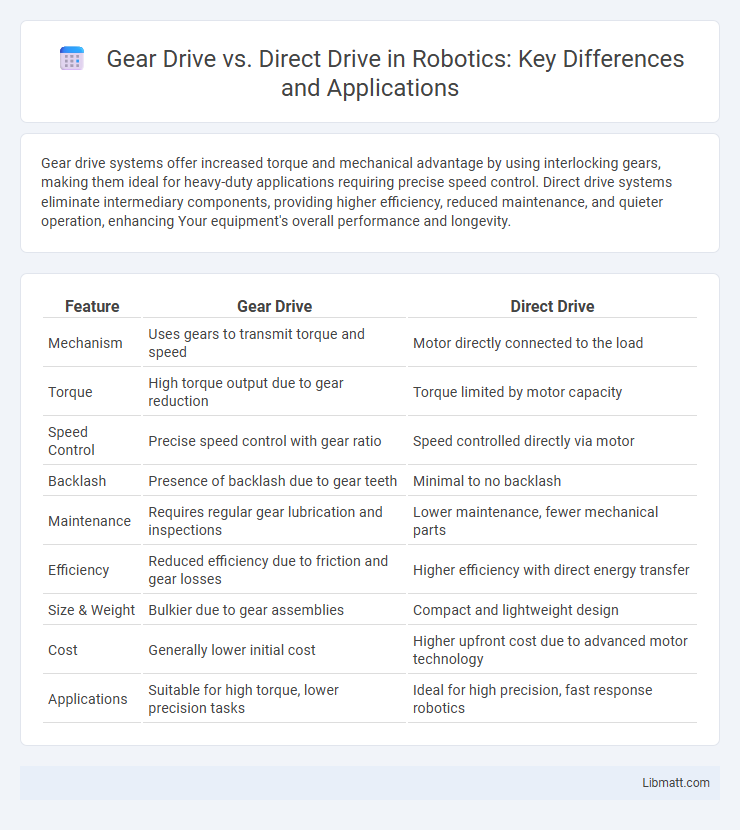
Gear drive systems offer increased torque and mechanical advantage by using interlocking gears, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring precise speed control. Direct drive systems eliminate intermediary components, providing higher efficiency, reduced maintenance, and quieter operation, enhancing Your equipment's overall performance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gear Drive | Direct Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Uses gears to transmit torque and speed | Motor directly connected to the load |
| Torque | High torque output due to gear reduction | Torque limited by motor capacity |
| Speed Control | Precise speed control with gear ratio | Speed controlled directly via motor |
| Backlash | Presence of backlash due to gear teeth | Minimal to no backlash |
| Maintenance | Requires regular gear lubrication and inspections | Lower maintenance, fewer mechanical parts |
| Efficiency | Reduced efficiency due to friction and gear losses | Higher efficiency with direct energy transfer |
| Size & Weight | Bulkier due to gear assemblies | Compact and lightweight design |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost due to advanced motor technology |
| Applications | Suitable for high torque, lower precision tasks | Ideal for high precision, fast response robotics |
Introduction to Gear Drive and Direct Drive
Gear drive systems use interconnected gears to transmit power efficiently through mechanical advantage, offering precise control and high torque at various speeds. Direct drive eliminates intermediary components by connecting the motor shaft directly to the load, resulting in reduced maintenance and increased energy efficiency. Your choice between gear drive and direct drive depends on factors such as torque requirements, speed control, and system complexity.
How Gear Drive Systems Work
Gear drive systems operate by transferring torque and rotational speed through a series of interlocking gears, which modify the output speed and force compared to the input. The meshing gears convert rotational motion efficiently, allowing for precise control of mechanical advantage and torque multiplication. This mechanism reduces the motor's workload by distributing force across the gear train, enhancing durability and performance in applications requiring high torque at varying speeds.
Understanding Direct Drive Mechanisms
Direct drive mechanisms eliminate intermediary components by connecting the motor shaft directly to the load, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced mechanical losses. This design minimizes vibrations and noise, enhancing precision and durability in applications like turntables, electric vehicles, and industrial machinery. High torque at low speeds and simplified maintenance are additional advantages distinguishing direct drive systems from traditional gear drive configurations.
Key Differences Between Gear and Direct Drive
Gear drive systems utilize interlocking gears to transfer torque and adjust speed, offering high torque multiplication and precise control, whereas direct drive systems connect the motor directly to the load, minimizing mechanical losses and reducing maintenance. Gear drives are typically bulkier with more moving parts, leading to increased wear and noise, while direct drives boast higher efficiency, quieter operation, and longer lifespan due to fewer components. The choice between gear and direct drive hinges on application requirements such as torque demand, speed control, maintenance preferences, and space constraints.
Performance Comparison: Torque, Speed, and Efficiency
Gear drive systems deliver higher torque at lower speeds due to mechanical advantage from gear ratios but experience increased friction losses that reduce overall efficiency. Direct drive motors offer faster response speeds with minimal mechanical loss, resulting in higher efficiency and smoother operation, especially beneficial in applications requiring precise control. Torque output in direct drives is often lower at startup compared to gear drives, but the reduced complexity enhances reliability and low-maintenance performance.
Maintenance and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Gear drive systems typically require more frequent maintenance due to moving parts subject to wear, including gears and chains that need lubrication and occasional replacement. Direct drive systems have fewer mechanical components, translating to lower maintenance needs and generally longer operational lifespan. Your choice should consider the balance between maintenance effort and durability, with direct drive favoring longevity.
Noise Levels and Vibration: User Experience
Gear drive systems typically produce higher noise levels and more vibration due to the mechanical contact between gears, impacting user comfort during operation. Direct drive systems offer quieter performance with significantly reduced vibration, enhancing the overall user experience by providing smoother and more silent functionality. This reduction in noise and vibration in direct drive devices is particularly preferred in environments where minimal disturbance is crucial.
Applications and Industry Preferences
Gear drives dominate heavy machinery and automotive applications due to their torque multiplication and precise speed control, making them ideal for industries like manufacturing, mining, and agriculture. Direct drives are preferred in robotics, precision machining, and renewable energy sectors, where efficiency, low maintenance, and smooth operation are critical. Your choice between gear drive and direct drive should align with the specific performance and reliability requirements of your industrial application.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-term Value
Gear drive systems generally require a lower initial investment compared to direct drive systems, making them more accessible for projects with budget constraints. However, direct drive systems offer higher long-term value due to reduced maintenance costs, improved energy efficiency, and longer operational lifespan. Your choice should balance upfront costs against ongoing savings and performance benefits to maximize return on investment.
Choosing the Right Drive System for Your Needs
Selecting the right drive system depends on your specific requirements for efficiency, maintenance, and torque delivery. Gear drives offer high torque and durability suited for heavy-duty applications, while direct drives provide quieter operation and lower maintenance with fewer components. Your choice should balance performance demands and long-term operational costs to optimize system reliability.
Gear Drive vs Direct Drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com