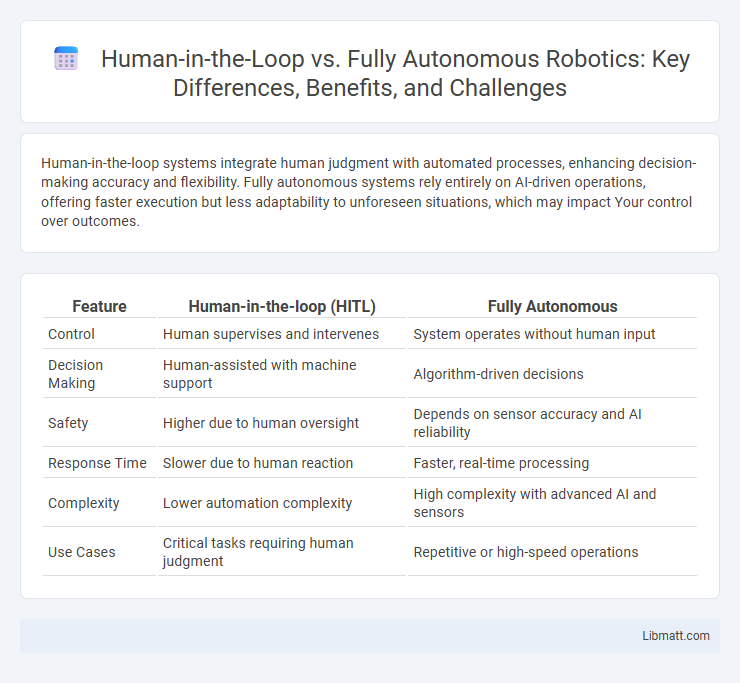
Human-in-the-loop systems integrate human judgment with automated processes, enhancing decision-making accuracy and flexibility. Fully autonomous systems rely entirely on AI-driven operations, offering faster execution but less adaptability to unforeseen situations, which may impact Your control over outcomes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Human-in-the-loop (HITL) | Fully Autonomous |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Human supervises and intervenes | System operates without human input |
| Decision Making | Human-assisted with machine support | Algorithm-driven decisions |
| Safety | Higher due to human oversight | Depends on sensor accuracy and AI reliability |
| Response Time | Slower due to human reaction | Faster, real-time processing |
| Complexity | Lower automation complexity | High complexity with advanced AI and sensors |
| Use Cases | Critical tasks requiring human judgment | Repetitive or high-speed operations |
Introduction to Human-in-the-Loop and Fully Autonomous Systems
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) systems integrate human judgment and decision-making within automated processes, enhancing accuracy and reliability by allowing human intervention in critical tasks. Fully Autonomous Systems operate independently without human input, relying entirely on AI, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data for decision-making and execution. The balance between HITL and fully autonomous approaches depends on application complexity, safety requirements, and the need for human oversight in dynamic environments.
Defining Key Concepts: Human-in-the-Loop vs Fully Autonomous
Human-in-the-loop systems integrate human intervention at critical decision points, enhancing reliability through continuous human oversight and real-time interaction. Fully autonomous systems operate independently, relying on advanced algorithms and sensor data to perform tasks without human input. The distinction lies in the level of human involvement, where human-in-the-loop emphasizes collaboration and control, while fully autonomous prioritizes self-sufficiency and automation.
Core Technologies Powering Each Approach
Human-in-the-loop systems rely heavily on interactive machine learning models and real-time data feedback loops to incorporate human judgment into automated processes, leveraging technologies like computer vision and natural language processing to assist decision-making. Fully autonomous systems depend on advanced deep learning, reinforcement learning algorithms, and sensor fusion from IoT devices to enable independent operation without human intervention. Both approaches utilize cloud computing and edge AI but differ fundamentally in their dependency on human input and adaptation capabilities.
Decision-Making Processes: Human Insight vs Algorithmic Control
Human-in-the-loop systems leverage human insight to interpret complex or ambiguous data, enhancing decision-making processes with contextual understanding and ethical judgment. Fully autonomous systems rely on algorithmic control, using predefined rules and machine learning to make rapid, data-driven decisions without human intervention. The integration of human experience ensures adaptability and nuance, while algorithmic control emphasizes consistency, speed, and scalability in decision outcomes.
Benefits of Human-in-the-Loop Systems
Human-in-the-loop systems enhance decision accuracy by integrating human judgment with automated processes, reducing errors in complex or ambiguous scenarios. These systems provide greater adaptability and ethical oversight, ensuring that critical decisions align with human values and contextual nuances. By involving Your expertise, human-in-the-loop systems improve system reliability, safety, and trustworthiness compared to fully autonomous models.
Advantages of Fully Autonomous Solutions
Fully autonomous solutions offer continuous operation without human intervention, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs significantly. These systems leverage advanced AI and machine learning algorithms to perform complex tasks with high accuracy, minimizing errors and enhancing consistency. You benefit from faster decision-making processes and scalable deployment, especially in environments where real-time responses are critical.
Limitations and Risks of Both Approaches
Human-in-the-loop systems face limitations such as slower decision-making and potential human errors, especially under high-pressure scenarios, which can impact efficiency and safety. Fully autonomous systems carry risks including unexpected behavior due to algorithmic biases, lack of contextual understanding, and vulnerabilities to cybersecurity attacks, posing significant challenges for reliability. When choosing between these approaches, your priorities must balance the trade-off between human judgment and the speed of automated processes to mitigate risks effectively.
Ideal Use Cases for Each System
Human-in-the-loop systems are ideal for high-stakes environments requiring nuanced judgment, such as medical diagnostics, military operations, and complex customer service, where human insight mitigates risks of automation errors. Fully autonomous systems excel in repetitive, high-volume tasks like manufacturing assembly lines, autonomous vehicles in controlled environments, and large-scale data processing, where efficiency and speed are paramount. Selecting between the two depends on balancing the need for human intuition against the advantages of scalability and consistency in automation.
Ethical and Accountability Considerations
Human-in-the-loop systems ensure ethical oversight by incorporating human judgment in critical decision-making processes, reducing biases and errors inherent in fully autonomous models. Fully autonomous systems raise significant ethical concerns due to lack of transparency and accountability, making it challenging to assign responsibility for erroneous or harmful outcomes. Implementing human oversight in automated workflows enhances accountability frameworks and aligns AI operations with regulatory standards and societal values.
Future Trends: Synergies and Evolution in Automation
Future trends in automation emphasize the synergy between human-in-the-loop (HITL) systems and fully autonomous technologies, integrating human judgment with machine precision to enhance decision-making and safety. Advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technology drive the evolution of hybrid automation models that adapt dynamically to complex environments. This convergence aims to optimize operational efficiency across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation by leveraging the strengths of both human oversight and autonomous capabilities.
Human-in-the-loop vs Fully Autonomous Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com