Passive sensors detect natural energy or signals emitted by objects without emitting any energy themselves, making them ideal for applications like thermal imaging and remote sensing. Active sensors emit their own energy, such as radar or sonar waves, and measure the reflected signals to determine distance or other characteristics, providing accurate data in various environmental conditions.
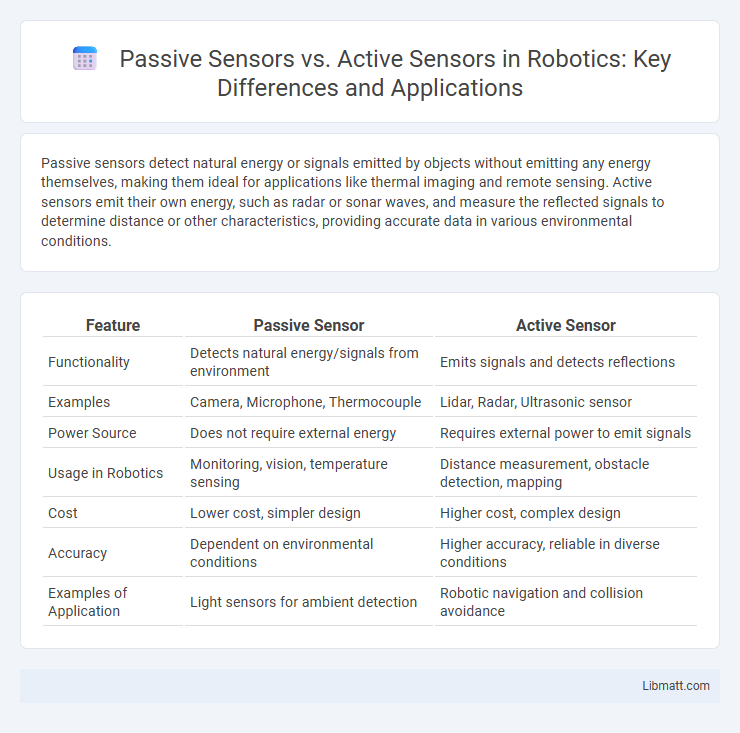
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Passive Sensor | Active Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Detects natural energy/signals from environment | Emits signals and detects reflections |
| Examples | Camera, Microphone, Thermocouple | Lidar, Radar, Ultrasonic sensor |
| Power Source | Does not require external energy | Requires external power to emit signals |
| Usage in Robotics | Monitoring, vision, temperature sensing | Distance measurement, obstacle detection, mapping |
| Cost | Lower cost, simpler design | Higher cost, complex design |
| Accuracy | Dependent on environmental conditions | Higher accuracy, reliable in diverse conditions |
| Examples of Application | Light sensors for ambient detection | Robotic navigation and collision avoidance |
Introduction to Passive and Active Sensors
Passive sensors detect energy naturally emitted or reflected by objects, such as infrared radiation or visible light, without emitting any signals themselves. Active sensors, in contrast, emit their own energy, like radar or lidar waves, and measure the reflection or return signal to gather information about the environment. Understanding the differences between passive and active sensors helps you choose the right technology for applications in remote sensing, surveillance, and environmental monitoring.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Sensors
Passive sensors detect natural energy emitted or reflected by objects, while active sensors emit their own signal and measure the response. Key differences include energy source dependence, with passive sensors relying on external sources like sunlight, and active sensors generating signals such as radar or laser pulses. Your choice between passive and active sensors depends on application needs like energy availability, detection range, and environmental conditions.
How Passive Sensors Work
Passive sensors detect natural energy radiated or reflected from objects, such as thermal infrared radiation or visible light, without emitting any signals themselves. These sensors rely on external energy sources like the sun or the temperature differences emitted by objects to gather information. Their ability to operate silently and without interfering signals makes them ideal for applications like remote sensing, environmental monitoring, and surveillance.
How Active Sensors Operate
Active sensors operate by emitting their own energy, such as radio waves or laser pulses, to illuminate a target and then measure the reflected signals to gather data. These sensors are commonly used in radar, LiDAR, and sonar systems to provide precise distance, speed, and positional information regardless of ambient light conditions. Their ability to actively generate signals allows for continuous monitoring and high-resolution imaging in various applications including weather tracking, autonomous vehicles, and environmental mapping.
Advantages of Passive Sensors
Passive sensors offer distinct advantages such as lower power consumption and reduced operational costs since they do not emit any signals, relying instead on detecting naturally occurring energy like thermal radiation or reflected sunlight. These sensors provide stealthy monitoring capabilities, making them ideal for applications requiring minimal disturbance or detection risk. Your choice of passive sensors ensures enhanced longevity and maintenance simplicity, especially in remote or hazardous environments.
Benefits of Active Sensors
Active sensors emit their own energy signals, enabling precise data collection regardless of ambient lighting or weather conditions. These sensors enhance object detection accuracy and range by directly interacting with the environment, making them ideal for applications such as radar, LiDAR, and sonar systems. The ability to operate independently of external energy sources ensures reliable performance in diverse scenarios, including night-time surveillance and remote sensing.
Common Applications of Passive Sensors
Passive sensors are widely used in applications such as thermal imaging, environmental monitoring, and remote sensing, where detection of naturally emitted or reflected energy is crucial. These sensors excel in observing temperature variations, light intensity, and atmospheric phenomena without emitting signals, making them ideal for surveillance, weather forecasting, and astronomy. Their non-intrusive nature allows for continuous data collection in both terrestrial and space environments.
Typical Uses of Active Sensors
Active sensors are commonly used in applications requiring precise distance measurements and mapping, such as LiDAR systems for autonomous vehicles and drones. They play a critical role in remote sensing for environmental monitoring, including radar-based weather prediction and terrain analysis. Industrial automation also relies on active sensors for object detection and quality control in manufacturing processes.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Needs
Passive sensors detect natural energy emitted or reflected by objects, making them ideal for applications requiring low power consumption and minimal interference. Active sensors emit their own energy signal and measure the reflection, providing precise distance or speed data even in low-light or obstructed conditions. Understanding your environment and measurement requirements helps you choose the right sensor, ensuring optimal performance and accuracy for your specific application.
Future Trends in Sensor Technology
Future trends in sensor technology highlight the growing integration of passive sensors, which harvest ambient energy to operate without power sources, making them ideal for sustainable IoT applications. Active sensors continue to advance with enhanced sensitivity and extended range through AI-driven signal processing and miniaturization for smart devices. Your choice between passive and active sensors will depend on specific needs such as energy efficiency, data accuracy, and environmental conditions in emerging smart infrastructure.
Passive Sensor vs Active Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com