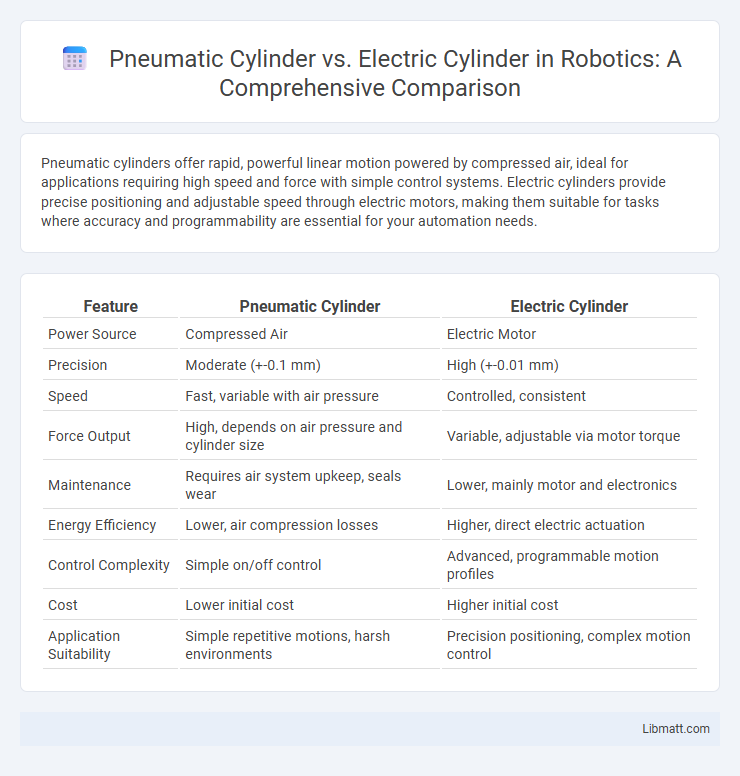
Pneumatic cylinders offer rapid, powerful linear motion powered by compressed air, ideal for applications requiring high speed and force with simple control systems. Electric cylinders provide precise positioning and adjustable speed through electric motors, making them suitable for tasks where accuracy and programmability are essential for your automation needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pneumatic Cylinder | Electric Cylinder |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Compressed Air | Electric Motor |
| Precision | Moderate (+-0.1 mm) | High (+-0.01 mm) |
| Speed | Fast, variable with air pressure | Controlled, consistent |
| Force Output | High, depends on air pressure and cylinder size | Variable, adjustable via motor torque |
| Maintenance | Requires air system upkeep, seals wear | Lower, mainly motor and electronics |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower, air compression losses | Higher, direct electric actuation |
| Control Complexity | Simple on/off control | Advanced, programmable motion profiles |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Application Suitability | Simple repetitive motions, harsh environments | Precision positioning, complex motion control |
Introduction to Pneumatic and Electric Cylinders
Pneumatic cylinders use compressed air to generate linear motion and force, making them ideal for fast, repetitive tasks in industrial automation. Electric cylinders utilize electric motors to provide precise control over position, speed, and force, offering enhanced accuracy and energy efficiency. Both types serve critical functions in manufacturing, with pneumatic cylinders favored for simplicity and electric cylinders preferred for applications requiring fine control.
Key Components and Working Principles
Pneumatic cylinders consist of a cylinder barrel, piston, piston rod, and end caps, using compressed air to generate linear motion through pressure differences inside the chamber. Electric cylinders incorporate a motor, lead screw or ball screw, and guide rails, converting rotary motion from the motor into precise linear movement controlled electronically. Understanding your application's load, speed, and control requirements helps determine whether the air-driven simplicity of pneumatic cylinders or the precise, programmable operation of electric cylinders is more suitable.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Force, and Precision
Pneumatic cylinders excel in delivering high-speed actuation with moderate force, relying on compressed air for rapid movement, while electric cylinders provide superior precision and controllable force, ideal for applications requiring exact positioning. Electric cylinders offer consistent force output throughout the stroke and better repeatability, whereas pneumatic cylinders may experience variability due to air compressibility. For operations demanding precise speed control and accurate positioning, electric cylinders outperform pneumatic systems, but pneumatic cylinders remain advantageous in cost-effective, high-speed, and high-force scenarios.
Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
Electric cylinders deliver higher energy efficiency by converting nearly all electrical power directly into mechanical motion, reducing waste and lowering operating costs over time. Pneumatic cylinders rely on compressed air, which involves significant energy loss during air compression and leakage, resulting in higher operating expenses. Maintenance costs for pneumatic systems also tend to be greater due to air leaks and component wear, while electric cylinders offer more precise control and reduced long-term expenses.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Pneumatic cylinders require compressed air systems and regular checks for air leaks, lubrication, and seal integrity, demanding routine maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Electric cylinders involve complex electrical wiring and control systems but generally offer simpler installation with fewer mechanical parts, leading to lower maintenance frequency. Proper installation of pneumatic cylinders often involves air supply alignment and pressure regulation, whereas electric cylinders require precise calibration of motor and feedback components for efficient operation.
Application Suitability Across Industries
Pneumatic cylinders excel in industries requiring high-speed, repetitive motion such as packaging, automotive assembly, and food processing due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Electric cylinders offer precise control and customizable force, making them ideal for applications in electronics manufacturing, medical devices, and semiconductor equipment. Your choice between pneumatic and electric cylinders should consider the specific requirements of speed, precision, and load capacity within your industry.
Control and Automation Capabilities
Pneumatic cylinders offer simple and rapid actuation with limited control precision, ideal for applications requiring fast, repetitive motion but less complex automation. Electric cylinders provide advanced control and automation capabilities through precise positioning, variable speed control, and programmable motion profiles, making them suitable for integrated systems requiring higher accuracy. The choice depends on the specific needs of automation complexity, speed, and precision in industrial applications.
Safety Considerations and Reliability
Pneumatic cylinders offer inherent safety advantages due to their simple design and use of compressed air, which reduces the risk of electrical hazards and overheating, making them highly reliable in hazardous environments. Electric cylinders provide precise control and repeatability but require careful integration of electrical safety features to prevent failures and ensure consistent performance. Reliability in pneumatic systems depends on air quality and maintenance, while electric cylinders benefit from advanced diagnostics and fewer mechanical parts prone to wear.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pneumatic cylinders rely on compressed air often generated by energy-intensive compressors, leading to higher carbon emissions and less energy efficiency compared to electric cylinders. Electric cylinders provide precise control and consume less energy, significantly reducing environmental footprint and promoting sustainable industrial automation. Material longevity and noise pollution are lower in electric cylinders, supporting eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Choosing the Right Cylinder for Your Application
Choosing the right cylinder for your application depends on factors like precision, speed, load capacity, and operating environment; pneumatic cylinders excel in high-speed, lightweight tasks with simple control systems, while electric cylinders offer superior precision, programmable control, and efficiency for complex or heavy-duty operations. Pneumatic cylinders are cost-effective and suitable for environments requiring clean, explosion-proof solutions, whereas electric cylinders provide better energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs, especially in applications demanding variable force and position control. Evaluating operational requirements and total cost of ownership ensures optimal cylinder selection to enhance performance and reliability in industrial automation.
Pneumatic Cylinder vs Electric Cylinder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com