Teleoperation allows you to remotely control machines in real-time, providing direct human input for complex or sensitive tasks. Autonomy enables systems to perform actions independently using AI and sensors, improving efficiency and scalability in repetitive or hazardous environments.
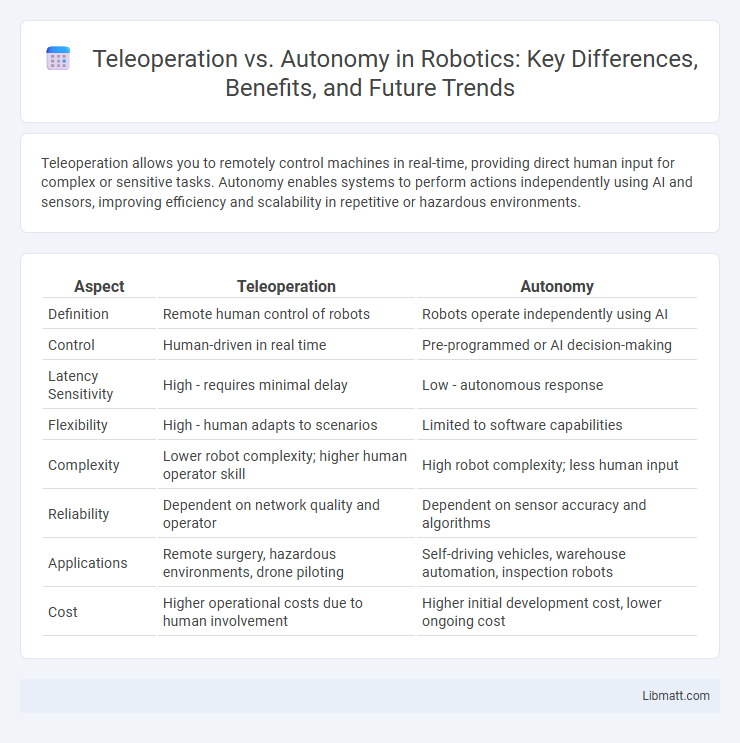
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Teleoperation | Autonomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Remote human control of robots | Robots operate independently using AI |
| Control | Human-driven in real time | Pre-programmed or AI decision-making |
| Latency Sensitivity | High - requires minimal delay | Low - autonomous response |
| Flexibility | High - human adapts to scenarios | Limited to software capabilities |
| Complexity | Lower robot complexity; higher human operator skill | High robot complexity; less human input |
| Reliability | Dependent on network quality and operator | Dependent on sensor accuracy and algorithms |
| Applications | Remote surgery, hazardous environments, drone piloting | Self-driving vehicles, warehouse automation, inspection robots |
| Cost | Higher operational costs due to human involvement | Higher initial development cost, lower ongoing cost |
Introduction to Teleoperation and Autonomous Systems
Teleoperation involves remotely controlling machines or robots via human input, enabling real-time decision-making and precise manipulation in hazardous or inaccessible environments. Autonomous systems operate independently using sensors, algorithms, and artificial intelligence to perform tasks without human intervention, enhancing efficiency and scalability in complex scenarios. Both approaches integrate advanced technologies but differ fundamentally in control dynamics and operational autonomy.
Key Differences Between Teleoperation and Autonomy
Teleoperation involves remote human control of machines, requiring continuous input from an operator, while autonomy enables systems to perform tasks independently using sensors and algorithms. Teleoperation is ideal for complex or unpredictable environments where human judgment is crucial, whereas autonomy excels in repetitive, well-defined tasks with minimal supervision. Understanding these differences helps you select the right approach for efficiency and safety in robotics and automated systems.
Advantages of Teleoperation
Teleoperation offers precise human control over machines, enabling complex tasks in unpredictable environments where full autonomy may fail. It enhances safety by allowing operators to manage hazardous operations remotely, reducing risk to human life. Your ability to intervene directly ensures real-time problem-solving and adaptability beyond the limitations of current autonomous technologies.
Benefits of Autonomous Systems
Autonomous systems enhance operational efficiency by reducing human error and enabling continuous, real-time decision-making through advanced sensors and AI algorithms. These systems improve safety in hazardous environments by minimizing the need for direct human intervention, while also lowering operational costs with optimized resource utilization. Enhanced scalability and adaptability allow autonomous technologies to perform complex tasks across diverse industries, including manufacturing, transportation, and robotics.
Technical Challenges and Limitations
Teleoperation faces technical challenges such as latency, limited bandwidth, and reliance on stable communication links, which can hinder real-time control and responsiveness in remote environments. Autonomy struggles with limitations in sensor accuracy, complex decision-making algorithms, and adapting to unpredictable scenarios, often requiring extensive machine learning and environmental modeling. Your choice between teleoperation and autonomy must consider these factors to optimize performance and reliability in specific use cases.
Applications in Robotics and Industry
Teleoperation enables precise human control over robots in hazardous or complex industrial environments, such as underwater exploration and remote surgical procedures, where direct human presence is impractical. Autonomous robots excel in repetitive manufacturing tasks, warehouse logistics, and agricultural operations by leveraging AI and machine learning for real-time decision-making and efficiency improvements. Your choice between teleoperation and autonomy depends on the level of human intervention required, operational complexity, and the specific industry application.
Human-in-the-Loop vs Fully Automated Approaches
Teleoperation involves a human-in-the-loop system where operators remotely control machines to ensure real-time decision-making and adaptability in complex environments. Fully automated approaches rely on advanced algorithms and AI to execute tasks without human intervention, offering higher efficiency and scalability. Your choice between teleoperation and autonomy depends on the balance between control precision needed and the desired level of automation in your application.
Safety, Reliability, and Risk Mitigation
Teleoperation enables human oversight, enhancing safety by allowing real-time intervention in hazardous environments, reducing the likelihood of accidents. Autonomous systems offer consistent reliability through advanced algorithms and sensors, minimizing human error but requiring robust fail-safes to address unexpected scenarios. Combining teleoperation with autonomy creates a hybrid approach that mitigates risks by leveraging human judgment alongside automated precision.
Future Trends in Teleoperation and Autonomy
Future trends in teleoperation emphasize enhanced human-machine interfaces, leveraging AI and machine learning to improve real-time decision-making and reduce operator fatigue. Autonomy advancements focus on self-learning algorithms, sensor fusion, and edge computing to enable fully independent operations across industries such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, and drones. Integration of teleoperation with autonomous systems is expected to create hybrid models, offering flexible control options and improving safety in complex environments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Specific Use Cases
Teleoperation excels in complex, unpredictable environments where human judgment is critical, such as remote medical surgeries or hazardous industrial inspections. Autonomy offers scalable efficiency and consistency for repetitive tasks like warehouse sorting and autonomous driving under well-mapped conditions. Selecting the right approach depends on balancing factors like environment complexity, required decision-making speed, and safety considerations to optimize performance and reliability.
Teleoperation vs Autonomy Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com